|
Citizens For A Canadian Republic
Citizens for a Canadian Republic (French language, French: ''Citoyens pour une République Canadienne'') (CCR) is a Canadian advocacy group founded in 2002 that advocates for the replacement of the Monarchy of Canada, Canadian monarchy with a head of state who could either be chosen directly through a general election, indirectly by the Parliament of Canada, the Legislative assemblies of Canadian provinces and territories, or some other electoral body. CCR favours the retention of the Westminster system, Westminster-style parliament, with the prime minister as head of government, in a parliamentary republic similar to Republic of Ireland, Ireland or India. It does not endorse any particular selection process, other than it should be democratic. The organization's general objective is "to promote replacing the British monarch as our head of state with a resident, democratically-selected Canadian. " History Founding Citizens for a Canadian Republic was formed in 2002 "in an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anchor of the Golden Horseshoe, an urban agglomeration of 9,765,188 people (as of 2021) surrounding the western end of Lake Ontario, while the Greater Toronto Area proper had a 2021 population of 6,712,341. Toronto is an international centre of business, finance, arts, sports and culture, and is recognized as one of the most multicultural and cosmopolitan cities in the world. Indigenous peoples have travelled through and inhabited the Toronto area, located on a broad sloping plateau interspersed with rivers, deep ravines, and urban forest, for more than 10,000 years. After the broadly disputed Toronto Purchase, when the Mississauga surrendered the area to the British Crown, the British established the town of York in 1793 and later designat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O'Donohue V
O'Donohue is a surname, and may refer to: *Becky O'Donohue (born 1980), reality television participant *Daniel Anthony O'Donohue (20th century), United States Ambassador to Burma *Edward O'Donohue (born 1974), Australian politician *Jessie O'Donohue (born 1980), reality television participant *John O'Donohue (1956–2008), poet and philosopher *John F. O'Donohue (21st century), American actor *Michael O'Donohue (1835–1912), Irish-American builder and architect *Peter O'Donohue (born 1923), former Australian rules footballer *Ryan O'Donohue (born 1984), American voice actor *Tony O'Donohue (born 1933), Canadian politician *William O'Donohue (born 1957), American psychologist See also *O'Donoghue *Donohue Donohue is a surname of Irish origin abbreviated from O'Donohue (). Notable people with the surname include: * Adam Donohue (born 1990), Australian rules footballer * Charles D. Donohue (1880–1928), New York politician and judge * David Donohue ... {{surname Anglicised Iri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
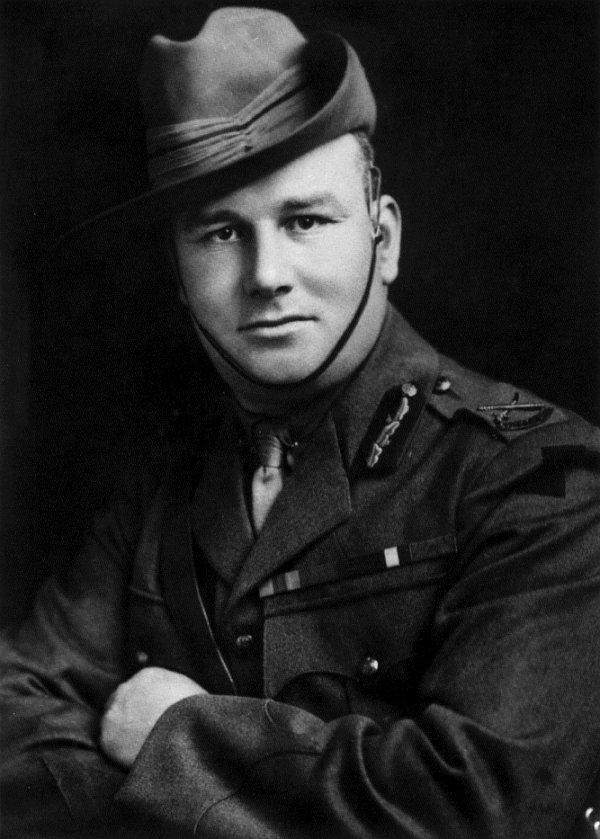
Brigadier-General
Brigadier general or Brigade general is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries. The rank is usually above a colonel, and below a major general or divisional general. When appointed to a field command, a brigadier general is typically in command of a brigade consisting of around 4,000 troops (four battalions). Variants Brigadier general Brigadier general (Brig. Gen.) is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries, usually sitting between the ranks of colonel and major general. When appointed to a field command, a brigadier general is typically in command of a brigade consisting of around 4,000 troops (four battalions). In some countries, this rank is given the name of ''brigadier'', which is usually equivalent to ''brigadier general'' in the armies of nations that use the rank. The rank can be traced back to the militaries of Europe where a "brigadier general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Moore (Canadian Historian)
Christopher Hugh Moore (born June 9, 1950) is a Canadian author, journalist, and blogger about Canadian history. A freelance writer since 1978, Moore is unusual among professionally trained Canadian historians in that he supports himself by writing for general audiences. He is a longtime columnist for ''Canada's History'' magazine (formerly ''The Beaver'') and the author of many books. He has twice won the Governor General's Literary Awards. Early life and education Christopher Hugh Moore was born in Stoke-on-Trent, England, on June 9, 1950. He immigrated to Canada with his family in 1954, was raised in Nelson and Vancouver, British Columbia, and did undergraduate studies at the University of British Columbia. He began his historical career as a researcher with the historic sites service of Parks Canada at Canada's largest historic site reconstruction, the eighteenth-century Fortress of Louisbourg on Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia.Canadian Who's Who, article "Christopher Hugh Moo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
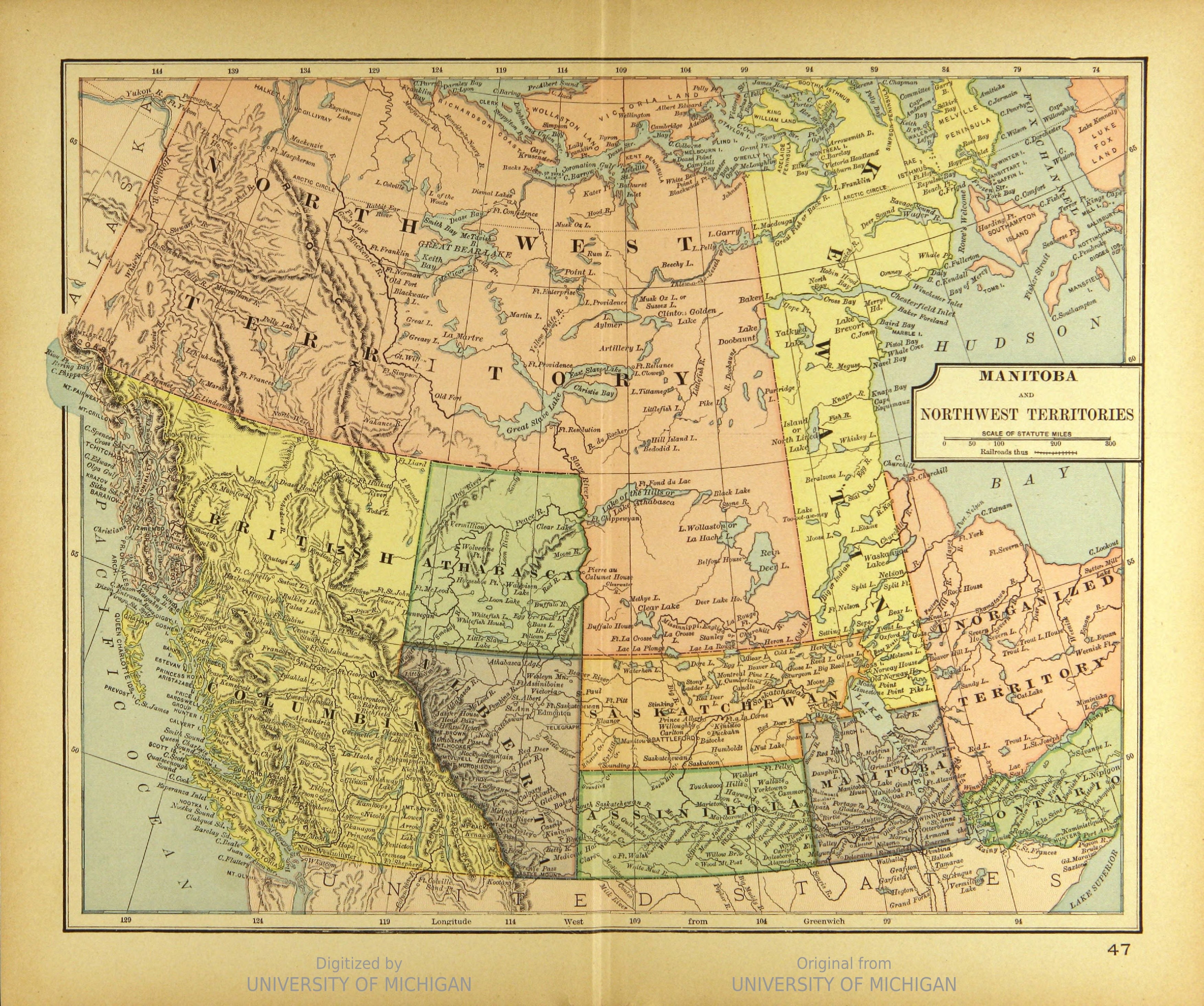
Western Canada
Western Canada, also referred to as the Western provinces, Canadian West or the Western provinces of Canada, and commonly known within Canada as the West, is a Canadian region that includes the four western provinces just north of the Canada–United States border namely (from west to east) British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba. The people of the region are often referred to as "Western Canadians" or "Westerners", and though diverse from province to province are largely seen as being collectively distinct from other Canadians along cultural, linguistic, socioeconomic, geographic, and political lines. They account for approximately 32% of Canada's total population. The region is further subdivided geographically and culturally between British Columbia, which is mostly on the western side of the Canadian Rockies and often referred to as the " west coast", and the "Prairie Provinces" (commonly known as "the Prairies"), which include those provinces on the easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francophone
French became an international language in the Middle Ages, when the power of the Kingdom of France made it the second international language, alongside Latin. This status continued to grow into the 18th century, by which time French was the language of European diplomacy and international relations. According to the 2022 report of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie (OIF), 409 million people speak French. The OIF states that despite a decline in the number of learners of French in Europe, the overall number of speakers is rising, largely because of its presence in African countries: of the 212 million who use French daily, 54.7% are living in Africa. The OIF figures have been contested as being inflated due to the methodology used and its overly broad definition of the word francophone. According to the authors of a 2017 book on the world distribution of the French language, a credible estimate of the number of "francophones réels" (real francophones), that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Canadian
