|
Clovis Oncology
Clovis Oncology is an American pharmaceutical company which mainly markets products for treatment in oncology. Clovis was founded in 2009 and is headquartered in Boulder, Colorado. The company is a publicly traded company on NASDAQ under the symbol CLVS and is in the NASDAQ Biotechnology Index with several products in its product pipeline. As of December 31, 2017, the company was not profitable and had incurred losses in each year since its inception in April 2009. In December 2022, Clovis Oncology filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy. History Clovis Oncology was founded in 2009 by Patrick Mahaffy in Boulder, Colorado. The company was named in honor of the Mahaffy cache, a collection of Clovis period stone tools dated to 11,000 BCE, discovered in the front yard Mahaffy's home in Boulder. Product development Rociletinib The company was developing rociletinib, as a treatment for non-small cell lung cancer. A phase III trial was completed in April 2016 and had it been appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rucaparib
Rucaparib, sold under the brand name Rubraca, is a PARP inhibitor used as an anti-cancer agent. Rucaparib is a first-in-class pharmaceutical drug targeting the DNA repair enzyme poly-ADP ribose polymerase-1 (PARP-1). It is taken by mouth. The most common side effects include tiredness or weakness, nausea (feeling sick), increased levels of creatinine (which may indicate kidney problems) and liver enzymes in the blood (which may indicate liver damage), vomiting, anaemia (low red blood cell counts), decreased appetite, dysgeusia (taste disturbances), diarrhoea, thrombocytopenia (low levels of platelets) and abdominal pain (belly ache). Medical uses Rucaparib is indicated as monotherapy for the maintenance treatment of adults with platinum-sensitive relapsed high-grade epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer who are in response (complete or partial) to platinum-based chemotherapy. In the United States, rucaparib is also indicated for the treatment of pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PARP Inhibitor
PARP inhibitors are a group of pharmacological inhibitors of the enzyme poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP). They are developed for multiple indications, including the treatment of heritable cancers. Several forms of cancer are more dependent on PARP than regular cells, making PARP (PARP1, PARP2 etc) an attractive target for cancer therapy. PARP inhibitors appear to improve progression-free survival in women with recurrent platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer, as evidenced mainly by olaparib added to conventional treatment. In addition to their use in cancer therapy, PARP inhibitors are considered a potential treatment for acute life-threatening diseases, such as stroke and myocardial infarction, as well as for long-term neurodegenerative diseases. Medical uses Approved for marketing * Olaparib: In December, 2014, the EMA and US FDA approved olaparib as monotherapy (at 400 mg taken twice per day) for patients with germline BRCA mutated (gBRCAm) advanced ovarian cancer wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
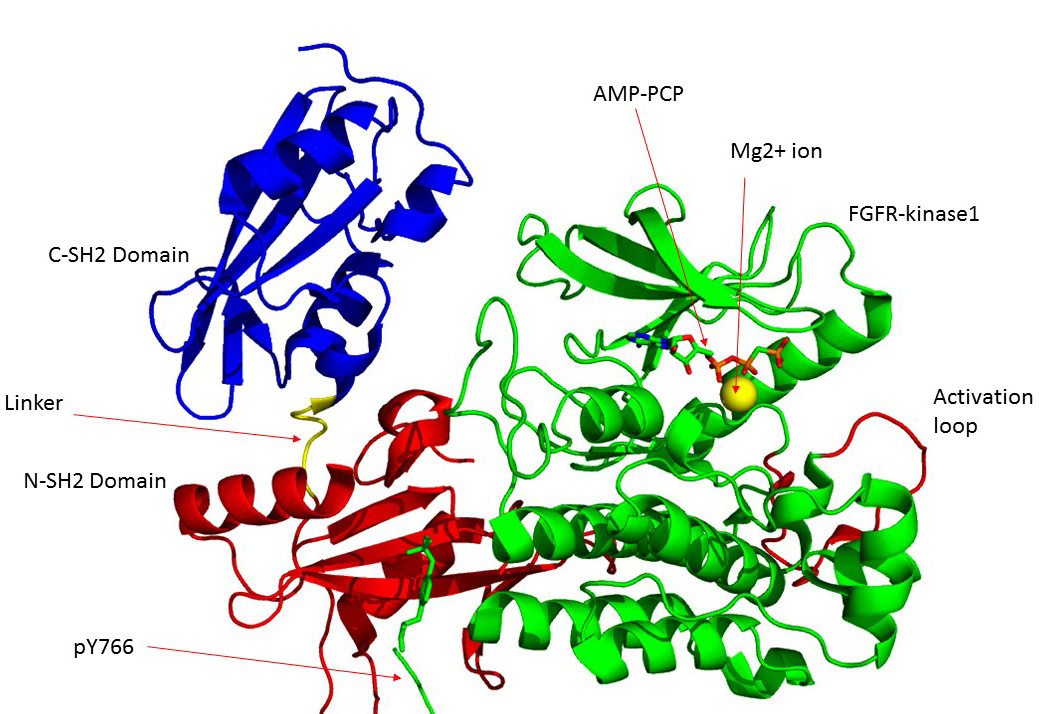
FGFR2
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) also known as CD332 (cluster of differentiation 332) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FGFR2'' gene residing on chromosome 10. FGFR2 is a receptor for fibroblast growth factor. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fibroblast growth factor receptor family, where amino acid sequence is highly conserved between members and throughout evolution. FGFR family members differ from one another in their ligand affinities and tissue distribution. A full-length representative protein consists of an extracellular region, composed of three immunoglobulin domains, a single hydrophobic membrane-spanning segment and a cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase domain. The extracellular portion of the protein interacts with fibroblast growth factors, setting in motion a cascade of downstream signals, ultimately influencing mitogenesis and differentiation. This particular family member is a high-affinity receptor for acidic, basic and/or ker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FGFR1
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1), also known as basic fibroblast growth factor receptor 1, fms-related tyrosine kinase-2 / Pfeiffer syndrome, and CD331, is a receptor tyrosine kinase whose ligands are specific members of the fibroblast growth factor family. FGFR1 has been shown to be associated with Pfeiffer syndrome, and clonal eosinophilias. Gene The ''FGFR1'' gene is located on human chromosome 8 at position p11.23 (i.e. 8p11.23), has 24 exons, and codes for a Precursor mRNA that is alternatively spliced at exons 8A or 8B thereby generating two mRNAs coding for two FGFR1 isoforms, FGFR1-IIIb (also termed FGFR1b) and FGFR1-IIIc (also termed FGFR1c), respectively. Although these two isoforms have different tissue distributions and FGF-binding affinities, FGFR1-IIIc appears responsible for most of functions of the FGFR1 gene while FGFR1-IIIb appears to have only a minor, somewhat redundant functional role. There are four other members of the ''FGFR1'' gene family: FGF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VEGFR Inhibitor
VEGF receptors are receptors for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). There are three main subtypes of VEGFR, numbered 1, 2 and 3. Also, they may be membrane-bound (mbVEGFR) or soluble (sVEGFR), depending on alternative splicing. Inhibitors of VEGFR are used in the treatment of cancer. VEGF Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is an important signaling protein involved in both vasculogenesis (the formation of the circulatory system) and angiogenesis (the growth of blood vessels from pre-existing vasculature). As its name implies, VEGF activity is restricted mainly to cells of the vascular endothelium, although it does have effects on a limited number of other cell types (e.g. stimulation monocyte/macrophage migration). ''In vitro'', VEGF has been shown to stimulate endothelial cell mitogenesis and cell migration. VEGF also enhances microvascular permeability and is sometimes referred to as vascular permeability factor. Receptor biology All members of the VEGF f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucitanib
Lucitanib (INN) is a drug that is being investigated by Clovis Oncology in clinical trials for the treatment of advanced solid tumours including metastatic breast cancer. It is a protein kinase inhibitor that blocks the VEGF receptors 1, 2 and 3, as well as the fibroblast growth factor receptors 1 and 2, and the platelet-derived growth factor receptor Platelet-derived growth factor receptors (PDGF-R) are cell surface tyrosine kinase receptors for members of the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) family. PDGF subunits -A and -B are important factors regulating cell proliferation, cellu ...s alpha and beta. References Receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors Carboxamides Experimental cancer drugs {{antineoplastic-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotherapies
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms ( palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or induce DNA damage, which is why inhibition of DNA repair can augment chemotherapy. The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somatic Evolution In Cancer
Somatic evolution is the accumulation of mutations and epimutations in somatic cells (the cells of a body, as opposed to germ plasm and stem cells) during a lifetime, and the effects of those mutations and epimutations on the fitness of those cells. This evolutionary process has first been shown by the studies of Bert Vogelstein in colon cancer. Somatic evolution is important in the process of aging as well as the development of some diseases, including cancer. Natural selection in cancer Cells in pre-malignant and malignant neoplasms (tumors) evolve by natural selection. This accounts for how cancer develops from normal tissue and why it has been difficult to cure. There are three necessary and sufficient conditions for natural selection, all of which are met in a neoplasm: # There must be variation in the population. Neoplasms are mosaics of different mutant cells with both genetic and epigenetic changes that distinguish them from normal cells. # The variable traits must be h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germline Mutation
A germline mutation, or germinal mutation, is any detectable variation within germ cells (cells that, when fully developed, become sperm and ova). Mutations in these cells are the only mutations that can be passed on to offspring, when either a mutated sperm or oocyte come together to form a zygote. After this fertilization event occurs, germ cells divide rapidly to produce all of the cells in the body, causing this mutation to be present in every somatic and germline cell in the offspring; this is also known as a constitutional mutation. Germline mutation is distinct from somatic mutation. Germline mutations can be caused by a variety of endogenous (internal) and exogenous (external) factors, and can occur throughout zygote development. A mutation that arises only in germ cells can result in offspring with a genetic condition that is not present in either parent; this is because the mutation is not present in the rest of the parents' body, only the germline. When mutagenesis oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BRCA Mutation
A ''BRCA'' mutation is a mutation in either of the ''BRCA1'' and ''BRCA2'' genes, which are tumour suppressor genes. Hundreds of different types of mutations in these genes have been identified, some of which have been determined to be harmful, while others have no proven impact. Harmful mutations in these genes may produce a hereditary breast–ovarian cancer syndrome in affected persons. Only 5–10% of breast cancer cases in women are attributed to ''BRCA1'' and ''BRCA2'' mutations (with ''BRCA1'' mutations being slightly more common than ''BRCA2'' mutations), but the impact on women with the gene mutation is more profound. Women with harmful mutations in either ''BRCA1'' or ''BRCA2'' have a risk of breast cancer that is about five times the normal risk, and a risk of ovarian cancer that is about ten to thirty times normal. The risk of breast and ovarian cancer is higher for women with a high-risk ''BRCA1'' mutation than with a ''BRCA2'' mutation. Having a high-risk mutation doe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accelerated Approval (FDA)
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) initiated the FDA Accelerated Approval Program in 1992 to allow faster approval of drugs for serious conditions that fill an unmet medical need. The faster approval relies on use of surrogate endpoints. Drug approval typically requires clinical trials with endpoints that demonstrate a clinical benefit, such as increased survival for cancer patients. Drugs with accelerated approval can initially be tested in clinical trials that use a surrogate endpoint, or something that is thought to predict clinical benefit. Surrogate endpoints typically require less time, and in the case of a cancer patient, it is much faster to measure a reduction in tumor size, for example, than overall patient survival. Drugs approved under the FDA Accelerated Approval Program still need to be tested in clinical trials using endpoints that demonstrate clinical benefit, and those trials are known as phase 4 confirmatory trials. If the drug later proves unabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, Prescription drug, prescription and Over-the-counter drug, over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, Animal feed, animal foods & feed and Veterinary medicine, veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C), but the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act, as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is not d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)