|
Clorotepine
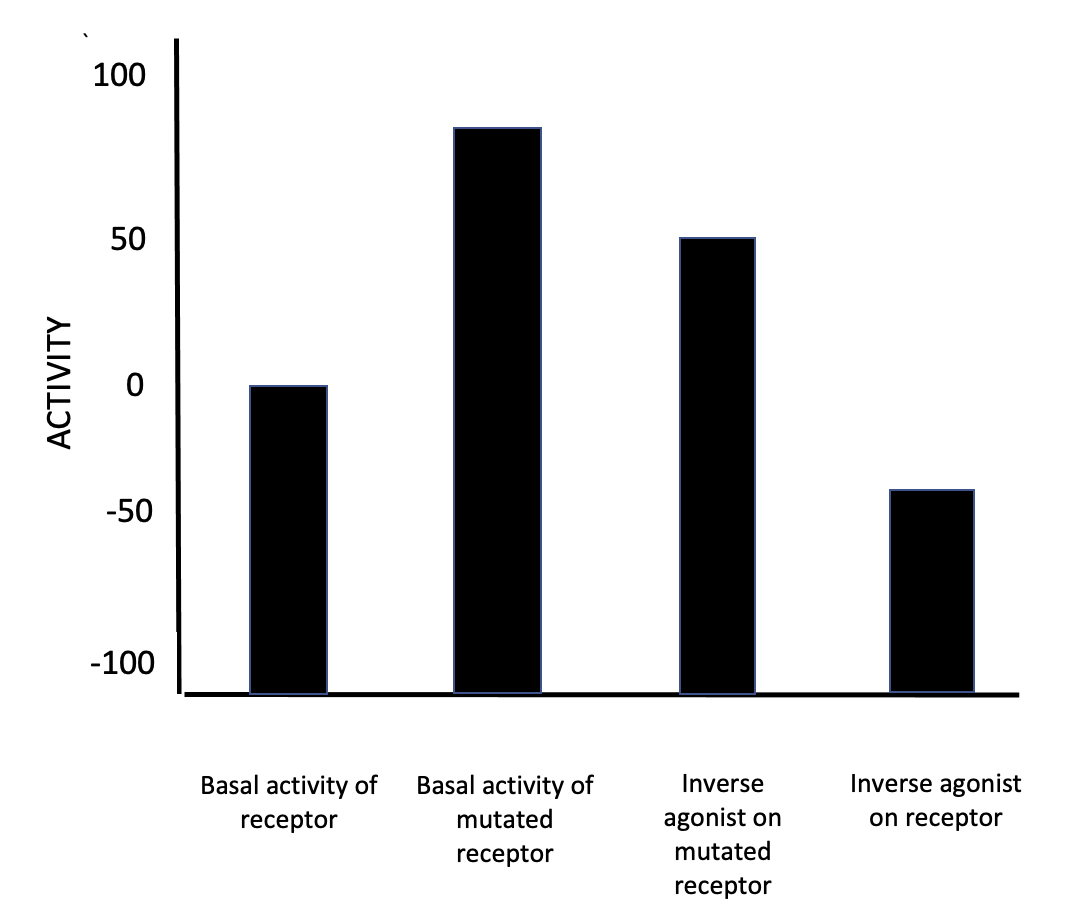
Clorotepine (; brand names Clotepin, Clopiben), also known as octoclothepin or octoclothepine, is an antipsychotic of the tricyclic group which was derived from perathiepin in 1965 and marketed in the Czech Republic by Spofa in or around 1971 for the treatment of schizophrenic psychosis. Clorotepine is known to have high affinity for the dopamine D1, D2, D3, and D4 receptors, the serotonin 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, 5-HT2C, 5-HT6, and 5-HT7 receptors, the α1A-, α1B-, and α1D-adrenergic receptors, and the histamine H1 receptors, where it has been it has been confirmed to act as an antagonist (or inverse agonist) at most sites (and likely is as such at all of them based on structure–activity relationships), and it also blocks the reuptake of norepinephrine via inhibition of the norepinephrine transporter. Due to its very potent activity at the D2 receptor, along with tefludazine, clorotepine was used as the basis for developing a 3-dimensional (3D) pharmacophore fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antipsychotic
Antipsychotics, also known as neuroleptics, are a class of Psychiatric medication, psychotropic medication primarily used to manage psychosis (including delusions, hallucinations, paranoia or disordered thought), principally in schizophrenia but also in a range of other psychotic disorders. They are also the mainstay together with mood stabilizers in the treatment of bipolar disorder. Prior research has shown that use of any antipsychotic is associated with smaller brain tissue volumes, including white matter reduction and that this brain shrinkage is dose dependent and time dependent. A more recent controlled trial suggests that second generation antipsychotics combined with intensive psychosocial therapy may potentially prevent pallidal brain volume loss in first episode psychosis. The use of antipsychotics may result in many unwanted side effects such as Extrapyramidal symptoms, involuntary movement disorders, gynecomastia, impotence, weight gain and metabolic syndrome. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perathiepin
Perathiepin is a neuroleptic drug of the tricyclic family which was developed in the 1960s but was never marketed. In animal studies it was found to possess central depressant, antihistamine, antiserotonergic, and analgesic effects. See also * Clorotepine * Metitepine Metitepine (; developmental code names Ro 8-6837 (maleate), VUFB-6276 ( mesylate)), also known as methiothepin, is a drug described as a " psychotropic agent" of the tricyclic group which was never marketed. It acts as a non-selective antagonist ... References {{Tricyclics Antipsychotics Dibenzothiepines Diphenylethylpiperazines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maleate
Maleic acid or ''cis''-butenedioic acid is an organic compound that is a dicarboxylic acid, a molecule with two carboxyl groups. Its chemical formula is HO2CCH=CHCO2H. Maleic acid is the ''cis''-isomer of butenedioic acid, whereas fumaric acid is the ''trans''-isomer. It is mainly used as a precursor to fumaric acid, and relative to its parent maleic anhydride, maleic acid has few applications. Physical properties Maleic acid has a '' heat of combustion'' of -1,355 kJ/mol., 22.7 kJ/mol higher than that of fumaric acid. Maleic acid is more soluble in water than fumaric acid. The melting point of maleic acid (135 °C) is also much lower than that of fumaric acid (287 °C). Both properties of maleic acid can be explained on account of the intramolecular hydrogen bonding that takes place in maleic acid at the expense of intermolecular interactions, and that are not possible in fumaric acid for geometric reasons. Production and industrial applications In industry, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT2C Receptor