English Canadians (french: Canadiens anglais or ), or Anglo-Canadians (french: Anglo-Canadiens), refers to either Canadians of English ethnic origin and heritage or to English-speaking or Anglophone Canadians of any ethnic origin; it is used primarily in contrast with French Canadians. Canada is an officially bilingual country, with English and French official language communities. Immigrant cultural groups ostensibly integrate into one or both of these communities, but often retain elements of their original cultures. The term English-speaking Canadian is sometimes used interchangeably with English Canadian. Although many English-speaking Canadians have strong historical roots traceable to England or other parts of the British Isles, English-speaking Canadians have a variety of ethnic backgrounds. They or their ancestors came from various Celtic, European, Asian, Caribbean, African, Latin American, and Pacific Island cultures, as well as French Canada and North American Ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontario Superior Court Of Justice
The Superior Court of Justice (French: ''Cour supérieure de justice'') is a superior court in Ontario. The Court sits in 52 locations across the province, including 17 Family Court locations, and consists of over 300 federally appointed judges. In 1999, the Superior Court of Justice was renamed from the Ontario Court (General Division). The Superior Court is one of two divisions of the Court of Ontario. The other division is the lower court, the Ontario Court of Justice. The Superior Court has three specialized branches: Divisional Court, Small Claims Court, and Family Court. The Superior Court has inherent jurisdiction over civil, criminal, and family law matters at common law. Although the Court has inherent jurisdiction, the authority of the Court has been entrenched in the Canadian Constitution. * Frank Marrocco (2005 to 2020; Associate Chief Justice 2013 to 2020) See also * Courts of Ontario References External linksSuperior Court of Justice [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oath Of Citizenship (Canada)
The Oath of Citizenship, or Citizenship Oath (in french: serment de citoyenneté), is a statement recited and signed by those who apply to become citizens of Canada. Administered at a ceremony presided over by a designated official, the oath is a promise or declaration of fealty to the Canadian monarch and a promise to abide by Canada's laws and uphold the duties of a Canadian citizen; upon signing the oath, citizenship is granted to the applicant. The vow's roots lie in the oath of allegiance taken in the United Kingdom, the modern form of which was implemented in 1689 by King William II and III and Queen Mary II and was inherited by and used in Canada prior to 1947. With the enactment of the Citizenship Act that year, the Canadian Oath of Citizenship was established. Proposals for modification of the oath have surfaced from time to time, including removing references to the sovereign, adding loyalty to societal principles, and/or adding specific mention to Canada. However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Roach
Charles Conliff Mende Roach (September 18, 1933 – October 2, 2012) was a Canadian civil rights lawyer and an activist in the Black community in Toronto. Early life Born in Belmont, Trinidad and Tobago, the son of a trade union organizer, Roach arrived in Canada in 1955 as an aspiring priest to study at the University of Saskatchewan. Roach was politicized by the civil rights movement, stating: "after the '50s, I started being more political... This was the spirit of the times. I'm really from the civil-rights era." He then studied law at the University of Toronto and was called to the bar in 1963. Activism and law Roach worked as a staff lawyer for the city of Toronto in the 1960s, while also participating and organizing marches and demonstrations for equal rights. He opened his own law practice in 1968, eventually becoming the firm of Roach and Schwartz Associates. Among his clients were Black Panthers attempting to seek refuge in Canada from prosecution in the United S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
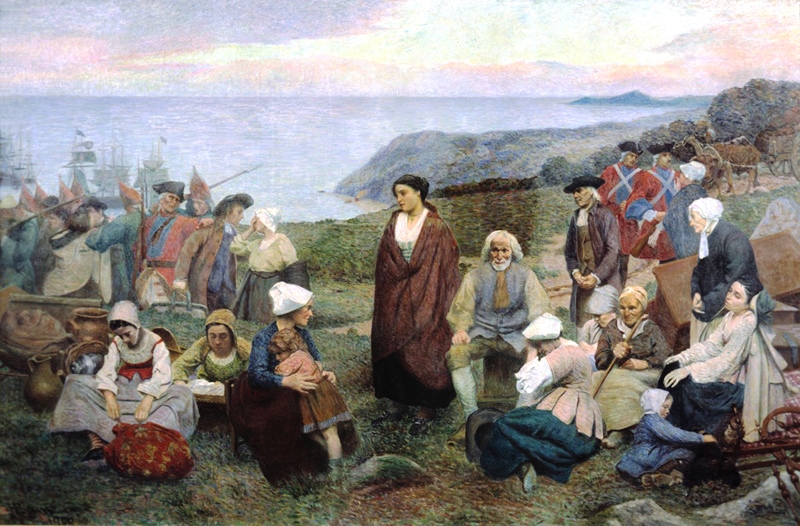
Acadian
The Acadians (french: Acadiens , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Most Acadians live in the region of Acadia, as it is the region where the descendants of a few Acadians who escaped the Expulsion of the Acadians (aka The Great Upheaval / ''Le Grand Dérangement'') re-settled. Most Acadians in Canada continue to live in majority French-speaking communities, notably those in New Brunswick where Acadians and Francophones are granted autonomy in areas such as education and health. Acadia was one of the 5 regions of New France. Acadia was located in what is now Eastern Canada's Maritime provinces, as well as parts of Quebec and present-day Maine to the Kennebec River. It was ethnically, geographically and administratively different from the other French colonies and the French colony of Canada (modern-day Quebec). As a result, the Acadians developed a distinct history and culture. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oath Of Allegiance (Canada)
The Canadian Oath of Allegiance is a promise or declaration of fealty to the Canadian monarch, as personification of the Canadian state, taken, along with other specific oaths of office, by new occupants of various federal and provincial government offices, members of federal, provincial, and municipal police forces, members of the Canadian Armed Forces, and, in some provinces, all lawyers upon admission to the bar. The Oath of Allegiance also makes up the first portion of the Oath of Citizenship, the taking of which is a requirement of obtaining Canadian nationality. The vow's roots lie in the oath taken in the United Kingdom, the modern form of which was implemented in 1689 by King William II and III and Queen Mary II and was used in Canada prior to Confederation. The Canadian oath was established at that time in the British North America Act, 1867 (now Constitution Act, 1867), meaning that alteration or elimination of the oath for parliamentarians requires a constitutional am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |