|
Clarinbridge
Clarinbridge () is a village in south County Galway, Ireland. It is on the mouth of the Clarin River at the end of Dunbulcaun Bay, which is the easternmost part of Galway Bay. The placename is also spelled Clarenbridge. Notable people *Alexander Young, recipient of the Victoria Cross See also *Galway International Oyster Festival The Galway International Oyster Festival is a food festival held annually in Galway on the west coast of Ireland on the last weekend of September, the first month of the oyster season. Inaugurated in 1954, it was the brainchild of the Great Sout ... References External linksClarenbridge Oyster Festival Towns and villages in County Galway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clarin River
{{ireland-river-stub ...
The River Clarin ( ga, Abhainn an Chláirín) is a fast-flowing river in Ireland, flowing through southern County Galway. Course The River Clarin rises in the townland of Gortnalone, north of Attymon and snakes westwards, turning southwards through Athenry. Athenry Castle was built at a fording point on the river. It flows southwestwards and passes under the N18 at Clarinbridge and enters Dunbulcaun Bay. Wildlife Fish species include Crayfish, trout, salmon, lamprey and eel. See also *Rivers of Ireland References Clarin Clarin or Clarín may refer to: Geography *Clarin, Bohol, a municipality in the province of Bohol, Philippines *Clarin, Misamis Occidental, a municipality in the province of Misamis Occidental, Philippines * River Clarin, a river in Ireland Media ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galway International Oyster Festival
The Galway International Oyster Festival is a food festival held annually in Galway on the west coast of Ireland on the last weekend of September, the first month of the oyster season. Inaugurated in 1954, it was the brainchild of the Great Southern Hotel (now Hotel Meyrick) manager, Brian Collins. In 2000 was described by the Sunday Times ''The Sunday Times'' is a British newspaper whose circulation makes it the largest in Britain's quality press market category. It was founded in 1821 as ''The New Observer''. It is published by Times Newspapers Ltd, a subsidiary of News UK, whi ... as "one of the 12 greatest shows on earth" and was listed in the 1987 AA Travel Guide as one of Europe's Seven Best Festivals. The Galway International Oyster Festival was created to celebrate the Galway Native Oyster as a "unique feature" of Galway city and county. Hotel manager Brian Collins had been searching for something to attract more visitors to Galway, in what was then a quieter month of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Galway
"Righteousness and Justice" , anthem = () , image_map = Island of Ireland location map Galway.svg , map_caption = Location in Ireland , area_footnotes = , area_total_km2 = 6151 , area_rank = 2nd , seat_type = County town , seat = Galway , population_total = 276451 , population_density_km2 = auto , population_rank = 5th , population_as_of = 2022 , population_footnotes = , leader_title = Local authorities , leader_name = County Council and City Council , leader_title2 = Dáil constituency , leader_name2 = , leader_title3 = EP constituency , leader_name3 = Midlands–North-West , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Ireland , subdivision_type1 = Province , subdivision_name1 = Connacht , subdivision ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Young (VC)
Alexander Young, VC (27 January 1873 – 19 October 1916) was an Irish-born South African soldier and a recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and Commonwealth forces. A native of Oranmore, County Galway, Young joined the Queen's Bays on 22 May 1890 at Renmore. He served for a time in India, and became a riding instructor. He first saw active service in the Mahdist War, Second Boer War, and First World War. VC details Young was 28 years old and a sergeant-major in the Cape Police, South African Forces during the Second Boer War when the following deed took place for which he was awarded the VC. First World War Young served with the South African Scottish Regiment with the rank of lieutenant in the First World War. He was killed in action during the Battle of the Somme The Battle of the Somme ( French: Bataille de la Somme), also known as the Somme offensive, was a battle of the First W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
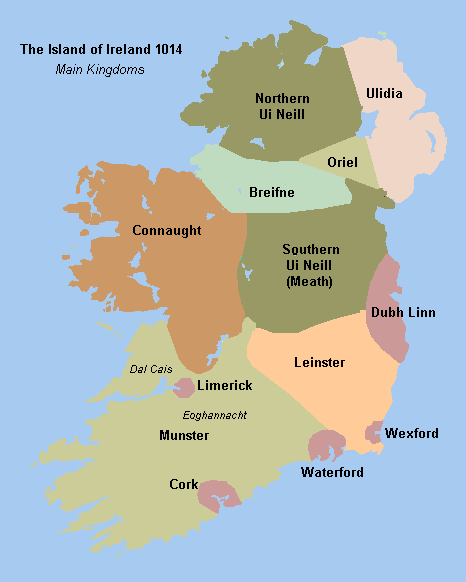
Provinces Of Ireland
There have been four Provinces of Ireland: Connacht (Connaught), Leinster, Munster, and Ulster. The Irish language, Irish word for this territorial division, , meaning "fifth part", suggests that there were once five, and at times Kingdom_of_Meath, Meath has been considered to be the fifth province; in the medieval period, however, there were often more than five. The number of provinces and their delimitation fluctuated until 1610, when they were permanently set by the English administration of James VI and I, James I. The provinces of Ireland no longer serve administrative or political purposes but function as historical and cultural entities. Etymology In modern Irish language, Irish the word for province is (pl. ). The modern Irish term derives from the Old Irish (pl. ) which literally meant "a fifth". This term appears in 8th-century law texts such as and in the legendary tales of the Ulster Cycle where it refers to the five kingdoms of the "Pentarchy". MacNeill enumer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connacht
Connacht ( ; ga, Connachta or ), is one of the provinces of Ireland, in the west of Ireland. Until the ninth century it consisted of several independent major Gaelic kingdoms (Uí Fiachrach, Uí Briúin, Uí Maine, Conmhaícne, and Delbhna). Between the reigns of Conchobar mac Taidg Mór (died 882) and his descendant, Aedh mac Ruaidri Ó Conchobair (reigned 1228–33), it became a kingdom under the rule of the Uí Briúin Aí dynasty, whose ruling sept adopted the surname Ua Conchobair. At its greatest extent, it incorporated the often independent Kingdom of Breifne, as well as vassalage from the lordships of western Mide and west Leinster. Two of its greatest kings, Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair (1088–1156) and his son Ruaidri Ua Conchobair (c. 1115–1198) greatly expanded the kingdom's dominance, so much so that both became High King of Ireland. The Kingdom of Connacht collapsed in the 1230s because of civil war within the royal dynasty, which enabled widespread Hiber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
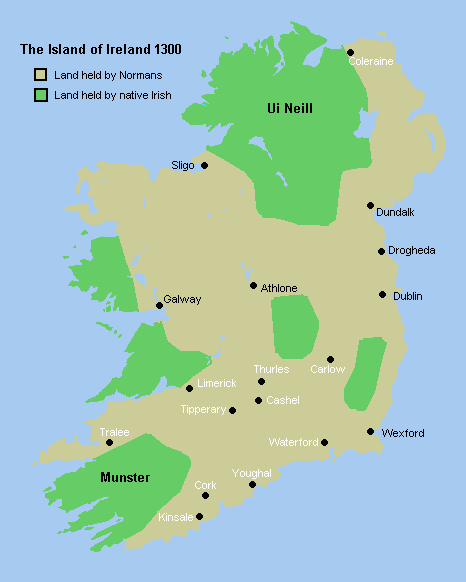
Counties Of Ireland
The counties of Ireland (Irish language, Irish: ) are historic administrative divisions of the island into thirty-two units. They began as Norman structures, and as the powers exercised by the Cambro-Norman barons and the Old English (Ireland), Old English nobility waned over time, new offices of political control came to be established at a county level. Upon the partition of Ireland in 1921, six of the traditional counties became part of Northern Ireland. In Northern Ireland, Counties of Northern Ireland, counties ceased to be longer used for local government in 1973; Local government in Northern Ireland, districts are instead used. In the Republic of Ireland, some counties have been split resulting in the creation of new counties: there are currently 26 counties, 3 cities and 2 cities and counties that demarcate areas of local government in the Republic of Ireland, local government in the Republic. Terminology The word "county" has come to be used in different senses for di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West European Time
Western European Time (WET, UTC±00:00) is a time zone covering parts of western Europe and consists of countries using UTC±00:00 (also known as Greenwich Mean Time, shortly called GMT). It is one of the three standard time zones in the European Union along with Central European Time and Eastern European Time. The following Western European countries and regions use UTC±00:00 in winter months: *Portugal, since 1912 with pauses (except Azores, UTC−01:00) *United Kingdom and Crown Dependencies, since 1847 in England, Scotland, Wales, the Channel Islands, and the Isle of Man, and since 1916 in Northern Ireland, with pauses *Ireland, since 1916, except between 1968 and 1971 *Canary Islands, since 1946 (rest of Spain is CET, UTC+01:00) *Faroe Islands, since 1908 *Madeira islands, since 1912 with pauses * North Eastern Greenland ( Danmarkshavn and surrounding area) *Iceland, since 1968, without summer time changes All the above countries except Iceland implement daylight savin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Standard Time
Republic of Ireland, Ireland uses Irish Standard Time (IST, UTC+01:00; ga, Am Caighdeánach Éireannach) in the summer months and Greenwich Mean Time (UTC+00:00; ''Meán-Am Greenwich'') in the winter period. (Roughly half of the state is in the 7.5°W to 22.5°W sector, half is in the same sector as Greenwich: 7.5°E to 7.5°W). In Ireland, the Standard Time Act 1968 legally established that ''the time for general purposes in the State (to be known as standard time) shall be one hour in advance of Greenwich mean time throughout the year''. This act was amended by the Standard Time (Amendment) Act 1971, which legally established Greenwich Mean Time as a winter time period. Ireland therefore operates one hour behind standard time during the winter period, and reverts to standard time in the summer months. This is defined in contrast to the other states in the European Union, which operate one hour ahead of standard time during the summer period, but produces the same end result. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western European Summer Time
Western European Summer Time (WEST, UTC+01:00) is a summer daylight saving time scheme, 1 hour ahead of Greenwich Mean Time and Coordinated Universal Time. It is used in: * the Canary Islands * Portugal (including Madeira but not the Azores) * the Faroe Islands The following countries also use the same time zone for their daylight saving time but use a different title: *United Kingdom, which uses British Summer Time (BST) *Ireland, which uses Irish Standard Time (IST) ( (ACÉ)). Also sometimes erroneously referred to as "Irish Summer Time" (). The scheme runs from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October each year. At both the start and end of the schemes, clock changes take place at 01:00 UTC+00:00. During the winter, Western European Time (WET, GMT+0 or UTC±00:00) is used. The start and end dates of the scheme are asymmetrical in terms of daylight hours: the vernal time of year with a similar amount of daylight to late October is mid-February, well before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Grid Reference System
The Irish grid reference system is a system of geographic grid references used for paper mapping in Ireland (both Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland). The Irish grid partially overlaps the British grid, and uses a similar co-ordinate system but with a meridian more suited to its westerly location. Usage In general, neither Ireland nor Great Britain uses latitude or longitude in describing internal geographic locations. Instead grid reference systems are used for mapping. The national grid referencing system was devised by the Ordnance Survey, and is heavily used in their survey data, and in maps (whether published by the Ordnance Survey of Ireland, the Ordnance Survey of Northern Ireland or commercial map producers) based on those surveys. Additionally grid references are commonly quoted in other publications and data sources, such as guide books or government planning documents. 2001 recasting: the ITM grid In 2001, the Ordnance Survey of Ireland and the Ordnance Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
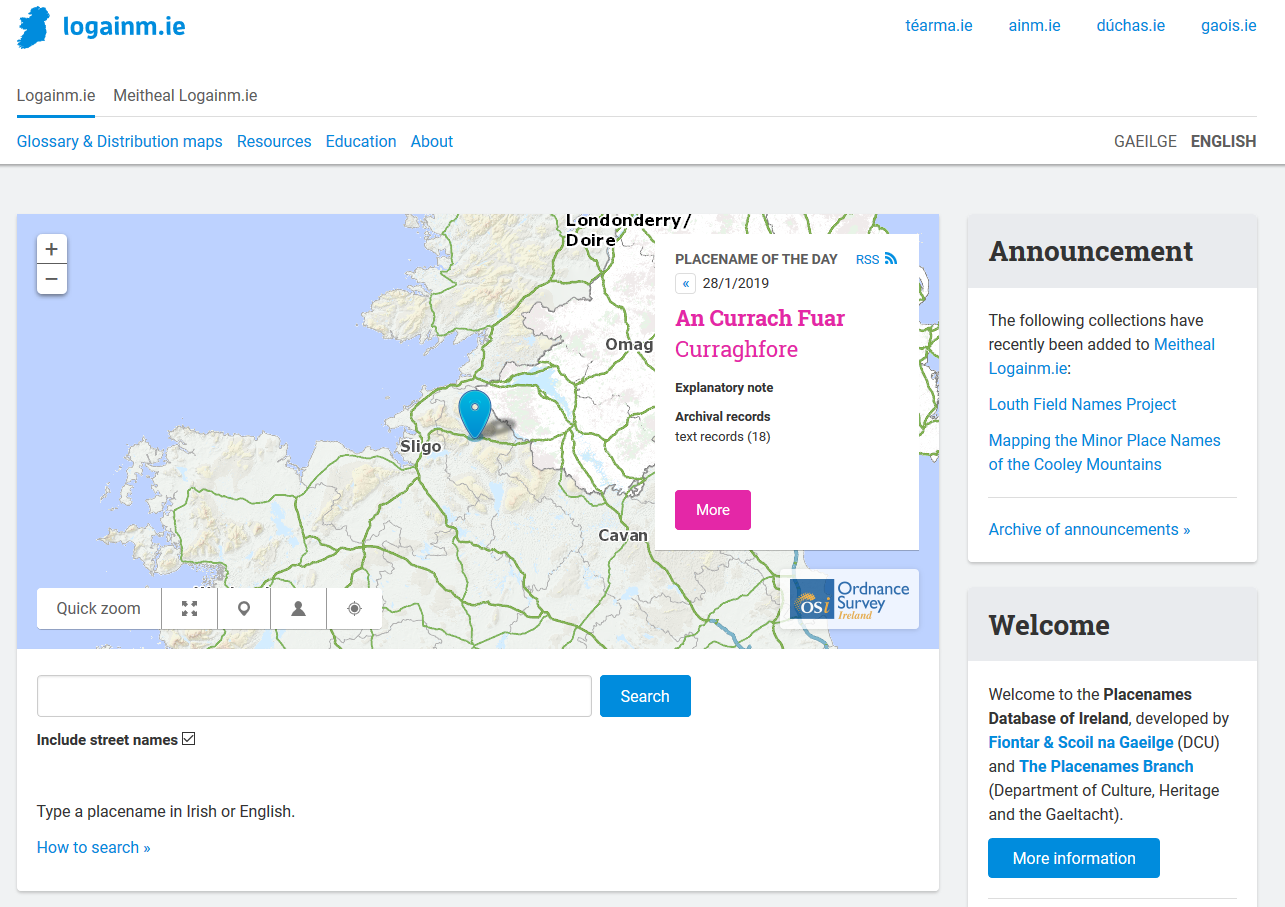
Placenames Database Of Ireland
The Placenames Database of Ireland ( ga, Bunachar Logainmneacha na hÉireann), also known as , is a database and archive of place names in Ireland. It was created by Fiontar, Dublin City University in collaboration with the Placenames Branch of the Department of Tourism, Culture, Arts, Gaeltacht, Sport and Media. The website is a public resource primarily aimed at journalists and translators, students and teachers, historians and researchers in genealogy. Placenames Commission and Placenames Branch The Placenames Commission ( ga, an Coimisiún Logainmneacha) was established by the Department of Finance (Ireland), Department of Finance in 1946 to advise Ordnance Survey Ireland and the government of what the Irish name of places should be. Although both the 1922 Constitution of the Irish Free State and the Constitution of Ireland, current constitution adopted in 1937 recognised Irish as the national language, the law in regard to placenames was carried over from the 19th-century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_Act_1916.jpg)