|
Clutter (toolkit)
Clutter is a discontinued GObject-based graphics library for creating hardware-accelerated user interfaces. Clutter is an OpenGL-based 'interactive canvas' library and does not contain any graphical control elements. It relies upon OpenGL (1.4+) or OpenGL ES (1.1 or 2.0) for rendering,. It also supports media playback using GStreamer and 2D graphics rendering using Cairo. Clutter was authored by OpenedHand Ltd, now part of Intel. Clutter is free and open-source software, subject to the requirements of the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL), version 2.1. In February 2022, the development team announced that the project would be discontinued. No more versions will be released and developers using Clutter are encouraged to port their applications to GTK 4 and libadwaita2. Adoption Popular programs that adopt Clutter are GNOME Videos (a.k.a. Totem), GNOME Shell, Pitivi, Cinnamon Desktop and GNOME Ease. Mx is a widget toolkit based on Clutter originally designed for the gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenedHand
OpenedHand, a computer software, was an embedded Linux start-up that was acquired by Intel in Q3, 2008. The firm developed an OpenEmbedded distribution called Poky Linux (now part of the Yocto Project) and the Clutter library. The latter is heavily used in the customized UIs of Maemo and Moblin, embedded Linux distributions from Nokia Nokia Corporation (natively Nokia Oyj, referred to as Nokia) is a Finnish multinational corporation, multinational telecommunications industry, telecommunications, technology company, information technology, and consumer electronics corporatio ... and Intel, respectively. References Intel software {{Linux-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free And Open-source Software
Free and open-source software (FOSS) is a term used to refer to groups of software consisting of both free software and open-source software where anyone is freely licensed to use, copy, study, and change the software in any way, and the source code is openly shared so that people are encouraged to voluntarily improve the design of the software. This is in contrast to proprietary software, where the software is under restrictive copyright licensing and the source code is usually hidden from the users. FOSS maintains the software user's civil liberty rights (see the Four Essential Freedoms, below). Other benefits of using FOSS can include decreased software costs, increased security and stability (especially in regard to malware), protecting privacy, education, and giving users more control over their own hardware. Free and open-source operating systems such as Linux and descendants of BSD are widely utilized today, powering millions of servers, desktops, smartphones (e.g., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casual Game
A casual game is a video game targeted at a mass market audience, as opposed to a hardcore game, which is targeted at hobbyist gamers. Casual games may exhibit any type of gameplay and genre. They generally involve simpler rules, shorter sessions, and require less learned skill. They don't expect familiarity with a standard set of mechanics, controls, and tropes. Countless casual games have been developed and published, alongside hardcore games, across the history of video games. A concerted effort to capitalize on casual games grew in the 1990s and 2000s, as many developers and publishers branded themselves as casual game companies, publishing games especially for PCs, web browsers, and, after 2007, smartphones. Overview Most casual games have: *Fun, simple gameplay that is easy to understand *Simple user interface, operated with a mobile phone tap-and-swipe interface or a one-button mouse interface *Short sessions, so a game can be played during work breaks, while on pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proof Of Concept
Proof of concept (POC or PoC), also known as proof of principle, is a realization of a certain method or idea in order to demonstrate its feasibility, or a demonstration in principle with the aim of verifying that some concept or theory has practical potential. A proof of concept is usually small and may or may not be complete. These collaborative trials aim to test feasibility of business concepts and proposals to solve business problems and accelerate business innovation goals. A proof of value (PoV) is sometimes used along proof of concept, and differs by focusing more on demonstrating the potential customers use case and value, and is usually less in-depth than a proof of concept. Usage history The term has been in use since 1967. In a 1969 hearing of the Committee on Science and Astronautics, Subcommittee on Advanced Research and Technology, ''proof of concept'' was defined as following: One definition of the term "proof of concept" was by Bruce Carsten in the context o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNOME Maps
GNOME Core Applications is a software suite of approximately 30 application software that are packaged as part of the standard free and open-source GNOME desktop environment. GNOME Core Applications have the look and feel of the GNOME desktop, and often utilize the Adwaita design language. Some applications have been written from scratch and others are ports. The employment of the newest graphical widgets offered by the latest version of GTK in order to implement the GNOME Human Interface Guidelines (HIG) ergonomically is the only feature which all GNOME Core Applications have in common. Some of the GNOME Core Applications are essential, while several are not, e.g. GNOME Weather. Most are graphical front-ends, e.g. GNOME Software, to underlying Linux system daemons, like e.g. journald, PackageKit, NetworkManager or PulseAudio. Configuration * Settings – main interface to configure various aspects of GNOME. Diverse panels represent graphical front-ends to configure the Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wayland Compositor
Wayland is a communication protocol that specifies the communication between a display server and its clients, as well as a C library implementation of that protocol. A display server using the Wayland protocol is called a ''Wayland compositor'', because it additionally performs the task of a compositing window manager. Wayland is developed by a group of volunteers initially led by Kristian Høgsberg as a free and open-source community-driven project with the aim of replacing the X Window System with a modern, secure simpler windowing system in Linux and other Unix-like operating systems. The project's source code is published under the terms of the MIT License, a permissive free software licence. As part of its efforts, the Wayland project also develops a reference implementation of a Wayland compositor called ''Weston''. Overview The Wayland Display Server project was started by Red Hat developer Kristian Høgsberg in 2008. Beginning around 2010, Linux desktop graphics h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
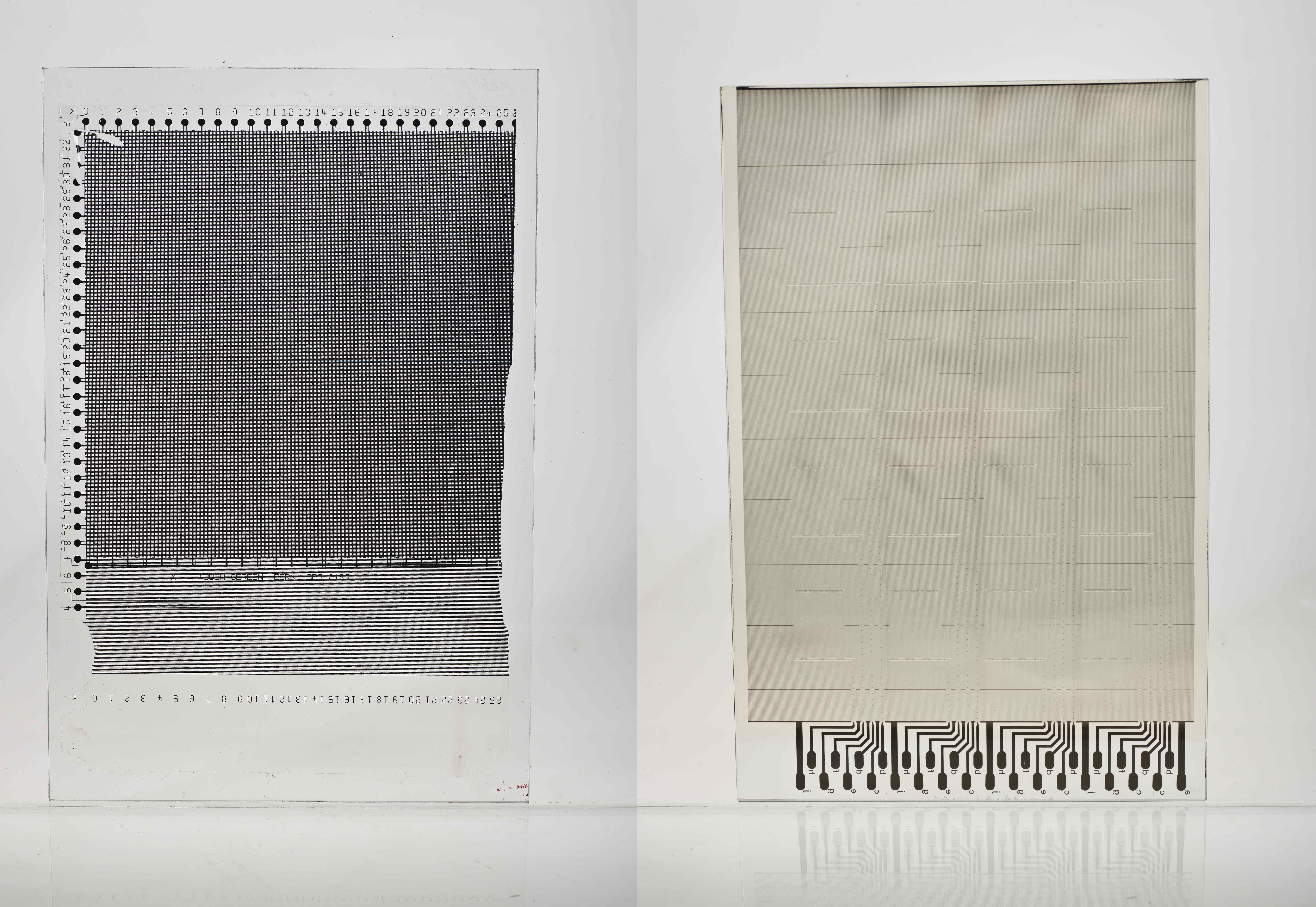
Multi-touch Gestures
In computing, multi-touch is technology that enables a surface (a touchpad or touchscreen) to recognize the presence of more than one point of contact with the surface at the same time. The origins of multitouch began at CERN, MIT, University of Toronto, Carnegie Mellon University and Bell Labs in the 1970s. CERN started using multi-touch screens as early as 1976 for the controls of the Super Proton Synchrotron. Capacitive multi-touch displays were popularized by Apple's iPhone in 2007. Plural-point awareness may be used to implement additional functionality, such as pinch to zoom or to activate certain subroutines attached to predefined gestures. Several uses of the term multi-touch resulted from the quick developments in this field, and many companies using the term to market older technology which is called ''gesture-enhanced single-touch'' or several other terms by other companies and researchers. Several other similar or related terms attempt to differentiate between whethe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MeeGo
MeeGo is a discontinued Linux distribution hosted by the Linux Foundation, using source code from the operating systems Moblin (produced by Intel) and Maemo (produced by Nokia). Primarily targeted at mobile devices and information appliances in the consumer electronics market, MeeGo was designed to act as an operating system for hardware platforms such as netbooks, entry-level desktops, nettops, tablet computers, mobile computing and communications devices, in-vehicle infotainment devices, SmartTV / ConnectedTV, IPTV-boxes, smart phones, and other embedded systems. Nokia wanted to make MeeGo its primary smartphone operating system in 2010, but after a change in direction it was stopped in February 2011, leaving Intel alone in the project. The Linux Foundation canceled MeeGo in September 2011 in favor of Tizen, which Intel then joined in collaboration with Samsung. A community-driven successor called Mer was formed that year. A Finnish start-up, Jolla, picked up Mer to develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moblin
Moblin, short for 'mobile Linux', is a discontinued open source operating system and application stack for Mobile Internet Devices (MIDs), netbooks, nettops and embedded devices. Built around the Intel Atom processor, all builds were designed to minimize boot times and power consumption as a netbook and MID-centric operating system. The netbook/desktop version of Moblin supported other chipsets based on the SSSE3 instruction set, such as the Core2 and some Celeron processors. OEM support was scarce but hit an all-time high in 2009 when Acer replaced Linpus Linux with Moblin on their Acer Aspire One netbooks. and LG Electronics chose Moblin OS 2.1 for its mobile Internet device class smartphone the LG GW990. Dell also once accepted orders for its Ubuntu Moblin Remix, a Canonical Ltd. which built Moblin on top of Ubuntu distribution as base. Few commercial products existed around Moblin 2 most prominently a Foxconn netbook and an InvenTech smartphone, both announced at Comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphical Shell
In computing, a shell is a computer program that exposes an operating system's services to a human user or other programs. In general, operating system shells use either a command-line interface (CLI) or graphical user interface (GUI), depending on a computer's role and particular operation. It is named a shell because it is the outermost layer around the operating system. Command-line shells require the user to be familiar with commands and their calling syntax, and to understand concepts about the shell-specific scripting language (for example, bash), while graphical shells place a low burden on beginning computer users and are characterized as being easy to use, yet most GUI-enabled operating systems also provide CLI shells, normally for performing advanced tasks. Overview Operating systems provide various services to their users, including file management, process management (running and terminating applications), batch processing, and operating system monitoring and con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNOME Ease
A gnome is a mythological creature and diminutive spirit in Renaissance magic and alchemy, first introduced by Paracelsus in the 16th century and later adopted by more recent authors including those of modern fantasy literature. Its characteristics have been reinterpreted to suit the needs of various story tellers, but it is typically said to be a small humanoid that lives underground. Diminutive statues of gnomes introduced as lawn ornaments during the 19th century grew in popularity during the 20th century and came to be known as garden gnomes. History Origins The word comes from Renaissance Latin ''gnomus'', which first appears in ''A Book on Nymphs, Sylphs, Pygmies, and Salamanders, and on the Other Spirits'' by Paracelsus, published posthumously in Nysa in 1566 (and again in the Johannes Huser edition of 1589–1591 from an autograph by Paracelsus). The term may be an original invention of Paracelsus, possibly deriving the term from Latin ''gēnomos'' (itself representi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinnamon (software)
Cinnamon is a free and open-source desktop environment for Linux and Unix-like operating systems, deriving from GNOME 3 but following traditional desktop metaphor conventions. The development of Cinnamon began by the Linux Mint team as a reaction to the April 2011 release of GNOME 3 in which the conventional desktop metaphor of GNOME 2 was abandoned in favor of GNOME Shell. Following several attempts to extend GNOME 3 such that it would suit the Linux Mint design goals, the Mint developers forked several GNOME 3 components to build an independent desktop environment. Separation from GNOME was completed in Cinnamon 2.0, which was released in October 2013. Applets and desklets are no longer compatible with GNOME 3. As the distinguishing factor of Linux Mint, Cinnamon has generally received favorable coverage by the press, in particular for its ease of use and gentle learning curve. With respect to its conservative design model, Cinnamon is similar to the Xfce, MATE, GNOME 2 (and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |