|
Claude Vellefaux
Claude Vellefaux was a 16th/17th-century French architect, who had the Hôpital Saint-Louis built in 1611 at the request of Henry IV of France. Biography Vellefaux was qualified as a master mason in 1585, sworn by the king as responsible of masonry works and topographer for Mr. Prince de Conti, in 1611, great topographer of Saint-Germain-des-Prés, sworn mason controller of the buildings of the Hôtel-Dieu, in 1625. Before 1610, he married Laurence Hébert, daughter of a merchant living in Saint-Germain-des-Prés and had three daughters: one, Laurence married a king's doctor, Valentin Hieraulme and the other, Anne, joined Gilles Sanglier, squire, lord of Noblaye in Touraine. The third, Étiennette Vellefaux, married architect Christophe Gamard who succeeded his father-in-law as seer of the abbey Saint-Germain-des-Prés., ''Demeures parisiennes sous Henri IV et Louis XIII'', , Éditions Hazan, Paris, 1991 ; He also contributed to many works in the City Hall of Paris. He wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
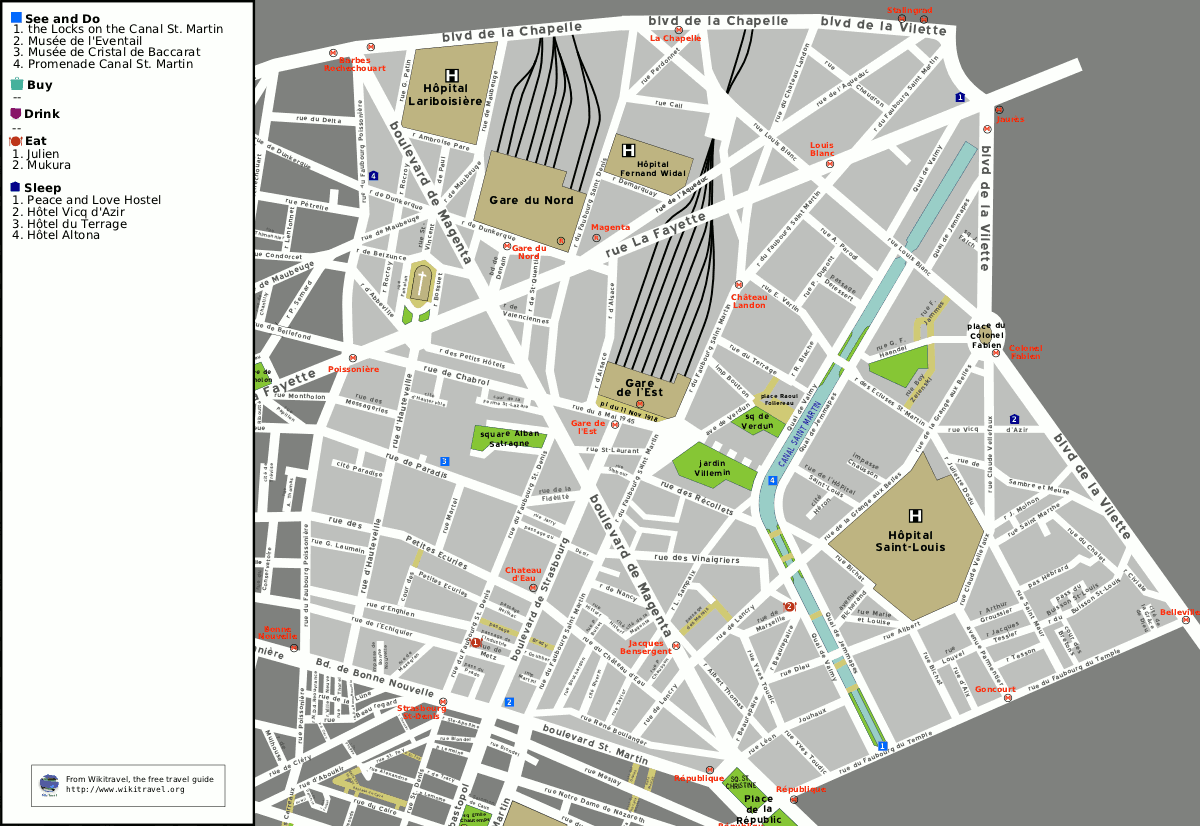
Hôpital Saint-Louis
Hôpital Saint-Louis is a hospital in Paris, France. It was built in 1611 by architect Claude Vellefaux at the request of Henry IV of France. It is part of the Assistance publique - Hôpitaux de Paris hospital system, and it is located at 1 avenue Claude-Vellefaux, in the 10th arrondissement near the metro station Goncourt. It was founded by King Henry IV (1553–1610) (King of France and Navarre) on May 17, 1607 to relieve the Hôtel-Dieu de Paris during the plague. It was named ''St. Louis'' in memory of Louis IX, who died of the dysentery that devastated Tunis in 1270. Today, Hôpital Saint-Louis uses its historical premises (parts of which are classified as historical monuments) for administrative functions. Following the 1980s new modern additions were made to house the current hospital and teaching hospital. Its primary specialties are dermatology and hematology, as well as oncology. The dermatology library was founded by Dr Henri Feulard. The hospital employs 2,500 peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry IV Of France
Henry IV (french: Henri IV; 13 December 1553 – 14 May 1610), also known by the epithets Good King Henry or Henry the Great, was King of Navarre (as Henry III) from 1572 and King of France from 1589 to 1610. He was the first monarch of France from the House of Bourbon, a cadet branch of the Capetian dynasty. He was assassinated in 1610 by François Ravaillac, a Catholic zealot, and was succeeded by his son Louis XIII. Henry was the son of Jeanne III of Navarre and Antoine de Bourbon, Duke of Vendôme. He was baptised as a Catholic but raised in the Protestant faith by his mother. He inherited the throne of Navarre in 1572 on his mother's death. As a Huguenot, Henry was involved in the French Wars of Religion, barely escaping assassination in the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre. He later led Protestant forces against the French royal army. Henry became king of France in 1589 upon the death of Henry III, his brother-in-law and distant cousin. He was the first Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Germain-des-Prés
Saint-Germain-des-Prés () is one of the four administrative quarters of the 6th arrondissement of Paris, France, located around the church of the former Abbey of Saint-Germain-des-Prés. Its official borders are the River Seine on the north, the ' on the west, between the ' and ' on the east, and the ' on the south. Residents of the quarter are known as '. The quarter's cafés include Les Deux Magots, Café de Flore, le Procope, and the Brasserie Lipp, as well as many bookstores and publishing houses. In the 1940s and 1950s, it was the centre of the existentialist movement (associated with Jean-Paul Sartre and Simone de Beauvoir). It is also home to the École des Beaux-Arts, Sciences Po, the Saints-Pères biomedical university center of the University of Paris, the School for Advanced Studies in the Social Sciences, and the Musée national Eugène Delacroix, in the former apartment and studio of painter Eugène Delacroix. History The Middle Ages Until the 17th century the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christophe Gamard
Christophe Gamard, Gamar or Gamart, was a 17th-century French architect, who worked in Paris and died there in 1649. Biography He was a master mason in 1613, an architect of the old Saint-Sulpice in 1623 (and began its reconstruction after 1643), and a city juror (''juré de la Ville'') in 1626. He was an assistant of Claude Vellefaux, the supervising architect (''architecte voyer'') of the Abbey of Saint-Germain-des-Prés, and succeeded him in that position in 1627. He became an architect of the king (''architecte du roi'') in 1639., ''Demeures parisiennes sous Henri IV et Louis XIII'', Paris, Éditions Hazan, 1991, , . Family He married Claude Vellefaux's daughter, Étiennette Vellefaux. They had two sons, Christophe and Hubert. Widowed, he married Marie Gillier in 1648, despite the opposition of his sons. His brother, Philippot Gamard, worked on the Hotel de Nemours, , in 1620, and at houses, current rues de Sévigné and between 1616 and 1619. Works * Houses in in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbey Of Saint-Germain-des-Prés
An abbey is a type of monastery used by members of a religious order under the governance of an abbot or abbess. Abbeys provide a complex of buildings and land for religious activities, work, and housing of Christian monks and nuns. The concept of the abbey has developed over many centuries from the early monastic ways of religious men and women where they would live isolated from the lay community about them. Religious life in an abbey may be monastic. An abbey may be the home of an enclosed religious order or may be open to visitors. The layout of the church and associated buildings of an abbey often follows a set plan determined by the founding religious order. Abbeys are often self-sufficient while using any abundance of produce or skill to provide care to the poor and needy, refuge to the persecuted, or education to the young. Some abbeys offer accommodation to people who are seeking spiritual retreat. There are many famous abbeys across the Mediterranean Basin and Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hôtel-Dieu De Paris
In French-speaking countries, a hôtel-Dieu ( en, hostel of God) was originally a hospital for the poor and needy, run by the Catholic Church. Nowadays these buildings or institutions have either kept their function as a hospital, the one in Paris being the oldest and most renowned, or have been converted into hotels, museums, or general purpose buildings (for instance housing a préfecture, the administrative head office of a French department). Therefore, as a secondary meaning, the term hôtel-Dieu can also refer to the building itself, even if it no longer houses a hospital. Examples include: ;Belgium * Notre Dame à la Rose, founded in 1242 ;France *Hôtel-Dieu d'Angers, founded in 1153 *Hôtel-Dieu de Beaune, founded in 1443 *Hôtel-Dieu of Carpentras, built in 1754 *Hôtel-Dieu of Château-Thierry, founded in 1304 *Hôtel-Dieu of Cluny, built in the 17th and 18th century *Hôtel-Dieu de Lyon, created in 1478 *Hôtel-Dieu of Nantes, completed in 1508 *Hôtel-Dieu de Paris, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François Quesnel
François Quesnel (c. 1543–1619) was a French painter of Scottish extraction. Biography The son of the French painter Pierre Quesnel and his Scottish wife Madeleine Digby, born in Edinburgh while his father worked for Mary of Guise, Quesnel found patronage at the French court of Catherine de Medici and her son, Henri III (''illustration''). He married Charlotte Richandeau, with whom he had four children. A widower, he remarried in 1584 Marguerite Le Masson, who gave him ten more children, among whom were Nicolas (died 1632) and Augustin, painters, and Jacques, bookseller. In le Paris he worked as a decorator and a designer of cartoons for tapestry, but it is as a portrait painter, both in oils and in delicately tinted pencil or red and black chalk, that he is chiefly remembered. Some portraits were engraved by Thomas de Leu and Michel Lasne, and in 1609 he drew a map of Paris for engraving by Pierre Vallet. He died in le Paris. Tapestry designs In 1585 François provided a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude Chastillon
Claude Chastillon or Chatillon (1559 or 1560 – 27 April 1616) was a French architect, military engineer, military and civil engineer, and topographer, topographical Drawing, draughtsman, who served under Henry IV of France. His most notable work, ''Topographie françoise'', published posthumously in 1641, is a collection of 500 views of French towns and buildings and constitutes a unique, if partial, historical account of French topography and architecture at the beginning of the 17th century.Boudon 1996. Life and career Chastillon was born in Châlons-en-Champagne. In the 1580s Chastillon became a part of the military retinue of Henry of Navarre (as Henry IV was known before he became king of France in 1589).Ballon 1991, p. 244. In 1591 Henry made Chastillon the Royal Topographer (Topographe du Roi), a post that at the time was otherwise unknown, and in 1595, a Royal Engineer (Ingénieur du Roi), a post established in the early 16th century which identified a member of a corp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rue De Seine
Rue de Seine is a street in the 6th arrondissement of Paris. Rue de Seine is one of the most sought after streets in Paris due to its history and very close proximity to the Louvre and other famous Parisian landmarks. The rue de Seine and surrounding streets are host to the highest concentration of art galleries and antique dealers in the world. Other nearby famous landmarks include the Café de Flore, Les Deux Magots and the beautiful Jardin du Luxembourg. The neighbourhood of Rue de Seine also includes famous fashion houses, such as Dior, Yves Saint Laurent and Hugo Boss. The Hotel La Louisiane at 60 rue de Seine is famous for having accommodated many notable jazz musicians and writers, including Miles Davis, Chet Baker, John Coltrane, Ernest Hemingway, Jean-Paul Sartre and Simone de Beauvoir. ''Rue de Seine'' is the title of a 2006 album by Martial Solal and Dave Douglas. In the French novel ''La Duchesse de Langeais'' by Honoré de Balzac, the aristocratic character Marqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th Arrondissement Of Paris
The 10th arrondissement of Paris (''Xe arrondissement'') is one of the 20 arrondissements of the capital city of France. In spoken French, this arrondissement is referred to as ''dixième'' ("10th arrondissement of Paris" = "dixième arrondissement de Paris"). The arrondissement, called Entrepôt (warehouse), is situated on the right bank of the River Seine. The arrondissement contains two of Paris's six main railway stations: the Gare du Nord and the Gare de l'Est. Built during the 19th century, these two termini are among the busiest in Europe. The 10th arrondissement also contains a large portion of the Canal Saint-Martin, linking the northeastern parts of Paris with the River Seine. Geography The land area of the arrondissement is 2.892 km2 (1.117 sq. miles, or 715 acres), and it had a 1999 population of 89,695. The 10th arrondissement is often referred to as ''l'Entrepôt''. Like all Parisian arrondissements, it is divided into four quartiers (districts):All demogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16th-century French Architects
The 16th century begins with the Julian year 1501 ( MDI) and ends with either the Julian or the Gregorian year 1600 ( MDC) (depending on the reckoning used; the Gregorian calendar introduced a lapse of 10 days in October 1582). The 16th century is regarded by historians as the century which saw the rise of Western civilization and the Islamic gunpowder empires. The Renaissance in Italy and Europe saw the emergence of important artists, authors and scientists, and led to the foundation of important subjects which include accounting and political science. Copernicus proposed the heliocentric universe, which was met with strong resistance, and Tycho Brahe refuted the theory of celestial spheres through observational measurement of the 1572 appearance of a Milky Way supernova. These events directly challenged the long-held notion of an immutable universe supported by Ptolemy and Aristotle, and led to major revolutions in astronomy and science. Galileo Galilei became a champion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th-century French Architects
The 17th century lasted from January 1, 1601 ( MDCI), to December 31, 1700 ( MDCC). It falls into the early modern period of Europe and in that continent (whose impact on the world was increasing) was characterized by the Baroque cultural movement, the latter part of the Spanish Golden Age, the Dutch Golden Age, the French ''Grand Siècle'' dominated by Louis XIV, the Scientific Revolution, the world's first public company and megacorporation known as the Dutch East India Company, and according to some historians, the General Crisis. From the mid-17th century, European politics were increasingly dominated by the Kingdom of France of Louis XIV, where royal power was solidified domestically in the civil war of the Fronde. The semi-feudal territorial French nobility was weakened and subjugated to the power of an absolute monarchy through the reinvention of the Palace of Versailles from a hunting lodge to a gilded prison, in which a greatly expanded royal court could be more easily k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |