|
Classification Of Indigenous Languages Of The Americas
This is a list of different language classification proposals developed for the indigenous languages of the Americas. The article is divided into North, Central, and South America sections; however, the classifications do not correspond to these divisions. North America ''Glottolog'' 4.1 (2019) ''Glottolog'' 4.1 (2019) recognizes 42 independent families and 31 isolates in North America (73 total). The vast majority are (or were) spoken in the United States, with 26 families and 26 isolates (52 total). ;North American languages families proposed in ''Glottolog'' 4.1 ;Families (42) # Otomanguean (180) #Arawakan (78) #Uto-Aztecan (69) #Algic (46) # Athabaskan-Eyak-Tlingit (45) # Mayan (33) # Chibchan (27) # Salishan (25) # Mixe-Zoque (19) #Siouan (18) # Eskimo–Aleut (12) #Totonacan (12) # Cochimi-Yuman (11) #Iroquoian (11) # Miwok-Costanoan (11) #Kiowa-Tanoan (8) #Muskogean (7) # Pomoan (7) # Chumashan (6) # Wakashan (6) #Caddoan (5) # Misumalpan (5) # Sahaptian (5) # Xincan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Languages Of The Americas
Over a thousand indigenous languages are spoken by the Indigenous peoples of the Americas. These languages cannot all be demonstrated to be related to each other and are classified into a hundred or so language families (including a large number of language isolates), as well as a number of extinct languages that are unclassified because of a lack of data. Many proposals have been made to relate some or all of these languages to each other, with varying degrees of success. The most notorious is Joseph Greenberg's Amerind hypothesis, which however nearly all specialists reject because of severe methodological flaws; spurious data; and a failure to distinguish cognation, contact, and coincidence. Nonetheless, there are indications that some of the recognized families are related to each other, such as widespread similarities in pronouns (e.g., ''n''/''m'' is a common pattern for 'I'/'you' across western North America, and ''ch''/''k''/''t'' for 'I'/'you'/'we' is similarly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
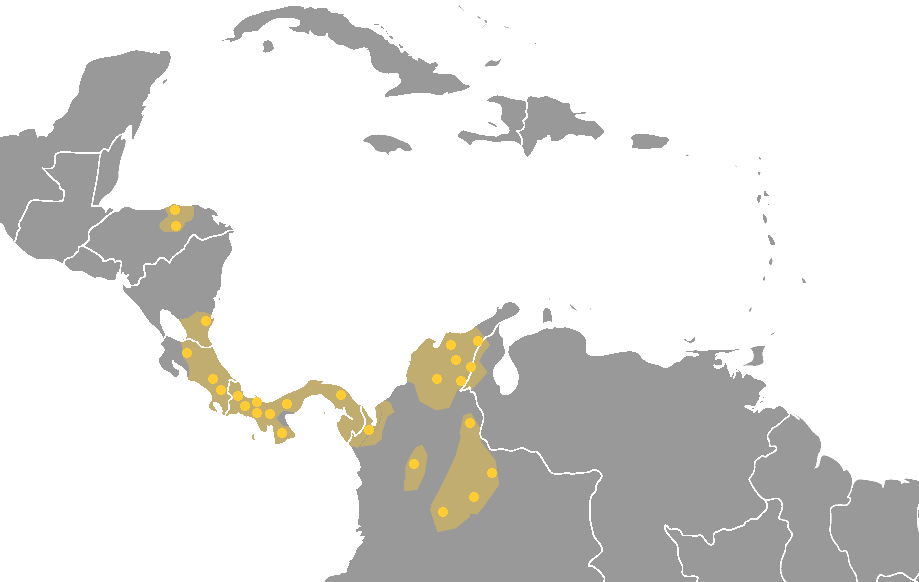
Totonacan Languages
The Totonacan languages (also known as Totonac–Tepehua languages) are a family of closely related languages spoken by approximately 290,000 Totonac (approx. 280,000) and Tepehua (approx. 10,000) people in the states of Veracruz, Puebla, and Hidalgo in Mexico. At the time of the Spanish conquest Totonacan languages were spoken all along the gulf coast of Mexico. During the colonial period, Totonacan languages were occasionally written and at least one grammar was produced. In the 20th century the number of speakers of most varieties have dwindled as indigenous identity increasingly became stigmatized encouraging speakers to adopt Spanish as their main language. The Totonacan languages have only recently been compared to other families on the basis of historical-comparative linguistics, though they share numerous areal features with other languages of the Mesoamerican Linguistic Area, such as the Mayan languages and Nahuatl. Recent work suggests a possible genetic link to the Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinookan Languages
The Chinookan languages were a small family of languages spoken in Oregon and Washington along the Columbia River by Chinook peoples. Although the last known native speaker of any Chinookan language died in 2012, the 2009-2013 American Community Survey found 270 self-identified speakers of Upper Chinook. Family division Chinookan consisted of three languages with multiple varieties. There is some dispute over classification, and there are two ISO 639-3 codes assignedchh(Chinook, Lower Chinook) anwac(Wasco-Wishram, Upper Chinook). For example, Ethnologue 15e classifies Kiksht as Lower Chinook, while others consider it instead Upper Chinookdiscussion, and others a separate language. * Lower Chinook (also known as Chinook-proper or Coastal Chinook) † * Kathlamet (also known as Katlamat, Cathlamet) † * Upper Chinook (also known as Kiksht, Columbia Chinook) † Phonology The vowels in the Chinookan languages are /a i ɛ ə u/. Stress is marked as /á/. Morphology As in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xincan Languages
Xinca (or ''Xinka'', ''Szinca'') is a small extinct family of Mesoamerican languages, formerly regarded as a single language isolate, once spoken by the indigenous Xinca people in southeastern Guatemala, much of El Salvador, and parts of Honduras. Classification The Xincan languages have no demonstrated affiliations with other language families. Lehmann (1920) tried linking Xincan with Lencan, but the proposal was never demonstrated.Lyle Campbell, 1997. ''American Indian Languages: The Historical Linguistics of Native America'' An automated computational analysis ( ASJP 4) by Müller et al. (2013)Müller, André, Viveka Velupillai, Søren Wichmann, Cecil H. Brown, Eric W. Holman, Sebastian Sauppe, Pamela Brown, Harald Hammarström, Oleg Belyaev, Johann-Mattis List, Dik Bakker, Dmitri Egorov, Matthias Urban, Robert Mailhammer, Matthew S. Dryer, Evgenia Korovina, David Beck, Helen Geyer, Pattie Epps, Anthony Grant, and Pilar Valenzuela. 2013. ASJP World Language Trees of Lexical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sahaptian Languages
Sahaptian (also Sahaptianic, Sahaptin, Shahaptian) is a two-language branch of the Plateau Penutian family spoken by Native American peoples in the Columbia Plateau region of Washington, Oregon, and Idaho in the northwestern United States. The terms ''Sahaptian'' (the family) and ''Sahaptin'' (the language) have often been confused and used interchangeably in the literature. Family division Sahaptian includes two languages: :1. Nez Perce (''Niimiipuutímt'') :2. Sahaptin (''Sħáptənəxw'') Nez Perce has two principle dialects, Upper and Lower. Sahaptin has somewhat greater internal diversity, with its main dialects being Umatilla and Yakima Yakima ( or ) is a city in and the county seat of Yakima County, Washington, and the state's 11th-largest city by population. As of the 2020 census, the city had a total population of 96,968 and a metropolitan population of 256,728. The uni .... Nodel Rude's (2012) classification of Sahaptian is as follows. *Proto-Sahaptia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Misumalpan Languages
The Misumalpan languages (also Misumalpa or Misuluan) are a small family of languages spoken by indigenous peoples on the east coast of Nicaragua and nearby areas. The name "Misumalpan" was devised by John Alden Mason and is composed of syllables from the names of the family's three members Miskito, Sumo languages and Matagalpan. It was first recognized by Walter Lehmann in 1920. While all the languages of the Matagalpan branch are now extinct, the Miskito and Sumu languages are alive and well: Miskito has almost 200,000 speakers and serves as a second language for speakers of other indigenous languages in the Mosquito Coast. According to Hale, most speakers of Sumu also speak Miskito. External relations Kaufman (1990) finds a connection with Macro-Chibchan to be "convincing", but Misumalpan specialist Ken Hale considered a possible connection between Chibchan and Misumalpan to be "too distant to establish".Hale & Salamanca 2001, p. 35 Classification * Miskito – nearly 200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caddoan Languages
The Caddoan languages are a family of languages native to the Great Plains spoken by tribal groups of the central United States, from present-day North Dakota south to Oklahoma. All Caddoan languages are critically endangered, as the number of speakers has declined markedly due to colonial legacy, lack of support, and other factors. Family division Five languages belong to the Caddoan language family: Kitsai and Wichita have no speakers left. Kitsai stopped being spoken in the 19th century when its members were absorbed into the Wichita tribe. Wichita stopped being spoken in 2016, when the last native speaker of Wichita, Doris McLemore (who left recordings and language materials), died. All of the remaining Caddoan languages spoken today are severely endangered. As of 2007, Caddo is spoken by only 25 people, Pawnee by 10, and Arikara by 10. Caddo and Pawnee are spoken in Oklahoma by small numbers of tribal elders. Arikara is spoken on the Fort Berthold Reservation in No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wakashan Languages
Wakashan is a family of languages spoken in British Columbia around and on Vancouver Island, and in the northwestern corner of the Olympic Peninsula of Washington state, on the south side of the Strait of Juan de Fuca. As is typical of the Northwest Coast, Wakashan languages have large consonant inventories—the consonants often occurring in complex clusters. Classification Family division The Wakashan language family consists of seven languages: I. Northern Wakashan (Kwakiutlan) languages : 1. Haisla (also known as Xaʼislak'ala, X̌àh̓isl̩ak̓ala or Haisla-Henaksiala, with two dialects, spoken by the Haisla) – about 200 speakers (2005) ::* C̓imo'c̓a/Cʼimaucʼa (Kitimaat/Kitamat) - X̄a'islak̓ala dialect (spoken by the Haisla/x̣àʼisəla) ::* Gitlo'p (Kitlope) - X̄enaksialak̓ala dialect (spoken by the Henaaksiala/X̄enaksiala) : 2. Kwak'wala (also known as Kwakiutl and Lekwala / Liq̓ʷala, with four dialects, spoken by and Kwakwaka'wakw or Northern Kwaki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chumashan Languages
Chumashan was a family of languages that were spoken on the southern California coast by Native American Chumash people, from the Coastal plains and valleys of San Luis Obispo to Malibu, neighboring inland and Transverse Ranges valleys and canyons east to bordering the San Joaquin Valley, to three adjacent Channel Islands: San Miguel, Santa Rosa, and Santa Cruz. The Chumashan languages may be, along with Yukian and perhaps languages of southern Baja such as Waikuri, one of the oldest language families established in California, before the arrival of speakers of Penutian, Uto-Aztecan, and perhaps even Hokan languages. Chumashan, Yukian, and southern Baja languages are spoken in areas with long-established populations of a distinct physical type. The population in the core Chumashan area has been stable for the past 10,000 years. However, the attested range of Chumashan is recent (within a couple thousand years). There is internal evidence that Obispeño replaced a Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomoan Languages
The Pomoan, or Pomo , languages are a small family of seven languages indigenous to northern California spoken by the Pomo people, whose ancestors lived in the valley of the Russian River and the Clear Lake basin. Four languages are extinct, and all surviving languages except Kashaya have fewer than ten speakers. Geographical distribution John Wesley Powell, who was the first to define the extent of the family, noted that its boundaries were the Pacific Ocean to the west, Wintuan territory in the Sacramento Valley to the east, the head of the Russian River to the north, and Bodega Head and present-day Santa Rosa to the south (Powell 1891:87-88). Only Northeastern Pomo was not contiguous with the other Pomoan languages, being separated by an intervening region of Wintuan speakers. Internal relationships of languages Pomoan is a family of seven languages. Their relationship to one another was first formally recognized by John Wesley Powell, who proposed that they be called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muskogean Languages
Muskogean (also Muskhogean, Muskogee) is a Native American language family spoken in different areas of the Southeastern United States. Though the debate concerning their interrelationships is ongoing, the Muskogean languages are generally divided into two branches, Eastern Muskogean and Western Muskogean. Typologically, Muskogean languages are agglutinative. One documented language, Apalachee, is extinct and the remaining languages are critically endangered. Genetic relationships Family division The Muskogean family consists of six languages that are still spoken: Alabama, Chickasaw, Choctaw, Creek-Seminole, Koasati, and Mikasuki, as well as the now-extinct Apalachee, Houma, and Hitchiti (the last is generally considered a dialect of Mikasuki). "Seminole" is listed as one of the Muskogean languages in Hardy's list, but it is generally considered a dialect of Creek rather than a separate language, as she comments. The major subdivisions of the family have long been con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiowa-Tanoan Languages
Tanoan , also Kiowa–Tanoan or Tanoan–Kiowa, is a family of languages spoken by indigenous peoples in present-day New Mexico, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Texas. Most of the languages – Tiwa (Taos, Picuris, Southern Tiwa), Tewa, and Towa – are spoken in the Native American Pueblos of New Mexico (with one outlier in Arizona). These were the first languages collectively given the name of ''Tanoan.'' Kiowa, which is a related language, is now spoken mostly in southwestern Oklahoma. The Kiowa historically inhabited areas of modern-day Texas and Oklahoma. Languages The Tanoan language family has seven languages in four branches: Kiowa–Towa might form an intermediate branch, as might Tiwa–Tewa. Name Tanoan has long been recognized as a major family of Pueblo languages, consisting of Tiwa, Tewa, and Towa. The inclusion of Kiowa into the family was at first controversial given the cultural differences between those groups. The once-nomadic Kiowa people of the Plains are c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |