|
Clement Edwards
(Allen) Clement Edwards (7 June 1869 – 23 June 1938), usually known as Clem, was a Welsh people, Welsh lawyer, journalist, trade union activist and Liberal Party (UK), Liberal Party politician. Family and education Edwards was born in Knighton, Powys, Knighton in Radnorshire, the son of a master tailor and draper, one of seven children. He was educated at the local school in Knighton, undertook private studies and also attended evening classes at Birkbeck Institute in London. In 1890, Edwards married Fanny Emerson, the daughter of the superintendent of Trinity House, Great Yarmouth. She died in 1920. Two years later Edwards was remarried, to Alice May Parker, a political colleague in the NDP. They had one son, John Charles Gordon Clement Edwards (1924–2004) who served in the Royal Naval Volunteer Reserve in the Second World War and later became a solicitor. In religion, although born into an Anglican family, Edwards became a Congregationalist and was considered a typical We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clement Edwards MP
Clement or Clément may refer to: People * Clement (name), a given name and surname * Saint Clement (other)#People Places * Clément, French Guiana, a town * Clement, Missouri, U.S. * Clement Township, Michigan, U.S. Other uses * Adolphe Clément-Bayard French industrialist (1855–1928), founder of a number of companies which incorporate the name "Clément", including: ** Clément Cycles, French bicycle and motorised cycle manufacturer ** Clément Motor Company, British automobile manufacturer and importer ** Clément Tyres, Franco-Italian cycle tyre manufacturer, licensed in America since 2010 * First Epistle of Clement, of the New Testament apocrypha * ''Clément'' (film), a 2001 French drama See also * * * * Clemens, a name * Clemente, a name * Clements (other) * Clementine (other) * Klement, a name * Kliment, a name * San Clemente (other) Pope Clement I (Saint Clement, died 99AD) is called San Clemente in Spanish and Italian and gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taff Vale Case
''Taff Vale Railway Co v Amalgamated Society of Railway Servants'' [1901UKHL 1 commonly known as the ''Taff Vale case'', is a formative case in UK labour law. It held that, at common law, Trade union, unions could be liable for loss of profits to employers that were caused by taking strike action. The Trade unions in the United Kingdom, labour movement reacted to ''Taff Vale'' with outrage; the case gave impetus to the establishment of the UK Labour Party (UK), Labour Party and was soon reversed by the Trade Disputes Act 1906. It was reversed at common law in ''Crofter Hand Woven Harris Tweed Co Ltd v Veitch'' [1942]. Events A trade union, called the Amalgamated Society of Railway Servants, went on Strike action, strike to protest against the company's treatment of John Ewington, who had been refused higher pay and was punished for his repeated requests by being moved to a different station. When the Taff Vale Railway Company employed replacement staff, the strikers engaged in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fabian Society
The Fabian Society is a British socialist organisation whose purpose is to advance the principles of social democracy and democratic socialism via gradualist and reformist effort in democracies, rather than by revolutionary overthrow. The Fabian Society was also historically related to radicalism, a left-wing liberal tradition. As one of the founding organisations of the Labour Representation Committee in 1900, and as an important influence upon the Labour Party which grew from it, the Fabian Society has had a powerful influence on British politics. Members of the Fabian Society have included political leaders from other countries, such as Jawaharlal Nehru, who adopted Fabian principles as part of their own political ideologies. The Fabian Society founded the London School of Economics in 1895. Today, the society functions primarily as a think tank and is one of twenty socialist societies affiliated with the Labour Party. Similar societies exist in Australia (the Australi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labour Party (UK)
The Labour Party is a political party in the United Kingdom that has been described as an alliance of social democrats, democratic socialists and trade unionists. The Labour Party sits on the centre-left of the political spectrum. In all general elections since 1922, Labour has been either the governing party or the Official Opposition. There have been six Labour prime ministers and thirteen Labour ministries. The party holds the annual Labour Party Conference, at which party policy is formulated. The party was founded in 1900, having grown out of the trade union movement and socialist parties of the 19th century. It overtook the Liberal Party to become the main opposition to the Conservative Party in the early 1920s, forming two minority governments under Ramsay MacDonald in the 1920s and early 1930s. Labour served in the wartime coalition of 1940–1945, after which Clement Attlee's Labour government established the National Health Service and expanded the welfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radicalism (historical)
Radicalism (from French , "radical") or classical radicalism was a historical political movement representing the leftward flank of liberalism during the late 18th and early 19th centuries and a precursor to social liberalism, social democracy and modern progressivism. Its earliest beginnings were found in Great Britain with the Levellers during the English Civil War, and the later Radical Whigs. During the 19th century in the United Kingdom, continental Europe, and Latin America, the term ''radical'' came to denote a progressive liberal ideology inspired by the French Revolution. Historically, radicalism emerged in an early form with the French Revolution and the similar movements it inspired in other countries. It grew prominent during the 1830s in the United Kingdom with the Chartists and Belgium with the Revolution of 1830, then across Europe in the 1840s–1850s during the Revolutions of 1848. In contrast to the social conservatism of existing liberal politics, radica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Daily News (UK)
''The Daily News'' was a national daily newspaper in the United Kingdom. The ''News'' was founded in 1846 by Charles Dickens, who also served as the newspaper's first editor. It was conceived as a radical rival to the right-wing ''Morning Chronicle''. The paper was not at first a commercial success. Dickens edited 17 issues before handing over the editorship to his friend John Forster, who had more experience in journalism than Dickens. Forster ran the paper until 1870.''London Daily News: General Description'', Rossetti Archive.Undated Accessed: 2007-09-14. , |
The Echo (London)
''The Echo'', founded in 1868 in London by Cassell, Petter, Galpin & Co., was London's first halfpenny evening newspaper (earlier provincial titles included Liverpool's ''Events'' and the ''South Shields Gazette'', both launched in 1855). It was published daily except on Sunday. Sometimes its Saturday edition appeared under the name ''The Cricket Echo'' or ''The Football Echo''. Issue Number 1 appeared on 8 December 1868. ''The Echo'' ceased publication with Issue Number 11,391 on 31 July 1905. History Arthur Arnold was the editor for Messrs. Cassell, Petter & Galpin, who owned ''The Echo'' from 1868 until they sold it to Albert Grant in 1875. Upon the purchase by Grant, Arnold resigned as editor and went on a long trip to Russia and Persia. In less than 12 months as owner, Grant sold the newspaper to John Passmore Edwards in 1876. Edwards was the editor until its eventual sale in 1896 to a syndicate created for the purpose of purchasing ''The Echo''. In 1884 Edwards sold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Sun (1893–1906)
''The Sun'' was a London evening newspaper published in England between 1893 and 1906.Dennis Griffiths (ed) ''The Encyclopedia of the British Press, 1422–1992'', London & Basingstoke: Macmillan, 1992, p.543 Intended to be a literary publication and explicitly without political allegiance, it was founded and initially edited by T. P. O'Connor. After O'Connor severed all links with the paper, it was edited by Theodore Dahl with financial support from Horatio Bottomley Horatio William Bottomley (23 March 1860 – 26 May 1933) was an English financier, journalist, editor, newspaper proprietor, swindler, and Member of Parliament. He is best known for his editorship of the popular magazine ''John Bull (maga ... for the remainder of its existence. It has no connection with the modern British newspaper of the same name. References Defunct newspapers published in the United Kingdom {{UK-newspaper-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syndicalism
Syndicalism is a Revolutionary politics, revolutionary current within the Left-wing politics, left-wing of the Labour movement, labor movement that seeks to unionize workers Industrial unionism, according to industry and advance their demands through Strike action, strikes with the eventual goal of gaining Social ownership, control over the means of production and the economy at large. Developed in French labor unions during the late 19th century, syndicalist movements were most predominant amongst the Socialism, socialist movement during the interwar period which preceded the outbreak of World War II. Major syndicalist organizations included the General Confederation of Labour (France), General Confederation of Labor in France, the National Confederation of Labour (CNT) in Spain, the Italian Syndicalist Union (USI), the Free Workers' Union of Germany, and the Argentine Regional Workers' Federation. Although they did not regard themselves as syndicalists, the Industrial Workers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senghenydd Colliery Disaster
The Senghenydd colliery disaster, also known as the Senghenydd explosion ( cy, Tanchwa Senghennydd), occurred at the Universal Colliery in Senghenydd, near Caerphilly, Glamorgan, Wales, on 14 October 1913. The explosion, which killed 439 coal mining, miners and a rescuer, is the worst mining accident in the United Kingdom. Universal Colliery, on the South Wales Coalfield, extracted steam coal, which was much in demand. Some of the region's coal seams contained high quantities of firedamp, a highly explosive gas consisting of methane and hydrogen. In an earlier disaster in May 1901, three underground explosions at the colliery killed 81 miners. The Inquests in England and Wales, inquest established that the colliery had high levels of airborne coal dust, which would have exacerbated the explosion and carried it further into the mine workings. The cause of the 1913 explosion is unknown, but the subsequent inquiry thought the most likely cause was a spark from underground signalli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RMS Titanic
RMS ''Titanic'' was a British passenger liner, operated by the White Star Line, which sank in the North Atlantic Ocean on 15 April 1912 after striking an iceberg during her maiden voyage from Southampton, England, to New York City, United States. Of the estimated 2,224 passengers and crew aboard, more than 1,500 died, making it the deadliest sinking of a single ship up to that time. It remains the deadliest peacetime sinking of a superliner or cruise ship. The disaster drew public attention, provided foundational material for the disaster film genre, and has inspired many artistic works. RMS ''Titanic'' was the largest ship afloat at the time she entered service and the second of three s operated by the White Star Line. She was built by the Harland and Wolff shipyard in Belfast. Thomas Andrews, the chief naval architect of the shipyard, died in the disaster. ''Titanic'' was under the command of Captain Edward Smith, who went down with the ship. The ocean liner carri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
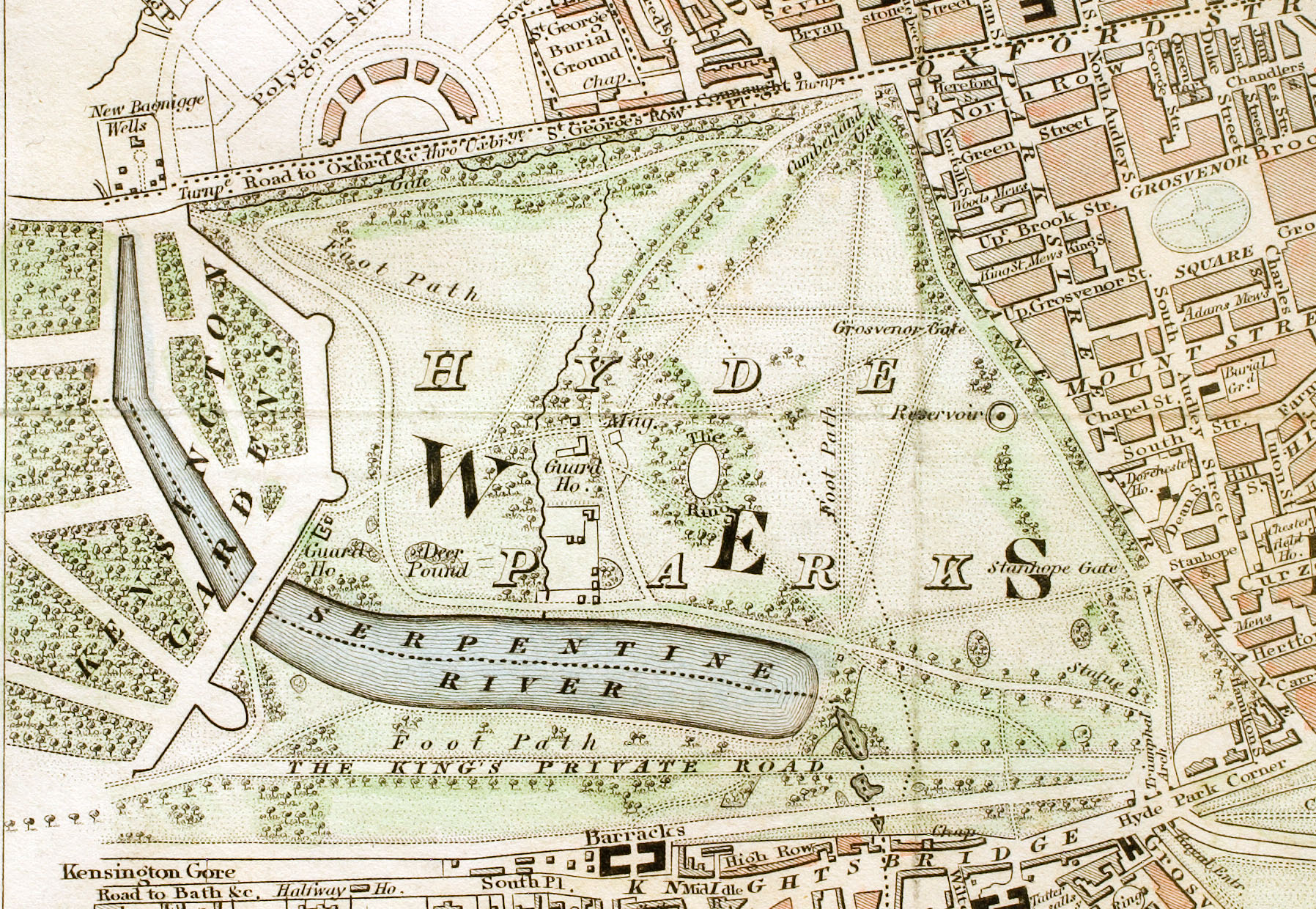
Hyde Park, London
Hyde Park is a Grade I-listed major park in Westminster, Greater London, the largest of the four Royal Parks that form a chain from the entrance to Kensington Palace through Kensington Gardens and Hyde Park, via Hyde Park Corner and Green Park past the main entrance to Buckingham Palace. The park is divided by the Serpentine and the Long Water lakes. The park was established by Henry VIII in 1536 when he took the land from Westminster Abbey and used it as a hunting ground. It opened to the public in 1637 and quickly became popular, particularly for May Day parades. Major improvements occurred in the early 18th century under the direction of Queen Caroline. Several duels took place in Hyde Park during this time, often involving members of the nobility. The Great Exhibition of 1851 was held in the park, for which The Crystal Palace, designed by Joseph Paxton, was erected. Free speech and demonstrations have been a key feature of Hyde Park since the 19th century. Speakers' Cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)