The 5-HT2C receptor is a subtype of 5-HT receptor that binds the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT). It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is coupled to Gq/G11 and mediates excitatory neurotransmission. ''HTR2C'' denotes the human gene encoding for the receptor, that in humans is located at the X chromosome. As males have one copy of the gene and in females one of the two copies of the gene is repressed, polymorphisms at this receptor can affect the two sexes to differing extent. Structure At the cell surface the receptor exists as a homodimer. The crystal structure is known since 2018. Distribution 5-HT2C receptors are located mainly in the choroid plexus, and in rats is also found in many other brain regions in high concentrations, including parts of the hippocampus, anterior olfactory nucleus, substantia nigra, several brainstem nuclei, amygdala, subthalamic nucleus and lateral habenula. 5-HT2C receptors are also found on epithel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reuptake
Reuptake is the reabsorption of a neurotransmitter by a neurotransmitter transporter located along the plasma membrane of an axon terminal (i.e., the pre-synaptic neuron at a synapse) or glial cell after it has performed its function of transmitting a neural impulse. Reuptake is necessary for normal synaptic physiology because it allows for the recycling of neurotransmitters and regulates the level of neurotransmitter present in the synapse, thereby controlling how long a signal resulting from neurotransmitter release lasts. Because neurotransmitters are too large and hydrophilic to diffuse through the membrane, specific transport proteins are necessary for the reabsorption of neurotransmitters. Much research, both biochemical and structural, has been performed to obtain clues about the mechanism of reuptake. Protein structure The first primary sequence of a reuptake protein was published in 1990. The technique for protein sequence determination relied upon the purification, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverse Agonist
In pharmacology, an inverse agonist is a drug that binds to the same receptor as an agonist but induces a pharmacological response opposite to that of the agonist. A neutral antagonist has no activity in the absence of an agonist or inverse agonist but can block the activity of either. Inverse agonists have opposite actions to those of agonists but the effects of both of these can be blocked by antagonists. A prerequisite for an inverse agonist response is that the receptor must have a constitutive (also known as intrinsic or basal) level of activity in the absence of any ligand. An agonist increases the activity of a receptor above its basal level, whereas an inverse agonist decreases the activity below the basal level. The efficacy of a full agonist is by definition 100%, a neutral antagonist has 0% efficacy, and an inverse agonist has < 0% (i.e., negative) efficacy. Examples Receptors for which inverse agonists have been identified include the[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor Antagonist
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of receptor proteins.Pharmacology Guide: In vitro pharmacology: concentration-response curves " '' GlaxoWellcome.'' Retrieved on December 6, 2007. They are sometimes called blockers; examples include alpha blockers, |
Receptor (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, receptors are chemical structures, composed of protein, that receive and transduce signals that may be integrated into biological systems. These signals are typically chemical messengers which bind to a receptor and cause some form of cellular/tissue response, e.g. a change in the electrical activity of a cell. There are three main ways the action of the receptor can be classified: relay of signal, amplification, or integration. Relaying sends the signal onward, amplification increases the effect of a single ligand, and integration allows the signal to be incorporated into another biochemical pathway. Receptor proteins can be classified by their location. Transmembrane receptors include ligand-gated ion channels, G protein-coupled receptors, and enzyme-linked hormone receptors. Intracellular receptors are those found inside the cell, and include cytoplasmic receptors and nuclear receptors. A molecule that binds to a receptor is called a ligand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H1 Receptor
The H1 receptor is a histamine receptor belonging to the family of rhodopsin-like G-protein-coupled receptors. This receptor is activated by the biogenic amine histamine. It is expressed in smooth muscles, on vascular endothelial cells, in the heart, and in the central nervous system. The H1 receptor is linked to an intracellular G-protein (Gq) that activates phospholipase C and the inositol triphosphate (IP3) signalling pathway. Antihistamines, which act on this receptor, are used as anti-allergy drugs. The crystal structure of the receptor has been determined (shown on the right/below) and used to discover new histamine H1 receptor ligands in structure-based virtual screening studies. Function The expression of NF-κB, the transcription factor that regulates inflammatory processes, is promoted by the constitutive activity of the H1 receptor as well as by agonists that bind at the receptor. H1-antihistamines have been shown to attenuate NF-κB expression and mitigate certain in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histamine Receptor
The histamine receptors are a class of G protein–coupled receptors which bind histamine as their primary endogenous ligand. There are four known histamine receptors: * H1 receptor * H2 receptor * H3 receptor * H4 receptor Comparison There are several splice variants of H3 present in various species. Though all of the receptors are 7-transmembrane g protein coupled receptors, H1 and H2 are quite different from H3 and H4 in their activities. H1 causes an increase in PIP2 hydrolysis, H2 stimulates gastric acid secretion, and H3 mediates feedback inhibition An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and blocks its activity. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions necessary for life, in which substrate molecules are converted into products. An enzyme facilitates a sp ... of histamine. References External links *Holger Stark: Histamine Receptors, BIOTREND Reviews No. 01, November 2007 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-1D Adrenergic Receptor
The alpha-1D adrenergic receptor (α1D adrenoreceptor), also known as ADRA1D, is an alpha-1 adrenergic receptor, and also denotes the human gene encoding it. Receptor There are 3 alpha-1 adrenergic receptor subtypes: alpha-1A, -1B and -1D, all of which signal through the Gq/11 family of G-proteins and different subtypes show different patterns of activation. They activate mitogenic responses and regulate growth and proliferation of many cells. Gene This gene encodes alpha-1D-adrenergic receptor. Similar to alpha-1B-adrenergic receptor gene, this gene comprises 2 exons and a single intron that interrupts the coding region. Ligands ; Antagonists * A-315456 * BMY 7378 (also α2C antagonist) See also *Adrenergic receptor The adrenergic receptors or adrenoceptors are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that are targets of many catecholamines like norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline) produced by the body, but also many medications like beta ... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |