|
Clione Okhotensis
''Clione okhotensis'' is a species of sea angel, a pelagic marine gastropod (sea slug) in the family Clionidae. Distribution The only known localities of ''Clione okhotensis'' are in the southern Sea of Okhotsk and the Kuril–Kamchatka Trench area in the western Pacific Ocean. It has been found at depths of 0.3 to 1.5 m below the surface of the water. Its distribution overlaps with those of '' C. limacina'' and '' C. elegantissima'', two separate species of the same genus found in the North Pacific. Description ''Clione okhotensis'' only reaches up to 0.8 cm (0.3 in) in body length, making the species substantially smaller than most other ''Clione'' species, such as ''C. limacina'', which has a body length of up to 3 cm (1.2 in) in comparison. The species is considered paedomorphic, as adults retain many juvenile characteristics upon maturing. As a result, ''Clione okhotensis'' strongly resemble and were previously mistaken for juvenile ''C. limacina''. Like all ''Clione'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Angel
Sea angels (clade Gymnosomata) are a large group of small free-swimming sea slugs, not to be confused with Cnidarians (Jellyfish and other similar creatures), classified into six different families. They are pelagic opisthobranchs in the clade Gymnosomata within the larger mollusc clade Heterobranchia. Sea angels were previously referred to as a type of pteropod. Sea angels are also sometimes known as "cliones" but this is potentially misleading because the family Clionidae is just one of the families within this clade. Recent molecular data suggest the Gymnosomata form a sister group to the Thecosomata (other planktonic, weakly or nonmineralized gastropods), but this long-standing hypothesis has also had some recent detractors. Fossils of the group go back to the Middle Frasnian stage of the Late Devonian period. Distribution These organisms have a wide geographic range, from polar regions, under sea ice, to equatorial (tropic) seas. Description In this clade, the foot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radula
The radula (, ; plural radulae or radulas) is an anatomical structure used by molluscs for feeding, sometimes compared to a tongue. It is a minutely toothed, chitinous ribbon, which is typically used for scraping or cutting food before the food enters the esophagus. The radula is unique to the molluscs, and is found in every class of mollusc except the bivalves, which instead use cilia, waving filaments that bring minute organisms to the mouth. Within the gastropods, the radula is used in feeding by both herbivorous and carnivorous snails and slugs. The arrangement of teeth ( denticles) on the radular ribbon varies considerably from one group to another. In most of the more ancient lineages of gastropods, the radula is used to graze, by scraping diatoms and other microscopic algae off rock surfaces and other substrates. Predatory marine snails such as the Naticidae use the radula plus an acidic secretion to bore through the shell of other molluscs. Other predatory marine snails ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aragonite
Aragonite is a carbonate mineral, one of the three most common naturally occurring crystal forms of calcium carbonate, (the other forms being the minerals calcite and vaterite). It is formed by biological and physical processes, including precipitation from marine and freshwater environments. The crystal lattice of aragonite differs from that of calcite, resulting in a different crystal shape, an orthorhombic crystal system with acicular crystal. Repeated twinning results in pseudo-hexagonal forms. Aragonite may be columnar or fibrous, occasionally in branching helictitic forms called ''flos-ferri'' ("flowers of iron") from their association with the ores at the Carinthian iron mines. Occurrence The type location for aragonite is Molina de Aragón in the Province of Guadalajara in Castilla-La Mancha, Spain, for which it was named in 1797. Aragonite is found in this locality as cyclic twins inside gypsum and marls of the Keuper facies of the Triassic. This type of arago ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
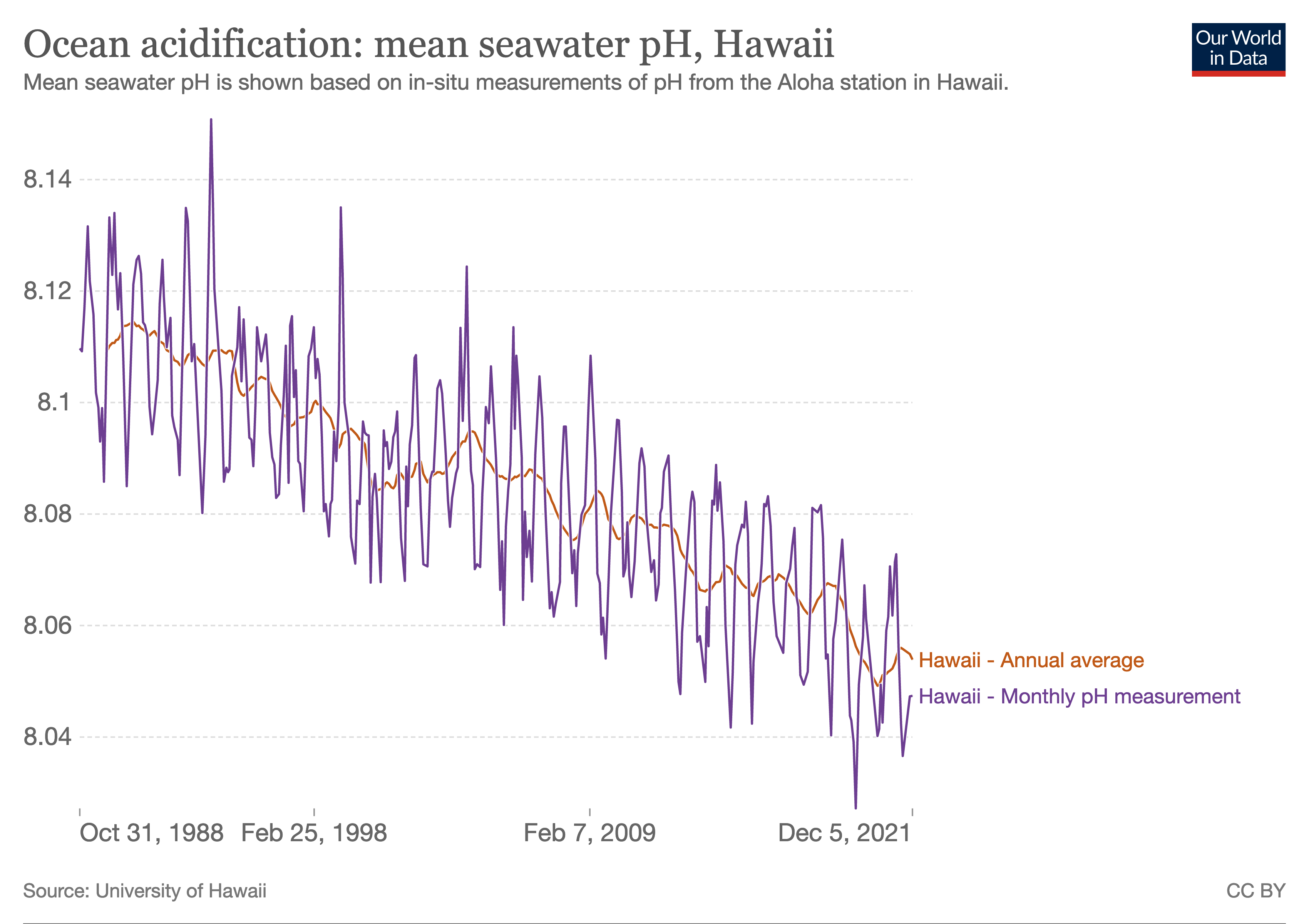
Ocean Acidification
Ocean acidification is the reduction in the pH value of the Earth’s ocean. Between 1751 and 2021, the average pH value of the ocean surface has decreased from approximately 8.25 to 8.14. The root cause of ocean acidification is carbon dioxide emissions from human activities which have led to atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) levels of more than 410 ppm (in 2020). The oceans absorb CO2 from the atmosphere. This leads to the formation of carbonic acid (H2CO3) which dissociates into a bicarbonate ion () and a hydrogen ion (H+). The free hydrogen ions (H+) decrease the pH of the ocean, therefore increasing acidity (this does not mean that seawater is acidic yet; it is still alkaline, with a pH higher than 8). A decrease in pH corresponds to a decrease in the concentration of carbonate ions, which are the main building block for calcium carbonate (CaCO3) shells and skeletons. Marine calcifying organisms, like mollusks, oysters and corals, are particularly affected by this as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices increase greenhouse gases, notably carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming. Due to climate change, deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Increased warming in the Arctic has contributed to melting permafrost, glacial retreat and sea ice loss. Higher temperatures are also causing m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pink Salmon
Pink salmon or humpback salmon (''Oncorhynchus gorbuscha'') is a species of anadromous fish in the salmon family. It is the smallest and most abundant of the Pacific salmon. The scientific species name is based on the Russian common name for this species ''gorbúša'' (горбуша), which literally means ''humpie''. Description In the ocean, pink salmon are bright silver fish. After returning to their spawning streams, their coloring changes to pale grey on the back with yellowish-white belly (although some turn an overall dull green color). As with all salmon, in addition to the dorsal fin, they also have an adipose fin. The fish is characterized by a white mouth with black gums, no teeth on the tongue, large oval-shaped black spots on the back, a v-shaped tail, and an anal fin with 13-17 soft rays. During their spawning migration, males develop a pronounced humped back, hence their nickname "humpies". Pink salmon average 4.8 pounds (2.2 kg) in weight. The maximu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limacina Helicina
''Limacina helicina'' is a species of small swimming planktonic sea snail in the family Limacinidae, which belong to the group commonly known as sea butterflies (Thecosomata). ''Limacina helicina'' is a keystone species of mesozooplankton in Arctic pelagic ecosystems. The first written record of this species was by Friderich Martens from Spitsbergen in 1675. ''Limacina helicina'' was also observed during a 1773 expedition to the Arctic led by Constantine John Phipps on the ships HMS ''Racehorse'' and on HMS ''Carcass'' and the species was described one year later, in 1774. ''Limacina helicina'' is the type species of the genus ''Limacina''. In contrast to the traditional view, it was shown in 2010 that the distribution of this species is not bipolar; Arctic and Antarctic individuals belong to two genetically distinct species: ''Limacina helicina'' in the Arctic, and ''Limacina antarctica'' in the Antarctic. Subspecies * ''Limacina helicina helicina'' (Phipps, 1774)Bouc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chitin are produced each year in the biosphere. It is a primary component of cell walls in fungi (especially basidiomycetes and filamentous fungi), the exoskeletons of arthropods such as crustaceans and insects, the radulae, cephalopod beaks and gladii of molluscs and in some nematodes and diatoms. It is also synthesised by at least some fish and lissamphibians. Commercially, chitin is extracted from the shells of crabs, shrimps, shellfishes and lobsters, which are major by-products of the seafood industry. The structure of chitin is comparable to cellulose, forming crystalline nanofibrils or whiskers. It is functionally comparable to the protein keratin. Chitin has proved useful for several medicinal, industrial and biotechnological purpos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoteny
Neoteny (), also called juvenilization,Montagu, A. (1989). Growing Young. Bergin & Garvey: CT. is the delaying or slowing of the physiological, or somatic, development of an organism, typically an animal. Neoteny is found in modern humans compared to other primates. In progenesis or paedogenesis, sexual development is accelerated. Both neoteny and progenesis result in paedomorphism (as having the form typical of children) or paedomorphosis (changing towards forms typical of children), a type of heterochrony. It is the retention in adults of traits previously seen only in the young. Such retention is important in evolutionary biology, domestication and evolutionary developmental biology. Some authors define paedomorphism as the retention of larval traits, as seen in salamanders.Schell, S. C. ''Handbook of Trematodes of North America North of Mexico'', 1985, pg. 22 History and etymology The origins of the concept of neoteny have been traced to the Bible (as argued by Ashley Monta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastropoda
The gastropods (), commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda (). This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from land. There are many thousands of species of sea snails and slugs, as well as freshwater snails, freshwater limpets, and land snails and slugs. The class Gastropoda contains a vast total of named species, second only to the insects in overall number. The fossil history of this class goes back to the Late Cambrian. , 721 families of gastropods are known, of which 245 are extinct and appear only in the fossil record, while 476 are currently extant with or without a fossil record. Gastropoda (previously known as univalves and sometimes spelled "Gasteropoda") are a major part of the phylum Mollusca, and are the most highly diversified class in the phylum, with 65,000 to 80,000 living snail and slug species. The anatomy, behavior, feeding, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clione Elegantissima
''Clione'' is a genus of small, floating sea slugs, pelagic marine gastropod mollusks in the family Clionidae, the sea angels.Gofas, S. (2012). Clione. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=137793 on 2012-07-23 ''Clione'' is the type genus of the family Clionidae. Species Species within the genus ''Clione'' include: *''Clione antarctica'' (Smith, 1902) *''Clione elegantissima'' (Dall, 1871) *''Clione limacina'' (Phipps, 1774) *''Clione okhotensis ''Clione okhotensis'' is a species of sea angel, a pelagic marine gastropod (sea slug) in the family Clionidae. Distribution The only known localities of ''Clione okhotensis'' are in the southern Sea of Okhotsk and the Kuril–Kamchatka Trench ...'' Yamazaki & Kuwahara, 2017 References * Vaught, K.C. (1989). ''A classification of the living Mollusca''. American Malacologists: Melbourne, FL (USA). . XII, 195 pp. * Gofas, S.; Le Renard, J.; Bouchet, P. (2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clione Limacina
''Clione limacina'', known as the naked sea butterfly, sea angel, and common clione, is a sea angel (pelagic sea slug) found from the surface to greater than depth.Gofas, S. (2012). ''Clione limacina''. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=139178 on 2012-07-23 It lives in the Arctic Ocean and cold regions of the North Atlantic Ocean. It was first described by Friderich Martens in 1676 and became the first gymnosomatous (without a shell) " pteropod" to be described. Subspecies * ''Clione limacina australis'' ( Bruguière, 1792)Gofas, S. (2011). ''Clione limacina''. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=139178 on 2011-01-29 * ''Clione limacina limacina'' (Phipps, 1774) Distribution ''Clione limacina'' is found in cold waters of the Arctic Ocean and North Atlantic Ocean, ranging south at least to the Sargasso Sea. There are three other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |