|
Circuit Utilization
Circuit underutilization also chip underutilization, programmable circuit underutilization, gate underutilization, logic block underutilization refers to a physical incomplete utility of semiconductor grade silicon on a standardized mass-produced circuit programmable chip, such as a gate array type ASIC, an FPGA, or a CPLD. Gate array In the example of a gate array, which may come in sizes of 5,000 or 10,000 gates, a design which utilizes even 5,001 gates would be required to use a 10,000 gate chip. This inefficiency results in underutilization of the silicon. FPGA Due to the design components of field-programmable gate array into logic blocks, simple designs that underutilize a single block suffer from gate underutilization, as do designs that overflow onto multiple blocks, such as designs that use wide gates. Additionally, the very generic architecture of FPGAs lends to high inefficiency; multiplexers occupy silicon real estate for programmable selection, and an abundan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circuit Minimization For Boolean Functions
Logic optimization is a process of finding an equivalent representation of the specified logic circuit under one or more specified constraints. This process is a part of a logic synthesis applied in digital electronics and integrated circuit design. Generally, the circuit is constrained to a minimum chip area meeting a predefined response delay. The goal of logic optimization of a given circuit is to obtain the smallest logic circuit that evaluates to the same values as the original one. The smaller circuit with the same function is cheaper, takes less space, consumes less power, have shorter latency, and minimizes risks of unexpected cross-talk, hazard of delayed signal processing, and other issues present at the nano-scale level of metallic structures on an integrated circuit. In terms of Boolean algebra, the optimization of a complex boolean expression is a process of finding a simpler one, which would upon evaluation ultimately produce the same results as the original on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystalline Silicon
Crystalline silicon or (c-Si) Is the crystalline forms of silicon, either polycrystalline silicon (poly-Si, consisting of small crystals), or monocrystalline silicon (mono-Si, a continuous crystal). Crystalline silicon is the dominant semiconducting material used in photovoltaic technology for the production of solar cells. These cells are assembled into solar panels as part of a photovoltaic system to generate solar power from sunlight. In electronics, crystalline silicon is typically the monocrystalline form of silicon, and is used for producing microchips. This silicon contains much lower impurity levels than those required for solar cells. Production of semiconductor grade silicon involves a chemical purification to produce Hyper-pure Polysilicon, followed by a recrystallization process to grow monocrystalline silicon. The cylindrical boules are then cut into wafers for further processing. Solar cells made of crystalline silicon are often called ''conventional'', ''trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programmable Logic Device
A programmable logic device (PLD) is an electronic component used to build reconfigurable digital circuits. Unlike digital logic constructed using discrete logic gates with fixed functions, a PLD has an undefined function at the time of manufacture. Before the PLD can be used in a circuit it must be programmed to implement the desired function. Compared to fixed logic devices, programmable logic devices simplify the design of complex logic and may offer superior performance. Unlike for microprocessors, programming a PLD changes the connections made between the gates in the device. PLDs can broadly be categorised into, in increasing order of complexity, Simple Programmable Logic Devices (SPLDs), comprising programmable array logic, programmable logic array and generic array logic; Complex Programmable Logic Devices (CPLDs) and Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs). History In 1969, Motorola offered the XC157, a mask-programmed gate array with 12 gates and 30 uncommitted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gate Array
A gate array is an approach to the design and manufacture of application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) using a prefabricated chip with components that are later interconnected into logic devices (e.g. NAND gates, flip-flops, etc.) according to a custom order by adding metal interconnect layers in the factory. It was popular during upheaval in semiconductor industry in 80s and its usage declined by end of 90s. Similar technologies have also been employed to design and manufacture analog, analog-digital, and structured arrays, but, in general, these are not called gate arrays. Gate arrays have also been known as ''uncommitted logic arrays'' (''ULAs''), which also offered linear circuit functions, and ''semi-custom chips''. History Development Gate arrays had several concurrent development paths. Ferranti in the UK pioneered commercializing bipolar ULA technology, offering circuits of "100 to 10,000 gates and above" by 1983. The company's early lead in semi-custom chips, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Application-specific Integrated Circuit
An application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC ) is an integrated circuit (IC) chip customized for a particular use, rather than intended for general-purpose use, such as a chip designed to run in a digital voice recorder or a high-efficiency video codec. Application-specific standard product (ASSP) chips are intermediate between ASICs and industry standard integrated circuits like the 7400 series or the 4000 series. ASIC chips are typically fabricated using metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) technology, as MOS integrated circuit chips. As feature sizes have shrunk and design tools improved over the years, the maximum complexity (and hence functionality) possible in an ASIC has grown from 5,000 logic gates to over 100 million. Modern ASICs often include entire microprocessors, memory blocks including ROM, RAM, EEPROM, flash memory and other large building blocks. Such an ASIC is often termed a SoC (system-on-chip). Designers of digital ASICs often use a hardware descrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field-programmable Gate Array
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by a customer or a designer after manufacturinghence the term '' field-programmable''. The FPGA configuration is generally specified using a hardware description language (HDL), similar to that used for an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC). Circuit diagrams were previously used to specify the configuration, but this is increasingly rare due to the advent of electronic design automation tools. FPGAs contain an array of programmable logic blocks, and a hierarchy of reconfigurable interconnects allowing blocks to be wired together. Logic blocks can be configured to perform complex combinational functions, or act as simple logic gates like AND and XOR. In most FPGAs, logic blocks also include memory elements, which may be simple flip-flops or more complete blocks of memory. Many FPGAs can be reprogrammed to implement different logic functions, allowing flexible reconfigur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
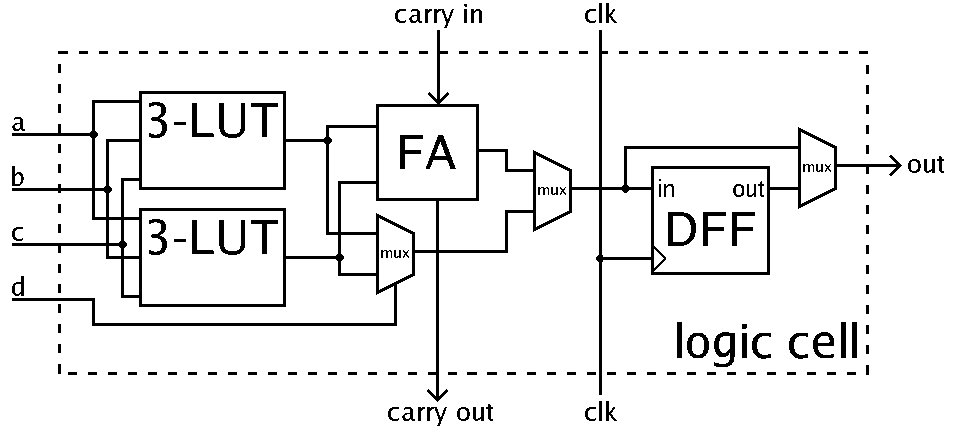
Logic Block
In computing, a logic block or configurable logic block (CLB) is a fundamental building block of field-programmable gate array (FPGA) technology. Logic blocks can be configured by the engineer to provide reconfigurable logic gates. Logic blocks are the most common FPGA architecture, and are usually laid out within a logic block array. Logic blocks require I/O pads (to interface with external signals), and routing channels (to interconnect logic blocks). Programmable logic blocks were invented by David W. Page and LuVerne R. Peterson, and defined within their 1985 patents.Google Patent Search,Re-programmable PLA. Filed January 11, 1983. Granted April 2, 1985. Retrieved February 5, 2009.Google Patent Search,Dynamic data re-programmable PLA. Filed January 11, 1983. Granted June 18, 1985. Retrieved February 5, 2009. Applications An application circuit must be mapped into an FPGA with adequate resources. While the number of logic blocks and I/Os required is easily determined from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiplexer
In electronics, a multiplexer (or mux; spelled sometimes as multiplexor), also known as a data selector, is a device that selects between several analog or digital input signals and forwards the selected input to a single output line. The selection is directed by a separate set of digital inputs known as select lines. A multiplexer of 2^n inputs has n select lines, which are used to select which input line to send to the output. A multiplexer makes it possible for several input signals to share one device or resource, for example, one analog-to-digital converter or one communications transmission medium, instead of having one device per input signal. Multiplexers can also be used to implement Boolean functions of multiple variables. Conversely, a demultiplexer (or demux) is a device taking a single input and selecting signals of the output of the compatible mux, which is connected to the single input, and a shared selection line. A multiplexer is often used with a complement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flip-flop (electronics)
In electronics, a flip-flop or latch is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information – a bistable multivibrator. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will have one or two outputs. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. Flip-flops and latches are fundamental building blocks of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems. Flip-flops and latches are used as data storage elements. A flip-flop is a device which stores a single ''bit'' (binary digit) of data; one of its two states represents a "one" and the other represents a "zero". Such data storage can be used for storage of ''state'', and such a circuit is described as sequential logic in electronics. When used in a finite-state machine, the output and next state depend not only on its current input, but also on its current state (and hence, previous inputs). It can also b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flip-flop (electronics)
In electronics, a flip-flop or latch is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information – a bistable multivibrator. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will have one or two outputs. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. Flip-flops and latches are fundamental building blocks of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems. Flip-flops and latches are used as data storage elements. A flip-flop is a device which stores a single ''bit'' (binary digit) of data; one of its two states represents a "one" and the other represents a "zero". Such data storage can be used for storage of ''state'', and such a circuit is described as sequential logic in electronics. When used in a finite-state machine, the output and next state depend not only on its current input, but also on its current state (and hence, previous inputs). It can also b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Cell
In semiconductor design, standard cell methodology is a method of designing application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) with mostly digital-logic features. Standard cell methodology is an example of design abstraction, whereby a low-level very-large-scale integration (VLSI) layout is encapsulated into an abstract logic representation (such as a NAND gate). Cell-based methodology — the general class to which standard cells belong — makes it possible for one designer to focus on the high-level (logical function) aspect of digital design, while another designer focuses on the implementation (physical) aspect. Along with semiconductor manufacturing advances, standard cell methodology has helped designers scale ASICs from comparatively simple single-function ICs (of several thousand gates), to complex multi-million gate system-on-a-chip (SoC) devices. Construction of a standard cell A standard cell is a group of transistor and interconnect structures that provides a boolean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |