|
Clément Juglar
Clément Juglar (15 October 1819 – 28 February 1905) was a French doctor and statistician. Juglar cycles He was one of the first to develop an economic theory of business cycles.The New Encyclopædia Britannica: Macropaedia 1998 "The first authority to explore economic cycles as periodically recurring phenomena was probably a French physician, Clément Juglar, in 1860." He identified the fixed investment cycle of six to ten years that is now associated with his name. Within the Juglar cycle one can observe oscillations of investments into fixed capital and not just changes in the level of employment of the fixed capital (and respective changes in inventories), as is observed with respect to Kitchin cycles. Juglar's impact Juglar's publications led to other business cycle theories by later economists such as Joseph Schumpeter. Publications of Clément Juglar *"Des crises commerciales", 1856, in ''Annuaire de l'economie politique''.''Des Crises commerciales et leur retour periodiq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juglar Cycle
The Juglar cycle is a fixed investment cycle of 7 to 11 years identified in 1862 by Clément Juglar. Within the Juglar cycle one can observe oscillations of investments into fixed capital and not just changes in the level of employment of the fixed capital (and respective changes in inventories), as is observed with respect to Kitchin cycles. 2010 research employing spectral analysis confirmed the presence of Juglar cycles in world GDP dynamics.See, e.g. See also *Fixed investment *Business cycle Business cycles are intervals of expansion followed by recession in economic activity. These changes have implications for the welfare of the broad population as well as for private institutions. Typically business cycles are measured by examin ... References Further reading * * {{cite book , last=Morgan , first=Mary S. , author-link=Mary S. Morgan , title=The History of Econometric Ideas , location=New York , publisher=Cambridge University Press , year=1990 , isbn=0-521-37398-0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
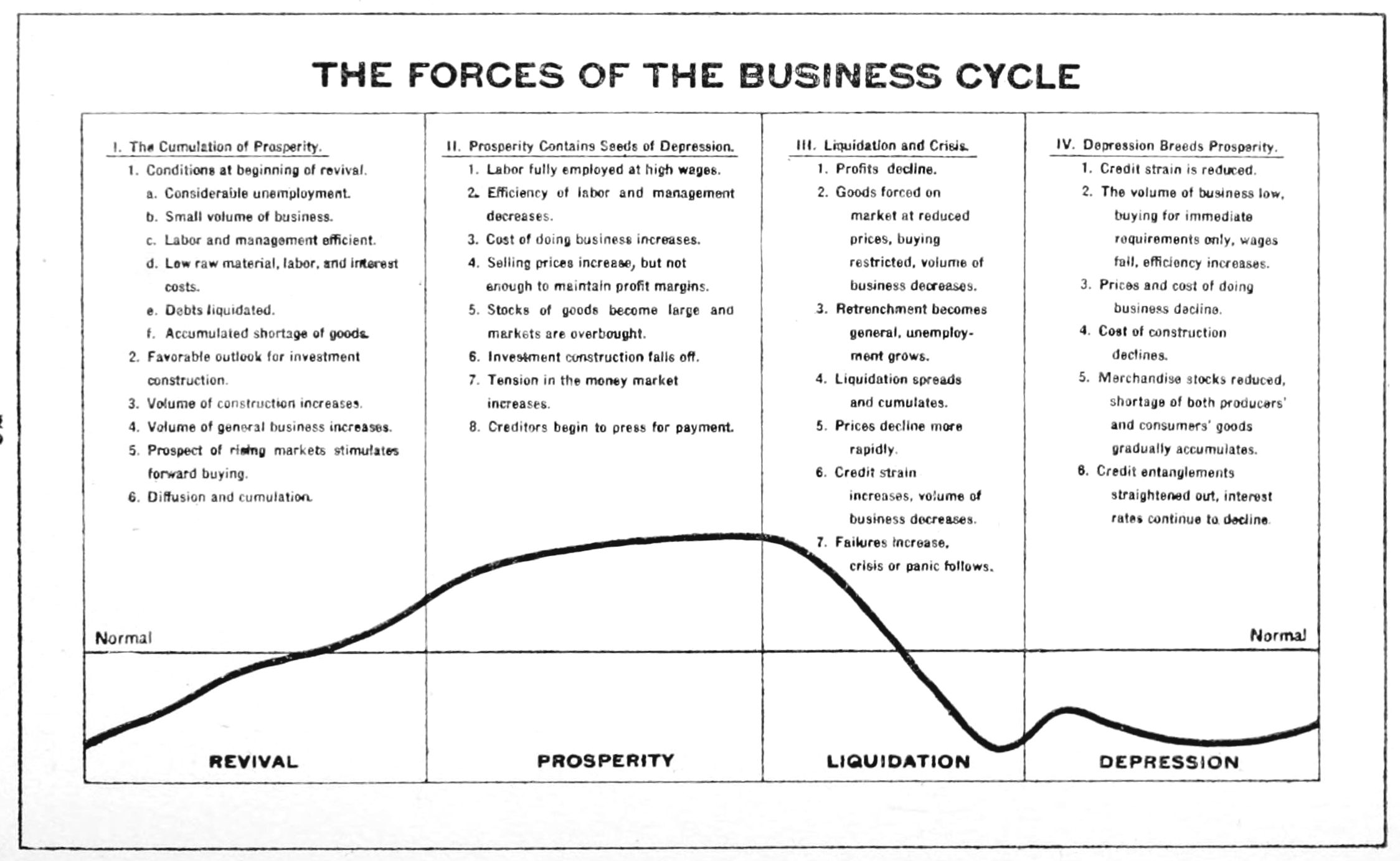
Business Cycle
Business cycles are intervals of Economic expansion, expansion followed by recession in economic activity. These changes have implications for the welfare of the broad population as well as for private institutions. Typically business cycles are measured by examining trends in a broad economic indicator such as Real Gross Domestic Production. Business cycle fluctuations are usually characterized by general upswings and downturns in a span of macroeconomic variables. The individual episodes of expansion/recession occur with changing duration and intensity over time. Typically their periodicity has a wide range from around 2 to 10 years (the technical phrase "stochastic cycle" is often used in statistics to describe this kind of process.) As in [Harvey, Trimbur, and van Dijk, 2007, ''Journal of Econometrics''], such flexible knowledge about the frequency of business cycles can actually be included in their mathematical study, using a Bayesian statistical paradigm. There are numer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed Investment
Fixed investment in economics is the purchasing of newly produced fixed capital. It is measured as a flow variable – that is, as an amount per unit of time. Thus, fixed investment is the accumulation of physical assets such as machinery, land, buildings, installations, vehicles, or technology. Normally, a company balance sheet will state both the amount of expenditure on fixed assets during the quarter or year, and the total value of the stock of fixed assets owned. Fixed investment contrasts with investments in labour, ongoing operating expenses, materials or financial assets. Financial assets may also be held for a fixed term (for example, bonds) but they are not usually called "fixed investment" because they do not involve the purchase of physical fixed assets. The more usual term for such financial investments is "fixed-term investments". Bank deposits committed for a fixed term such as one or two years in a savings account are similarly called "fixed-term deposits". Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed Capital
In accounting, fixed capital is any kind of real, physical asset that is used repeatedly in the production of a product. In economics, fixed capital is a type of capital good that as a real, physical asset is used as a means of production which is durable or isn't fully consumed in a single time period.Varri P. (1987) Fixed Capital. In: Durlauf S., Blume L. (eds) The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics. Palgrave Macmillan, London. "fixed capital", '' The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics'', 1st Editio/ref> It contrasts with circulating capital such as raw materials, operating expenses etc. The concept was first theoretically analyzed in some depth by the economist Adam Smith in The Wealth of Nations (1776) and by David Ricardo in On the Principles of Political Economy and Taxation (1821). Ricardo studied the use of machines in place of labor and concluded that workers' fear of technology replacing them might be justified. Thus fixed capital is that portion of the total ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kitchin Cycle
Kitchin cycle is a short business cycle of about 40 months discovered in the 1920s by Joseph Kitchin. This cycle is believed to be accounted for by time lags in information movements affecting the decision making of commercial firms. Firms react to the improvement of commercial situation through the increase in output through the full employment of the extant fixed capital assets. As a result, within a certain period of time (ranging between a few months and two years) the market gets ‘flooded’ with commodities whose quantity becomes gradually excessive. The demand declines, prices drop, the produced commodities get accumulated in inventories, which informs entrepreneurs of the necessity to reduce output. However, this process takes some time. It takes some time for the information that supply significantly exceeds demand to get to the business people. As it takes entrepreneurs time to check this information and to make the decision to reduce production, time is also necessa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Schumpeter
Joseph Alois Schumpeter (; February 8, 1883 – January 8, 1950) was an Austrian-born political economist. He served briefly as Finance Minister of German-Austria in 1919. In 1932, he emigrated to the United States to become a professor at Harvard University, where he remained until the end of his career, and in 1939 obtained American citizenship. Schumpeter was one of the most influential economists of the early 20th century, and popularized the term "creative destruction", which was coined by Werner Sombart. Early life and education Schumpeter was born in Triesch, Habsburg Moravia (now Třešť in the Czech Republic, then part of Austria-Hungary) in 1883 to German-speaking Catholic parents. Both of his grandmothers were Czech. Schumpeter did not acknowledge his Czech ancestry; he considered himself an ethnic German. His father owned a factory, but he died when Joseph was only four years old. In 1893, Joseph and his mother moved to Vienna. Schumpeter was a loyal supporter of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed Investment
Fixed investment in economics is the purchasing of newly produced fixed capital. It is measured as a flow variable – that is, as an amount per unit of time. Thus, fixed investment is the accumulation of physical assets such as machinery, land, buildings, installations, vehicles, or technology. Normally, a company balance sheet will state both the amount of expenditure on fixed assets during the quarter or year, and the total value of the stock of fixed assets owned. Fixed investment contrasts with investments in labour, ongoing operating expenses, materials or financial assets. Financial assets may also be held for a fixed term (for example, bonds) but they are not usually called "fixed investment" because they do not involve the purchase of physical fixed assets. The more usual term for such financial investments is "fixed-term investments". Bank deposits committed for a fixed term such as one or two years in a savings account are similarly called "fixed-term deposits". Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Cycle
Business cycles are intervals of Economic expansion, expansion followed by recession in economic activity. These changes have implications for the welfare of the broad population as well as for private institutions. Typically business cycles are measured by examining trends in a broad economic indicator such as Real Gross Domestic Production. Business cycle fluctuations are usually characterized by general upswings and downturns in a span of macroeconomic variables. The individual episodes of expansion/recession occur with changing duration and intensity over time. Typically their periodicity has a wide range from around 2 to 10 years (the technical phrase "stochastic cycle" is often used in statistics to describe this kind of process.) As in [Harvey, Trimbur, and van Dijk, 2007, ''Journal of Econometrics''], such flexible knowledge about the frequency of business cycles can actually be included in their mathematical study, using a Bayesian statistical paradigm. There are numer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed Capital
In accounting, fixed capital is any kind of real, physical asset that is used repeatedly in the production of a product. In economics, fixed capital is a type of capital good that as a real, physical asset is used as a means of production which is durable or isn't fully consumed in a single time period.Varri P. (1987) Fixed Capital. In: Durlauf S., Blume L. (eds) The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics. Palgrave Macmillan, London. "fixed capital", '' The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics'', 1st Editio/ref> It contrasts with circulating capital such as raw materials, operating expenses etc. The concept was first theoretically analyzed in some depth by the economist Adam Smith in The Wealth of Nations (1776) and by David Ricardo in On the Principles of Political Economy and Taxation (1821). Ricardo studied the use of machines in place of labor and concluded that workers' fear of technology replacing them might be justified. Thus fixed capital is that portion of the total ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1819 Births
Events January–March * January 2 – The Panic of 1819, the first major peacetime financial crisis in the United States, begins. * January 25 – Thomas Jefferson founds the University of Virginia. * January 29 – Sir Stamford Raffles lands on the island of Singapore. * February 2 – ''Dartmouth College v. Woodward'': The Supreme Court of the United States under John Marshall rules in favor of Dartmouth College, allowing Dartmouth to keep its charter and remain a private institution. * February 6 – A formal treaty, between Hussein Shah of Johor and the British Sir Stamford Raffles, establishes a trading settlement in Singapore. * February 15 – The United States House of Representatives agrees to the Tallmadge Amendment, barring slaves from the new state of Missouri (the opening vote in a controversy that leads to the Missouri Compromise). * February 19 – Captain William Smith of British merchant brig ''Williams'' sights Williams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1905 Deaths
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20 * one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album ''63/19'' by Kool A.D. * ''Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle. * "Nineteen", a song by Bad4Good from the 1992 album ''Refugee'' * "Nineteen", a song by Karma to Burn from the 2001 album ''Almost Heathen''. * "Nineteen" (song), a 2007 song by American singer Billy Ray Cyrus. * "Nineteen", a song by Tegan and Sara from the 2007 album '' The Con''. * "XIX" (song), a 2014 song by Slipkno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Statisticians
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to France ** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents ** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with France ** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices Fortnite French places Arts and media * The French (band), a British rock band * "French" (episode), a live-action episode of ''The Super Mario Bros. Super Show!'' * ''Française'' (film), 2008 * French Stewart (born 1964), American actor Other uses * French (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) * French (tunic), a particular type of military jacket or tunic used in the Russian Empire and Soviet Union * French's, an American brand of mustard condiment * French catheter scale, a unit of measurement of diameter * French Defence, a chess opening * French kiss, a type of kiss involving the tongue See also * France (other) * Franch, a surname * Fren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |