|
Cirrus SR22T
The Cirrus SR22 is a single-engine four- or five-seat composite material, composite aircraft built from 2001 by Cirrus Aircraft of Duluth, Minnesota. It is a development of the Cirrus SR20, with a larger wing, higher fuel capacity, and a more powerful, 310-horsepower (231 kW) engine. The SR22 series has been the world's best-selling general aviation (GA) airplane every year since 2003. With 6,149 units delivered from 2001–19, and in combination with the SR20, a total of 7,645, it is the List of most-produced aircraft, most-produced GA aircraft of the 21st century, and is the single most-produced GA aircraft made from composite material, accounting for over 30% of the entire piston engine, piston aircraft market. The Cirrus SR22 is equipped with a whole-plane emergency recovery parachute system: the Cirrus Airframe Parachute System (CAPS). This has contributed to its market success and has given it the nickname "the plane with the parachute". Design and development T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cirrus Aircraft
The Cirrus Design Corporation, doing business as Cirrus Aircraft (formally Cirrus Design), is an aircraft manufacturer that was founded in 1984 by Alan and Dale Klapmeier to produce the VK-30 kit aircraft. The company is owned by a subsidiary of the Chinese government-owned AVIC, and is headquartered in Duluth, Minnesota, United States, with additional operational locations in six other states across the US, including North Dakota, Tennessee (where its customer headquarters are based), Texas, Arizona, Florida and Michigan, as well as sales locations in France and the Netherlands. Cirrus markets several versions of its three certificated single-engine light aircraft models: the SR20 (certified in 1998), SR22 (certified in 2000), and SR22T (certified in 2010). As of January 2021, the company had delivered more than 8,000 SR-aircraft in over 20 years of production, and has been the world's largest producer of piston-powered aircraft since 2013. Sales of the SR-series gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Side Stick
__NOTOC__ A side-stick or sidestick controller is an aircraft control stick that is located on the side console of the pilot, usually on the righthand side, or outboard on a two-seat flightdeck. Typically this is found in aircraft that are equipped with fly-by-wire control systems.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 463. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. The throttle controls are typically located to the left of a single pilot or centrally on a two-seat flightdeck. Only one hand is required to operate it; two hand operation is neither possible nor necessary. The side-stick is used in many modern military fighter aircraft, such as the F-16 Fighting Falcon, Mitsubishi F-2, Dassault Rafale, and F-22 Raptor, and also on civil aircraft, such as the Sukhoi Superjet 100, Airbus A320 and all subsequent Airbus aircraft, including the largest passenger jet in service, the Airbus A380. It is also used in new helicopter models such as the Bell 525. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement. The current categorisation is that a turbocharger is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gasses, whereas a supercharger is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft). However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. History Prior to the invention of the turbocharger, |
AOPA
The Aircraft Owners and Pilots Association (AOPA) is a Frederick, Maryland-based American non-profit political organization that advocates for general aviation. AOPA's membership consists mainly of general aviation pilots in the United States. AOPA exists to serve the interests of its members as aircraft owners and pilots and to promote the economy, safety, utility, and popularity of flight in general aviation aircraft. With 384,915 members in 2012, AOPA is the largest aviation association in the world, although it had decreased in membership from 414,224 in 2010, a loss of 7% in two years. AOPA is affiliated with other similar organizations in other countries through membership in the International Council of Aircraft Owner and Pilot Associations (IAOPA). In 2015, AOPA was inducted into the International Air & Space Hall of Fame at the San Diego Air & Space Museum. History The organization started at Wings Field in Blue Bell, Pennsylvania. On 24 April 1932, The Philadelp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
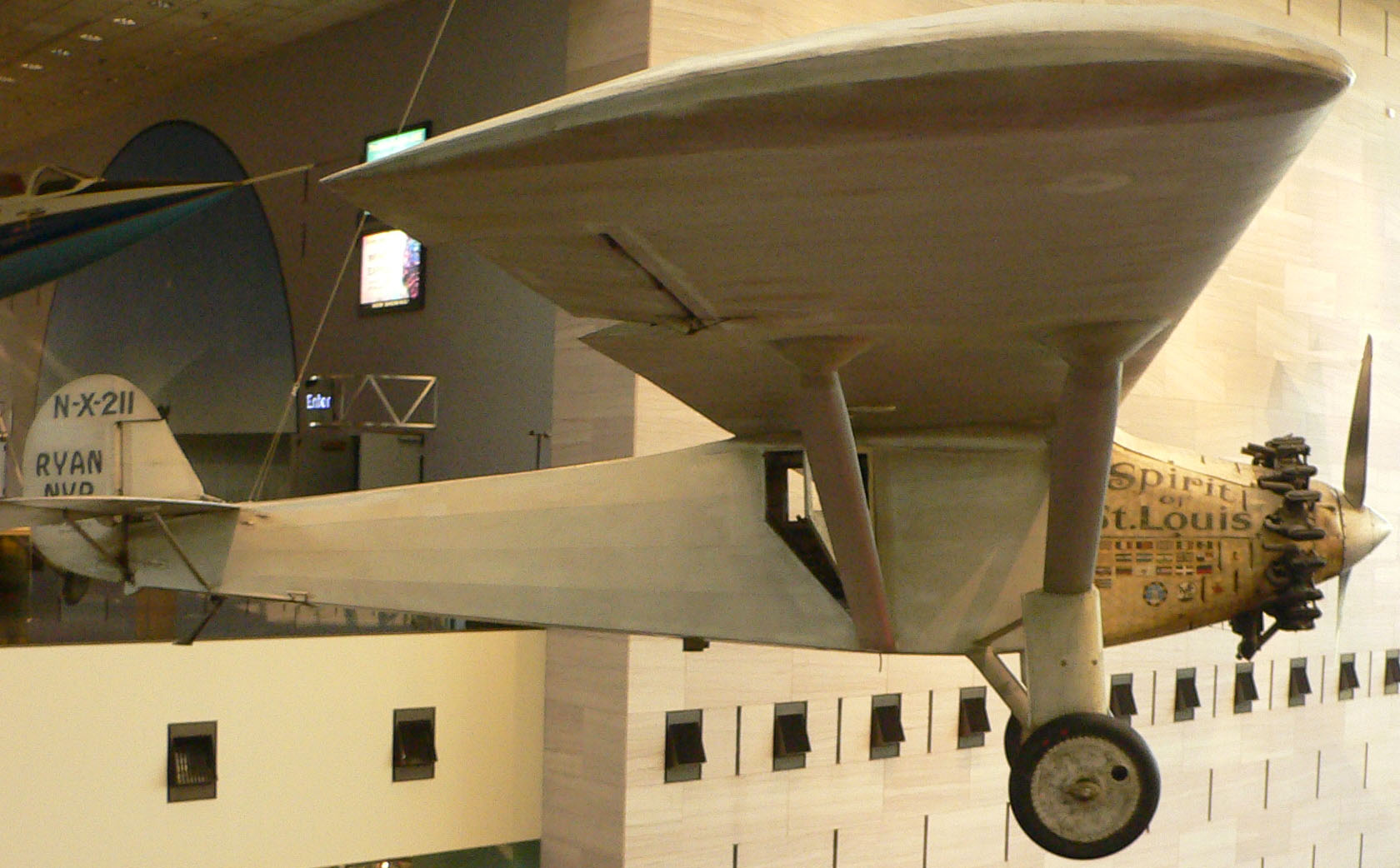
National Air And Space Museum
The National Air and Space Museum of the Smithsonian Institution, also called the Air and Space Museum, is a museum in Washington, D.C., in the United States. Established in 1946 as the National Air Museum, it opened its main building on the National Mall near L'Enfant Plaza in 1976. In 2018, the museum saw about 6.2 million visitors, making it the fifth-most-visited museum in the world, and the second-most-visited museum in the United States. In 2020, due to long closures and a drop in foreign tourism caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, museum attendance dropped to 267,000. The National Air and Space Museum is a center for research into the history and science of aviation and spaceflight, as well as planetary science and terrestrial geology and geophysics. Almost all spacecraft and aircraft on display are originals or the original backup craft. The museum contains the Apollo 11 Command Module ''Columbia'', the ''Friendship 7'' capsule which was flown by John Glenn, Charles Lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded on August 10, 1846, it operates as a trust instrumentality and is not formally a part of any of the three branches of the federal government. The institution is named after its founding donor, British scientist James Smithson. It was originally organized as the United States National Museum, but that name ceased to exist administratively in 1967. Called "the nation's attic" for its eclectic holdings of 154 million items, the institution's 19 museums, 21 libraries, nine research centers, and zoo include historical and architectural landmarks, mostly located in the District of Columbia. Additional facilities are located in Maryland, New York, and Virginia. More than 200 institutions and museums in 45 states,States without Smithsonian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobile App
A mobile application or app is a computer program or software application designed to run on a mobile device such as a phone, tablet, or watch. Mobile applications often stand in contrast to desktop applications which are designed to run on desktop computers, and web applications which run in mobile web browsers rather than directly on the mobile device. Apps were originally intended for productivity assistance such as email, calendar, and contact databases, but the public demand for apps caused rapid expansion into other areas such as mobile games, factory automation, GPS and location-based services, order-tracking, and ticket purchases, so that there are now millions of apps available. Many apps require Internet access. Apps are generally downloaded from app stores, which are a type of digital distribution platforms. The term "app", short for " application", has since become very popular; in 2010, it was listed as "Word of the Year" by the American Dialect Society. Apps a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Owners And Pilots Association
The Aircraft Owners and Pilots Association (AOPA) is a Frederick, Maryland-based American non-profit political organization that advocates for general aviation. AOPA's membership consists mainly of general aviation pilots in the United States. AOPA exists to serve the interests of its members as aircraft owners and pilots and to promote the economy, safety, utility, and popularity of flight in general aviation aircraft. With 384,915 members in 2012, AOPA is the largest aviation association in the world, although it had decreased in membership from 414,224 in 2010, a loss of 7% in two years. AOPA is affiliated with other similar organizations in other countries through membership in the International Council of Aircraft Owner and Pilot Associations (IAOPA). In 2015, AOPA was inducted into the International Air & Space Hall of Fame at the San Diego Air & Space Museum. History The organization started at Wings Field in Blue Bell, Pennsylvania. On 24 April 1932, The Philadelp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landing Gear
Landing gear is the undercarriage of an aircraft or spacecraft that is used for takeoff or landing. For aircraft it is generally needed for both. It was also formerly called ''alighting gear'' by some manufacturers, such as the Glenn L. Martin Company. For aircraft, Stinton makes the terminology distinction ''undercarriage (British) = landing gear (US)''. For aircraft, the landing gear supports the craft when it is not flying, allowing it to take off, land, and taxi without damage. Wheeled landing gear is the most common, with skis or floats needed to operate from snow/ice/water and skids for vertical operation on land. Faster aircraft have retractable undercarriages, which fold away during flight to reduce drag. Some unusual landing gear have been evaluated experimentally. These include: no landing gear (to save weight), made possible by operating from a catapult cradle and flexible landing deck: air cushion (to enable operation over a wide range of ground obstacles and wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Traffic Control
Air traffic control (ATC) is a service provided by ground-based air traffic controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and through a given section of controlled airspace, and can provide advisory services to aircraft in non-controlled airspace. The primary purpose of ATC worldwide is to prevent collisions, organize and expedite the flow of air traffic, and provide information and other support for pilots. Air traffic controllers monitor the location of aircraft in their assigned airspace by radar and communicate with the pilots by radio. To prevent collisions, ATC enforces traffic separation rules, which ensure each aircraft maintains a minimum amount of empty space around it at all times. In many countries, ATC provides services to all private, military, and commercial aircraft operating within its airspace. Depending on the type of flight and the class of airspace, ATC may issue ''instructions'' that pilots are required to obey, or ''advisories'' (known as ''flight infor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navigation Light
A navigation light, also known as a running or position light, is a source of illumination on a watercraft, aircraft or spacecraft, meant to give information on the craft's position, heading, or status. Some navigation lights are colour-coded red and green to aid traffic control by identifying the craft's orientation. Their placement is mandated by international conventions or civil authorities such as the International Maritime Organization (IMO). A common misconception is that marine or aircraft navigation lights indicate which of two approaching vessels has the "right of way" as in ground traffic; this is never true. However, the red and green colours are chosen to indicate which vessel has the duty to "give way" or "stand on" (obligation to hold course and speed). Consistent with the ground traffic convention, the rightmost of the two vehicles is usually given stand-on status and the leftmost must give way. Therefore a red light is used on the ( left (port)) side to indicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avionics
Avionics (a blend word, blend of ''aviation'' and ''electronics'') are the Electronics, electronic systems used on aircraft. Avionic systems include communications, Air navigation, navigation, the display and management of multiple systems, and the hundreds of systems that are fitted to aircraft to perform individual functions. These can be as simple as a searchlight for a police helicopter or as complicated as the tactical system for an airborne early warning platform. History The term "avionics" was coined in 1949 by Philip J. Klass, senior editor at ''Aviation Week & Space Technology'' magazine as a portmanteau of "aviation electronics". Radio communication was first used in aircraft just prior to World War I. The first Airborne radio relay, airborne radios were in zeppelins, but the military sparked development of light radio sets that could be carried by heavier-than-air craft, so that aerial reconnaissance biplanes could report their observations immediately in case ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |