|
Clifton Observatory
Clifton Observatory () is a former mill, now used as an observatory, located on Clifton Down, close to the Clifton Suspension Bridge, Bristol, England. The building was erected, with the permission of the Society of Merchant Venturers, as a windmill for corn in 1766 and later converted to the grinding of snuff, when it became known as 'The Snuff Mill'. This was damaged by fire on 30 October 1777, when the sails were left turning during a gale and caused the equipment to catch alight. It was then derelict for 52 years until in 1828 William West, an artist, rented the old mill, for 5 shillings (25p) a year, as a studio. In 1977, the Merchant Venturers sold the observatory to Honorbrook Inns; however, they were obliged to maintain public access to the camera obscura whose ownership was retained by the Merchant Venturers. It has been designated by English Heritage as a grade II* listed building and is on the Buildings at Risk Register. In February 2015 the Observatory was boug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in South West England. The wider Bristol Built-up Area is the eleventh most populous urban area in the United Kingdom. Iron Age hillforts and Roman villas were built near the confluence of the rivers Frome and Avon. Around the beginning of the 11th century, the settlement was known as (Old English: 'the place at the bridge'). Bristol received a royal charter in 1155 and was historically divided between Gloucestershire and Somerset until 1373 when it became a county corporate. From the 13th to the 18th century, Bristol was among the top three English cities, after London, in tax receipts. A major port, Bristol was a starting place for early voyages of exploration to the New World. On a ship out of Bristol in 1497, John Cabot, a Venetia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol City Museum And Art Gallery
Bristol Museum & Art Gallery is a large museum and art gallery in Bristol, England. The museum is situated in Clifton, about from the city centre. As part of Bristol Culture it is run by the Bristol City Council with no entrance fee. It holds designated museum status, granted by the national government to protect outstanding museums. The designated collections include: geology, Eastern art, and Bristol's history, including English delftware. In January 2012 it became one of sixteen Arts Council England Major Partner Museums. The museum includes sections on natural history as well as local, national and international archaeology. The art gallery contains works from all periods, including many by internationally famous artists, as well a collection of modern paintings of Bristol. In the summer of 2009 the museum hosted an exhibition by Banksy featuring more than 70 works of art, including animatronics and installations; it is his largest exhibition yet. It was developed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Downs, Bristol
The Downs are an area of public open limestone downland in Bristol, England. They consist of Durdham Down to the north and east and Clifton Down to the south, separated by Stoke Road. Durdham Down Durdham Down is the north and east part of the Downs, extending to Westbury Park and Henleaze, with an area of . It is owned by Bristol City Council for the benefit of the people of Bristol. Clifton Down Clifton Down is the part of the Downs southwest of the southern part of Stoke Road, between Sneyd Park and Clifton and extending to the edge of the Avon Gorge, with an area of . It is owned by the Society of Merchant Venturers. Management Since an Act of Parliament in 1861, when Bristol Corporation acquired Durdham Down, the Downs have been managed as a single unit by the Downs Committee, a joint committee of the corporation and the Merchant Venturers. They have been designated common land since the early 1970s by Bristol City Council. Background They are used for leisure, wal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structures On The Heritage At Risk Register
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as biological organisms, minerals and chemicals. Abstract structures include data structures in computer science and musical form. Types of structure include a hierarchy (a cascade of one-to-many relationships), a network featuring many-to-many links, or a lattice featuring connections between components that are neighbors in space. Load-bearing Buildings, aircraft, skeletons, anthills, beaver dams, bridges and salt domes are all examples of load-bearing structures. The results of construction are divided into buildings and non-building structures, and make up the infrastructure of a human society. Built structures are broadly divided by their varying design approaches and standards, into categories including building structures, archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Buildings Completed In 1766
Industrial may refer to: Industry * Industrial archaeology, the study of the history of the industry * Industrial engineering, engineering dealing with the optimization of complex industrial processes or systems * Industrial city, a city dominated by one or more industries * Industrial loan company, a financial institution in the United States that lends money, and may be owned by non-financial institutions * Industrial organization, a field that builds on the theory of the firm by examining the structure and boundaries between firms and markets * Industrial Revolution, the development of industry in the 18th and 19th centuries * Industrial society, a society that has undergone industrialization * Industrial technology, a broad field that includes designing, building, optimizing, managing and operating industrial equipment, and predesignated as acceptable for industrial uses, like factories * Industrial video, a video that targets “industry” as its primary audience * Industrial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Downs (Bristol)
The Downs are an area of public open limestone downland in Bristol, England. They consist of Durdham Down to the north and east and Clifton Down to the south, separated by Stoke Road. Durdham Down Durdham Down is the north and east part of the Downs, extending to Westbury Park and Henleaze, with an area of . It is owned by Bristol City Council for the benefit of the people of Bristol. Clifton Down Clifton Down is the part of the Downs southwest of the southern part of Stoke Road, between Sneyd Park and Clifton and extending to the edge of the Avon Gorge, with an area of . It is owned by the Society of Merchant Venturers. Management Since an Act of Parliament in 1861, when Bristol Corporation acquired Durdham Down, the Downs have been managed as a single unit by the Downs Committee, a joint committee of the corporation and the Merchant Venturers. They have been designated common land since the early 1970s by Bristol City Council. Background They are used for leisure, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grade II* Listed Buildings In Bristol
There are 212 Grade II* listed buildings in Bristol, England. In England and Wales the authority for listing is granted by the Planning (Listed Buildings and Conservation Areas) Act 1990 and is administered by English Heritage, an agency of the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport In the United Kingdom the term listed building refers to a building or other structure officially designated as being of special architectural, historical or cultural significance. Buildings Notes References See also * Buildings and architecture of Bristol * Grade I listed buildings in Bristol * Grade II listed buildings in Bristol {{DEFAULTSORT:Grade II listed buildings in Bristol Listed buildings in Bristol Bristol Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for limes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and porcelain. The place where such wares are made by a ''potter'' is also called a ''pottery'' (plural "potteries"). The definition of ''pottery'', used by the ASTM International, is "all fired ceramic wares that contain clay when formed, except technical, structural, and refractory products". In art history and archaeology, especially of ancient and prehistoric periods, "pottery" often means vessels only, and sculpted figurines of the same material are called "terracottas". Pottery is one of the oldest human inventions, originating before the Neolithic period, with ceramic objects like the Gravettian culture Venus of Dolní Věstonice figurine discovered in the Czech Republic dating back to 29,000–25,000 BC, and pottery vessels that were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
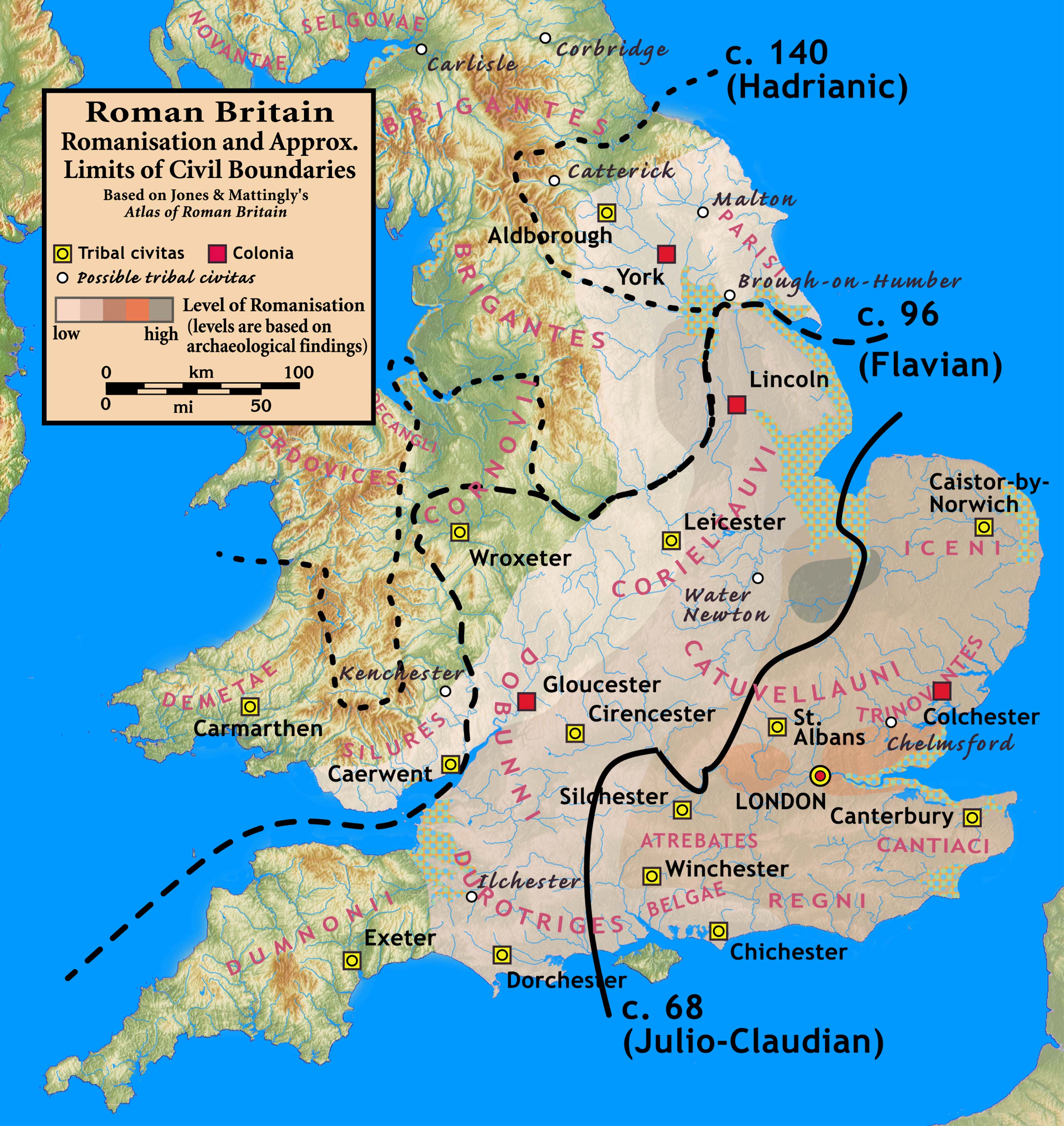
Romano-British
The Romano-British culture arose in Britain under the Roman Empire following the Roman conquest in AD 43 and the creation of the province of Britannia. It arose as a fusion of the imported Roman culture with that of the indigenous Britons, a people of Celtic language and custom. Scholars such as Christopher Snyder believe that during the 5th and 6th centuries – approximately from 410 when the Roman legions withdrew, to 597 when St Augustine of Canterbury arrived – southern Britain preserved an active sub-Roman culture that survived the attacks from the Anglo-Saxons and even used a vernacular Latin when writing. Arrival of the Romans Roman troops, mainly from nearby provinces, invaded in AD 43, in what is now part of England, during the reign of Emperor Claudius. Over the next few years the province of Britannia was formed, eventually including the whole of what later became England and Wales and parts of Scotland.Kinder, H. & Hilgemann W. ''The Penguin Atlas of World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |