|
Cluer Dicey
Cluer Dicey (28 January 1715 – 3 October 1775) was an English newspaper proprietor, publisher of street literature, printseller and patent medicine seller, in London and later in Northampton. He was also proprietor of the Northampton Mercury newspaper from 1756 until his death in October 1775. Likewise he inherited and developed a huge distribution network in England for patent medicines. Family Cluer was born 28 January 1715 at London, the son of William Dicey (1690- 1756) and Mary his wife (nee Atkins). He was named after his uncle, John Cluer, a London printer and music publisher. He married Mary ometimes given as MariaNutshawe 7 October 1738. They had two sons, William (who died in infancy 1739) and Thomas, b. 1742. They also had three daughters, Charlotte, b. 1740; Sarah Ann b. 1746, and Elizabeth (dates not known). Maria died 3 February 1761, at Northampton. Businesses In 1732 William Dicey attempted to buy the Stamford Mercury newspaper for his son to manage, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Romans as '' Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national government and parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London, governed by the Greater London Authority.The Greater London Authority consists of the Mayor of London and the London Assembly. The London Mayor is distinguished fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almanac
An almanac (also spelled ''almanack'' and ''almanach'') is an annual publication listing a set of current information about one or multiple subjects. It includes information like weather forecasts, farmers' planting dates, tide tables, and other tabular data often arranged according to the calendar. Celestial figures and various statistics are found in almanacs, such as the rising and setting times of the Sun and Moon, dates of eclipses, hours of high and low tides, and religious festivals. The set of events noted in an almanac may be tailored for a specific group of readers, such as farmers, sailors, or astronomers. Etymology The etymology of the word is disputed. The earliest documented use of the word in any language is in Latin in 1267 by Roger Bacon, where it meant a set of tables detailing movements of heavenly bodies including the Moon. It has been suggested that the word ''almanac'' derives from a Greek word meaning ''calendar''. However, that word appears only o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1715 Births
Events For dates within Great Britain and the British Empire, as well as in the Russian Empire, the "old style" Julian calendar was used in 1715, and can be converted to the "new style" Gregorian calendar (adopted in the British Empire in 1752 and in Russia in 1923) by adding 11 days. January–March * January 13 – A fire in London, described by some as the worst since the Great Fire of London (1666) almost 50 years earlier, starts on Thames Street when fireworks prematurely explode "in the house of Mr. Walker, an oil man"; more than 100 houses are consumed in the blaze, which continues over to Tower Street before it is controlled. * January 22 – Voting begins for the British House of Commons and continues for the next 46 days in different constituencies on different days. * February 11 – Tuscarora War: The Tuscarora and their allies sign a peace treaty with the Province of North Carolina, and agree to move to a reservation near Lake Mattamusk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hannah More
Hannah More (2 February 1745 – 7 September 1833) was an English religious writer, philanthropist, poet and playwright in the circle of Johnson, Reynolds and Garrick, who wrote on moral and religious subjects. Born in Bristol, she taught at a school her father founded there and began writing plays. She became involved in the London literary elite and a leading Bluestocking member. Her later plays and poetry became more evangelical. She joined a group opposing the slave trade. In the 1790s she wrote Cheap Repository Tracts on moral, religious and political topics, to distribute to the literate poor (as a retort to Thomas Paine's Rights of Man). Meanwhile, she broadened her links with schools she and her sister Martha had founded in rural Somerset. These curbed their teaching of the poor, allowing limited reading but no writing. More was noted for her political conservatism, being described as an anti-feminist, a "counter-revolutionary", or a conservative feminist. Early life B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Sayer
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe it entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including English, German, Dutch, Norwegian, Swedish, Scots, Danish, and Icelandic. It can be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court Of Common Pleas (England)
The Court of Common Pleas, or Common Bench, was a common law court in the English legal system that covered "common pleas"; actions between subject and subject, which did not concern the king. Created in the late 12th to early 13th century after splitting from the Exchequer of Pleas, the Common Pleas served as one of the central English courts for around 600 years. Authorised by Magna Carta to sit in a fixed location, the Common Pleas sat in Westminster Hall for its entire existence, joined by the Exchequer of Pleas and Court of King's Bench. The court's jurisdiction was gradually undercut by the King's Bench and Exchequer of Pleas with legal fictions, the Bill of Middlesex and Writ of Quominus respectively. The Common Pleas maintained its exclusive jurisdiction over matters of real property until its dissolution, and due to its wide remit was considered by Sir Edward Coke to be the "lock and key of the common law". It was staffed by one Chief Justice and a varying number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daffy's Elixir
Daffy's Elixir (also sometimes known as Daffey's Elixir or Daffye's Elixir) is a name that has been used by several patent medicines over the years. It was originally designed for diseases of the stomach, but was later marketed as a universal cure. It remained a popular remedy in Britain and later the United States of America throughout the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. Origins Daffy's Elixir was one of the most popular and frequently advertised patent medicines in Britain during the 18th century. It is reputed to have been invented by clergyman Thomas Daffy, rector of Redmile, Leicestershire, in 1647. He named it elixir salutis (lit. ''elixir of health'') and promoted it as a generic cure-all. Ingredients An early recipe for "True Daffy" from 1700 lists the following ingredients: aniseed, brandy, cochineal, elecampane, fennel seed, jalap, manna, parsley seed, raisin, rhubarb, saffron, senna and spanish liquorice. Chemical analysis has shown this to be a lax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dr Bateman's Pectoral Drops
Dr Bateman's Pectoral Drops (also known as ‘Batemans Original Pectoral Drops’, and 'Bateman's and Stoughton's drops’) was a popular patent medicine for disorders of the chest or lungs during the 18th, 19th, and early 20th centuries in Britain and North America. It was later marketed as a remedy for ‘all Rheumatic and Chronic complaints, in pains of the limbs, bones, and joints, for influenza, and in violent colds,. Ingredients The medicine was similar to paregoric; a tincture of opium and camphor. To this was added catechu together with anise flavouring and a colouring agent. Over the years there were several different formulas. Bateman’s Drops were advertised as being intended for infants and adults and was dosed accordingly. Origins The original formula was developed by Benjamin Okell of Northampton, before 1711, when a patent was granted for its manufacture. Advertisements are first known in the ''Northampton Mercury'' newspaper in 1720. Marketing UK Okell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
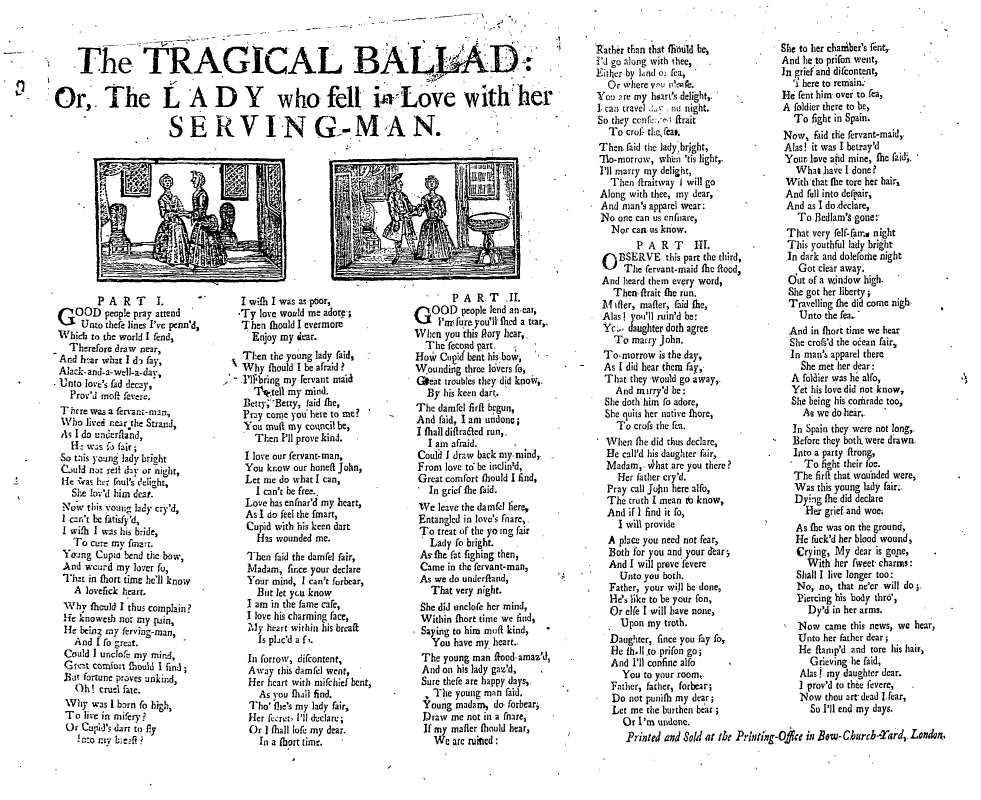
Popular Print
Popular prints is a term for printed images of generally low artistic quality which were sold cheaply in Europe and later the New World from the 15th to 18th centuries, often with text as well as images. They were some of the earliest examples of mass media. After about 1800, the types and quantity of images greatly increased, but other terms are usually used to categorise them. 15th century From about 1400, there began a "visual revolution that inundated Europe with images during the fifteenth century" (Field) as the woodcut technique was applied to paper, which was now manufactured in Christian Europe, instead of being imported from Islamic Spain. In the 15th century, the great majority of these images were religious, if playing cards are excluded. They were sold at churches, fairs and places of pilgrimage. Most were coloured, usually crudely, by hand or later by stencil. One political cartoon relating to events in 1468–1470 has survived in several different versions (ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chapbook
A chapbook is a small publication of up to about 40 pages, sometimes bound with a saddle stitch. In early modern Europe a chapbook was a type of printed street literature. Produced cheaply, chapbooks were commonly small, paper-covered booklets, usually printed on a single sheet folded into books of 8, 12, 16 and 24 pages. They were often illustrated with crude woodcuts, which sometimes bore no relation to the text (much like today's stock photos), and were often read aloud to an audience. When illustrations were included in chapbooks, they were considered popular prints. The tradition of chapbooks arose in the 16th century, as soon as printed books became affordable, and rose to its height during the 17th and 18th centuries. Many different kinds of ephemera and popular or folk literature were published as chapbooks, such as almanacs, children's literature, folk tales, ballads, nursery rhymes, pamphlets, poetry, and political and religious tracts. The term "chapbook" for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadside Ballad
A broadside (also known as a broadsheet) is a single sheet of inexpensive paper printed on one side, often with a ballad, rhyme, news and sometimes with woodcut illustrations. They were one of the most common forms of printed material between the sixteenth and nineteenth centuries, particularly in Britain, Ireland and North America because they are easy to produce and are often associated with one of the most important forms of traditional music from these countries, the ballad. Development of broadsides Ballads developed out of minstrelsy from the fourteenth and fifteenth century. These were narrative poems that had combined with French courtly romances and Germanic legends that were popular at the King’s court, as well as in the halls of lords of the realm. By the seventeenth century, minstrelsy had evolved into ballads whose authors wrote on a variety of topics. The authors could then have their ballads printed and distributed. Printers used a single piece of paper known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prediction
A prediction (Latin ''præ-'', "before," and ''dicere'', "to say"), or forecast, is a statement about a future event or data. They are often, but not always, based upon experience or knowledge. There is no universal agreement about the exact difference from "estimation"; different authors and disciplines ascribe different connotations. Future events are necessarily uncertain, so guaranteed accurate information about the future is impossible. Prediction can be useful to assist in making plans about possible developments. Opinion In a non-statistical sense, the term "prediction" is often used to refer to an informed guess or opinion. A prediction of this kind might be informed by a predicting person's abductive reasoning, inductive reasoning, deductive reasoning, and experience; and may be useful—if the predicting person is a knowledgeable person in the field. The Delphi method is a technique for eliciting such expert-judgement-based predictions in a controlled way. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |