|
Cis-acting Replication Element
''Cis-acting replication elements'' bring together the 5′ and 3′ ends during replication of positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses (for example Picornavirus, Flavivirus, coronavirus, togaviruses, Hepatitis C virus) and double-stranded RNA viruses (for example rotavirus and reovirus). See also *Cis-regulatory element *List of cis-regulatory RNA elements *Enterovirus cis-acting replication element and Enterovirus 5′ cloverleaf cis-acting replication element *Cardiovirus cis-acting replication element (CRE) *Coronavirus SL-III cis-acting replication element (CRE) *Rotavirus cis-acting replication element *Hepatitis C virus cis-acting replication element *Flavivirus 3′ UTR cis-acting replication element (CRE) *Potato virus X cis-acting regulatory element *Human rhinovirus internal cis-acting regulatory element (CRE) Human rhinovirus internal cis-acting regulatory element (CRE) is a CRE from the human rhinoviruses. The CRE is located within the genome segment encoding the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cis-regulatory Element
''Cis''-regulatory elements (CREs) or ''Cis''-regulatory modules (CRMs) are regions of non-coding DNA which regulate the transcription of neighboring genes. CREs are vital components of genetic regulatory networks, which in turn control morphogenesis, the development of anatomy, and other aspects of embryonic development, studied in evolutionary developmental biology. CREs are found in the vicinity of the genes that they regulate. CREs typically regulate gene transcription by binding to transcription factors. A single transcription factor may bind to many CREs, and hence control the expression of many genes ( pleiotropy). The Latin prefix ''cis'' means "on this side", i.e. on the same molecule of DNA as the gene(s) to be transcribed. CRMs are stretches of DNA, usually 100–1000 DNA base pairs in length, where a number of transcription factors can bind and regulate expression of nearby genes and regulate their transcription rates. They are labeled as ''cis'' because they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cis-regulatory RNA Elements
This is a list of ''cis''-regulatory RNAs. These are RNA motifs which regulate nucleic acid regions on the same molecule, as opposed to ''trans''-acting motifs which regulate a distal molecule. Some of these RNAs are broadly distributed while others are single RNA families. {{horizontal ToC, nonum=yes # * 23S methyl RNA motif * 6C RNA A * Actino-pnp RNA motif * AdoCbl riboswitch *Alfalfa mosaic virus coat protein binding (CPB) RNA *Alfalfa mosaic virus RNA 1 5′ UTR stem-loop *Alpha operon ribosome binding site * Antizyme RNA frameshifting stimulation element * APC internal ribosome entry site (IRES) * Aphthovirus internal ribosome entry site (IRES) * Apolipoprotein B (apoB) 5′ UTR cis-regulatory element * AtoC RNA motif * ATPC RNA motif *AU-rich element B * Bag-1 internal ribosome entry site (IRES) * Bamboo mosaic potexvirus (BaMV) cis-regulatory element * Bamboo mosaic virus satellite RNA cis-regulatory element * Bovine leukaemia virus RNA packaging signal C * Citrus tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterovirus Cis-acting Replication Element
Enterovirus cis-acting replication element is a small RNA hairpin in the coding region of protein 2C as the site in PV1(M) RNA that is used as the primary template for the ''in vitro'' uridylylation. The first step in the replication of the plus-stranded poliovirus RNA is the synthesis of a complementary minus strand. This process is initiated by the covalent attachment of uridine monophosphate (UMP) to the terminal protein VPg VPg (viral protein genome-linked) is a protein that is covalently attached to the 5′ end of positive strand viral RNA and acts as a primer during RNA synthesis in a variety of virus families including Picornaviridae, Potyviridae and Caliciviri ..., yielding VPgpU and VPgpUpU. See also * Enteroviral 3′ UTR element * Enterovirus 5′ cloverleaf cis-acting replication element References External links * Cis-regulatory RNA elements Enteroviruses {{molecular-cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterovirus 5′ Cloverleaf Cis-acting Replication Element
The Enterovirus 5′ cloverleaf cis-acting replication element is an RNA element found in the 5′ UTR of Enterovirus genomes. The element has a cloverleaf like secondary structure and is known to be a multifunctional cis-acting replication element (CRE), required for the initiation of negative strand RNA synthesis. See also * Enteroviral 3′ UTR element *Enterovirus cis-acting replication element Enterovirus cis-acting replication element is a small RNA hairpin in the coding region of protein 2C as the site in PV1(M) RNA that is used as the primary template for the ''in vitro'' uridylylation. The first step in the replication of the plus ... References External links * Cis-regulatory RNA elements Enteroviruses {{molecular-cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiovirus Cis-acting Replication Element (CRE)
This family represents a Cardiovirus cis-acting replication element (CRE) which is located within the region encoding the capsid protein VP2 and is required for viral replication Viral replication is the formation of biological viruses during the infection process in the target host cells. Viruses must first get into the cell before viral replication can occur. Through the generation of abundant copies of its genome an .... See also * Citrus tristeza virus replication signal * Rubella virus 3' cis-acting element References External links * Cis-regulatory RNA elements Cardioviruses {{molecular-cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronavirus SL-III Cis-acting Replication Element (CRE)
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the common cold (which is also caused by other viruses, predominantly rhinoviruses), while more lethal varieties can cause SARS, MERS and COVID-19, which is causing the ongoing pandemic. In cows and pigs they cause diarrhea, while in mice they cause hepatitis and encephalomyelitis. Coronaviruses constitute the subfamily ''Orthocoronavirinae'', in the family ''Coronaviridae'', order '' Nidovirales'' and realm '' Riboviria''. They are enveloped viruses with a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome and a nucleocapsid of helical symmetry. The genome size of coronaviruses ranges from approximately 26 to 32 kilobases, one of the largest among RNA viruses. They have characteristic club-shaped spikes that project from their surface, which in el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotavirus Cis-acting Replication Element
This family represents a rotavirus cis-acting replication element (CRE) found at the 3'-end of rotavirus mRNAs. The family is thought to promote the synthesis of minus strand RNA to form viral dsRNA Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra .... References External links * Cis-regulatory RNA elements {{molecular-cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis C Virus Cis-acting Replication Element
The Hepatitis C virus (HCV) cis-acting replication element (CRE) is an RNA element which is found in the coding region of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase NS5B. Mutations in this family have been found to cause a blockage in RNA replication RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) or RNA replicase is an enzyme that catalyzes the replication of RNA from an RNA template. Specifically, it catalyzes synthesis of the RNA strand complementary to a given RNA template. This is in contrast to ... and it is thought that both the primary sequence and the structure of this element are crucial for HCV RNA replication. See also * Hepatitis C alternative reading frame stem-loop * Hepatitis C virus 3'X element * Hepatitis C virus stem-loop VII * Hepatitis C stem-loop IV * Hepatitis C References External links * Cis-regulatory RNA elements Hepatitis C virus {{molecular-cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
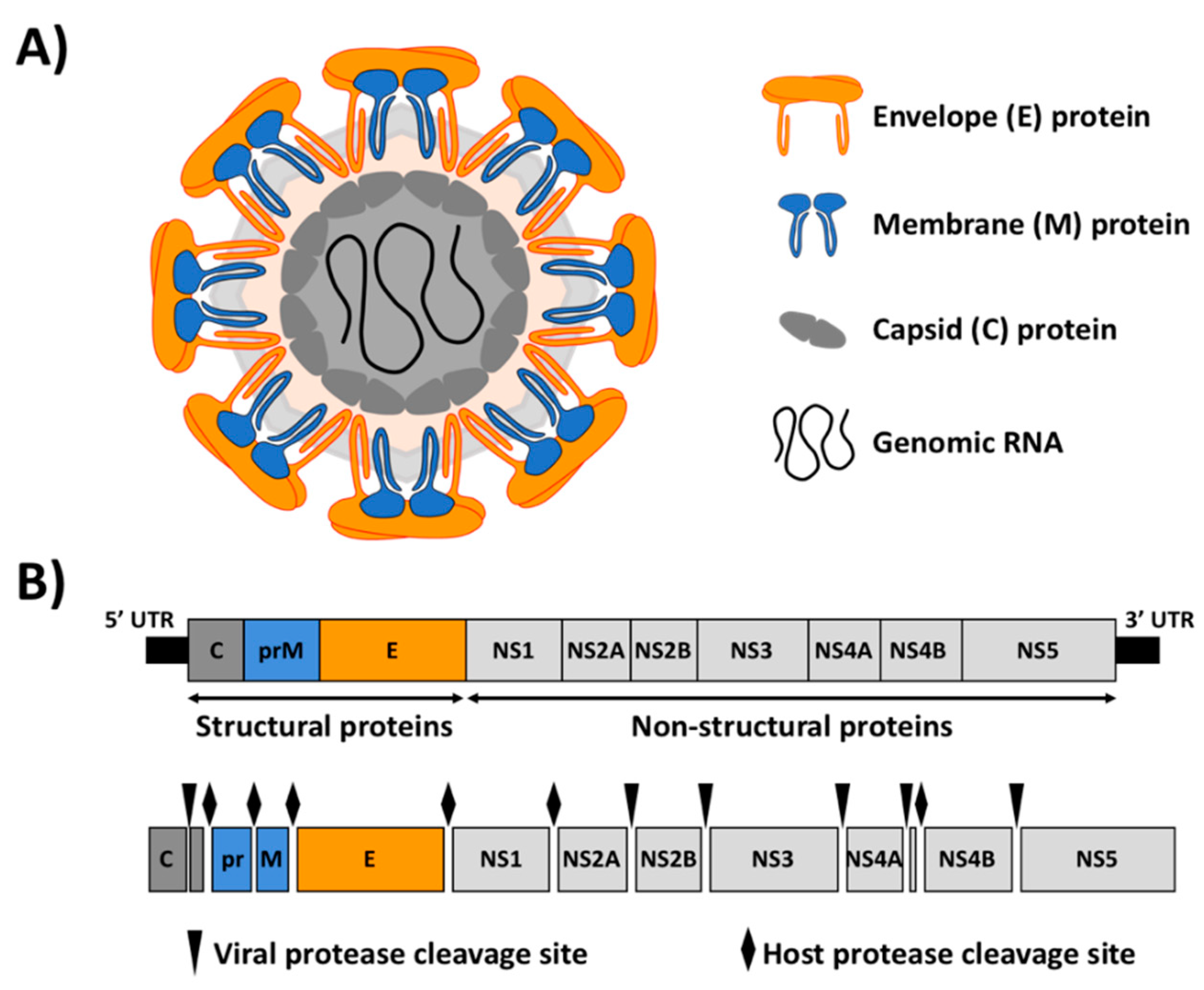
Flavivirus 3′ UTR Cis-acting Replication Element (CRE)
''Flavivirus'' is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family ''Flaviviridae''. The genus includes the West Nile virus, dengue virus, tick-borne encephalitis virus, yellow fever virus, Zika virus and several other viruses which may cause encephalitis, as well as insect-specific flaviviruses (ISFs) such as cell fusing agent virus (CFAV), Palm Creek virus (PCV), and Parramatta River virus (PaRV). While dual-host flaviviruses can infect vertebrates as well as arthropods, insect-specific flaviviruses are restricted to their competent arthropods. The means by which flaviviruses establish persistent infection in their competent vectors and cause disease in humans depends upon several virus-host interactions, including the intricate interplay between flavivirus-encoded immune antagonists and the host antiviral innate immune effector molecules. Flaviviruses are named for the yellow fever virus; the word ''flavus'' means 'yellow' in Latin, and yellow fever in turn is named from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potato Virus X Cis-acting Regulatory Element
The Potato virus X cis-acting regulatory element is a cis-acting regulatory element found in the 3' UTR of the Potato virus X genome In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding g .... This element has been found to be required for minus strand RNA accumulation and is essential for efficient viral replication. See also * Poxvirus AX element late mRNA ''cis''-regulatory element References External links * Cis-regulatory RNA elements {{molecular-cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Rhinovirus Internal Cis-acting Regulatory Element (CRE)
Human rhinovirus internal cis-acting regulatory element (CRE) is a CRE from the human rhinoviruses. The CRE is located within the genome segment encoding the capsid A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or ma ... proteins so is found in a protein coding region. The element is essential for efficient viral replication and it has been suggested that the CRE is required for initiation of minus-strand RNA synthesis. See also * Human parechovirus 1 (HPeV1) cis regulatory element (CRE) * Rotavirus cis-acting replication element (CRE) References External links * Cis-regulatory RNA elements Enteroviruses {{molecular-cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |