|
Churche's Mansion
Churche's Mansion is a timber-framed, black-and-white Elizabethan mansion house at the eastern end of Hospital Street in Nantwich, Cheshire, England. The Grade I listed building dates from 1577, and is one of the very few to have survived the Great Fire of Nantwich in 1583. Built for Richard Churche, a wealthy Nantwich merchant, and his wife, it remained in their family until the 20th century. In 1930, it was rescued from being shipped to the US by Edgar Myott and his wife, who began restoration work. As well as a dwelling, the mansion has been used as a school, restaurant, shop, and granary and hay store. The building has four gables to the front; the upper storey and the attics all overhang with jetties. The upper storeys feature decorative panels, and the exterior has many gilded carvings. The principal rooms have oak panelling, some of which is Elizabethan in date. The architectural historian Nikolaus Pevsner considered Churche's Mansion to be among the best timber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabethan Architecture
Elizabethan architecture refers to buildings of a certain style constructed during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I of England and Ireland from 1558–1603. Historically, the era sits between the long era of the dominant architectural style of religious buildings by the Catholic Church, which ended abruptly at the Dissolution of the Monasteries from c.1536, and the advent of a court culture of pan-European artistic ambition under James I (1603–25). Stylistically, Elizabethan architecture is notably pluralistic. It came at the end of insular traditions in design and construction called the Perpendicular style in the church building, the fenestration, vaulting techniques, and open truss designs of which often affected the detail of larger domestic buildings. However, English design had become open to the influence of early printed architectural texts (namely Vitruvius and Alberti) imported to England by members of the church as early as the 1480s. Into the 16th century, illus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antix Productions
Antix Productions is a television production company founded by Yvette Fielding and Karl Beattie in 2001. The company have produced shows for broadcasters such as Living and ITV in the UK and Travel Channel in the United States. Their output includes successful shows such as ''Most Haunted'' and its various sister shows such as ''Most Haunted Live!''. Originally, Antix Productions was based in Cheadle in the Metropolitan Borough of Stockport, Greater Manchester, but relocated to an office within MediaCityUK in Salford, Greater Manchester in 2011. Productions Most Haunted *''Most Haunted'' *''Most Haunted Live!'' *''Most Haunted Extra'' *''Most Haunted: Recurring Nightmares'' Other * '' Ghosthunting with...'' * ''The Ride'' * ''Pop Talk'' * ''Celebrity Daredevils'' * '' Celebrity Ghost Stories UK'' * ''Death in Venice'' * ''Living with Yvette and Karl'' * ''Spook School'' * ''The Enfield Poltergeist'' * ''Ghosthunters'' The Paranormal Channel In 2008, Antix Productions launch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overmantel
The fireplace mantel or mantelpiece, also known as a chimneypiece, originated in medieval times as a hood that projected over a fire grate to catch the smoke. The term has evolved to include the decorative framework around the fireplace, and can include elaborate designs extending to the ceiling. ''Mantelpiece'' is now the general term for the jambs, mantel shelf, and external accessories of a fireplace. For many centuries, the ''chimneypiece'' was the most ornamental and most artistic feature of a room, but as fireplaces have become smaller, and modern methods of heating have been introduced, its artistic as well as its practical significance has lessened. Where the fireplace continues up the wall with an elaborate construction, as in historic grand buildings, this is known as an overmantel.''OED'' first citation, 1882. Mirrors and paintings designed to be hung above a mantel shelf may be called "mantel mirror", "mantel painting" and so on. History Up to the twelfth century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panelling
Panelling (or paneling in the U.S.) is a millwork wall covering constructed from rigid or semi-rigid components. These are traditionally interlocking wood, but could be plastic or other materials. Panelling was developed in antiquity to make rooms in stone buildings more comfortable both by insulating the room from the stone, and reflecting radiant heat from wood fires, making heat more evenly distributed in the room. In more modern buildings, such panelling is often installed for decorative purposes. Panelling, such as wainscoting and boiserie in particular, may be extremely ornate and is particularly associated with 17th and 18th century interior design, Victorian architecture in Britain, and its international contemporaries. Wainscot panelling The term wainscot ( or ) originally applied to high quality riven oak boards. Wainscot oak came from large, slow-grown forest trees, and produced boards that were knot-free, low in tannin, light in weight, and easy to work wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stained Glass
Stained glass is coloured glass as a material or works created from it. Throughout its thousand-year history, the term has been applied almost exclusively to the windows of churches and other significant religious buildings. Although traditionally made in flat panels and used as windows, the creations of modern stained glass artists also include three-dimensional structures and sculpture. Modern vernacular usage has often extended the term "stained glass" to include domestic lead light and ''objets d'art'' created from foil glasswork exemplified in the famous lamps of Louis Comfort Tiffany. As a material ''stained glass'' is glass that has been coloured by adding metallic salts during its manufacture, and usually then further decorating it in various ways. The coloured glass is crafted into ''stained glass windows'' in which small pieces of glass are arranged to form patterns or pictures, held together (traditionally) by strips of lead and supported by a rigid frame. Painte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transom (architectural)
In architecture, a transom is a transverse horizontal structural beam or bar, or a crosspiece separating a door from a window above it. This contrasts with a mullion, a vertical structural member. Transom or transom window is also the customary U.S. word used for a transom light, the window over this crosspiece. In Britain, the transom light is usually referred to as a fanlight, often with a semi-circular shape, especially when the window is segmented like the slats of a folding hand fan. A prominent example of this is at the main entrance of 10 Downing Street, the official residence of the British prime minister. History In early Gothic ecclesiastical work, transoms are found only in belfry unglazed windows or spire lights, where they were deemed necessary to strengthen the mullions in the absence of the iron stay bars, which in glazed windows served a similar purpose. In the later Gothic, and more especially the Perpendicular Period, the introduction of transoms became common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mullion
A mullion is a vertical element that forms a division between units of a window or screen, or is used decoratively. It is also often used as a division between double doors. When dividing adjacent window units its primary purpose is a rigid support to the glazing of the window. Its secondary purpose is to provide structural support to an arch or lintel above the window opening. Horizontal elements separating the head of a door from a window above are called transoms. History Stone mullions were used in Armenian, Saxon and Islamic architecture prior to the 10th century. They became a common and fashionable architectural feature across Europe in Romanesque architecture, with paired windows divided by a mullion, set beneath a single arch. The same structural form was used for open arcades as well as windows, and is found in galleries and cloisters. In Gothic architecture windows became larger and arrangements of multiple mullions and openings were used, both for structure and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salamander (legendary Creature)
The salamander is an amphibian of the order Urodela which, as with many real creatures, often has been ascribed fantastic and sometimes occult qualities by pre-modern authors (as in the allegorical descriptions of animals in medieval bestiaries) not possessed by the real organism. The legendary salamander is often depicted as a typical salamander in shape with a lizard-like form, but is usually ascribed an affinity with fire, sometimes specifically elemental fire. Classical, Medieval, and Renaissance lore This legendary creature embodies the fantastic qualities that ancient and medieval commentators ascribed to the natural salamander. Many of these qualities are rooted in verifiable traits of the natural creature but often exaggerated. A large body of legend, mythology, and symbolism has developed around this creature over the centuries. Carl Linnaeus in the 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' of 1758 established the scientific description of the salamander and noted the chief char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corbel
In architecture, a corbel is a structural piece of stone, wood or metal jutting from a wall to carry a superincumbent weight, a type of bracket. A corbel is a solid piece of material in the wall, whereas a console is a piece applied to the structure. A piece of timber projecting in the same way was called a "tassel" or a "bragger" in England. The technique of corbelling, where rows of corbels deeply keyed inside a wall support a projecting wall or parapet, has been used since Neolithic (New Stone Age) times. It is common in medieval architecture and in the Scottish baronial style as well as in the vocabulary of classical architecture, such as the modillions of a Corinthian cornice. The corbel arch and corbel vault use the technique systematically to make openings in walls and to form ceilings. These are found in the early architecture of most cultures, from Eurasia to Pre-Columbian architecture. A console is more specifically an "S"-shaped scroll bracket in the classic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
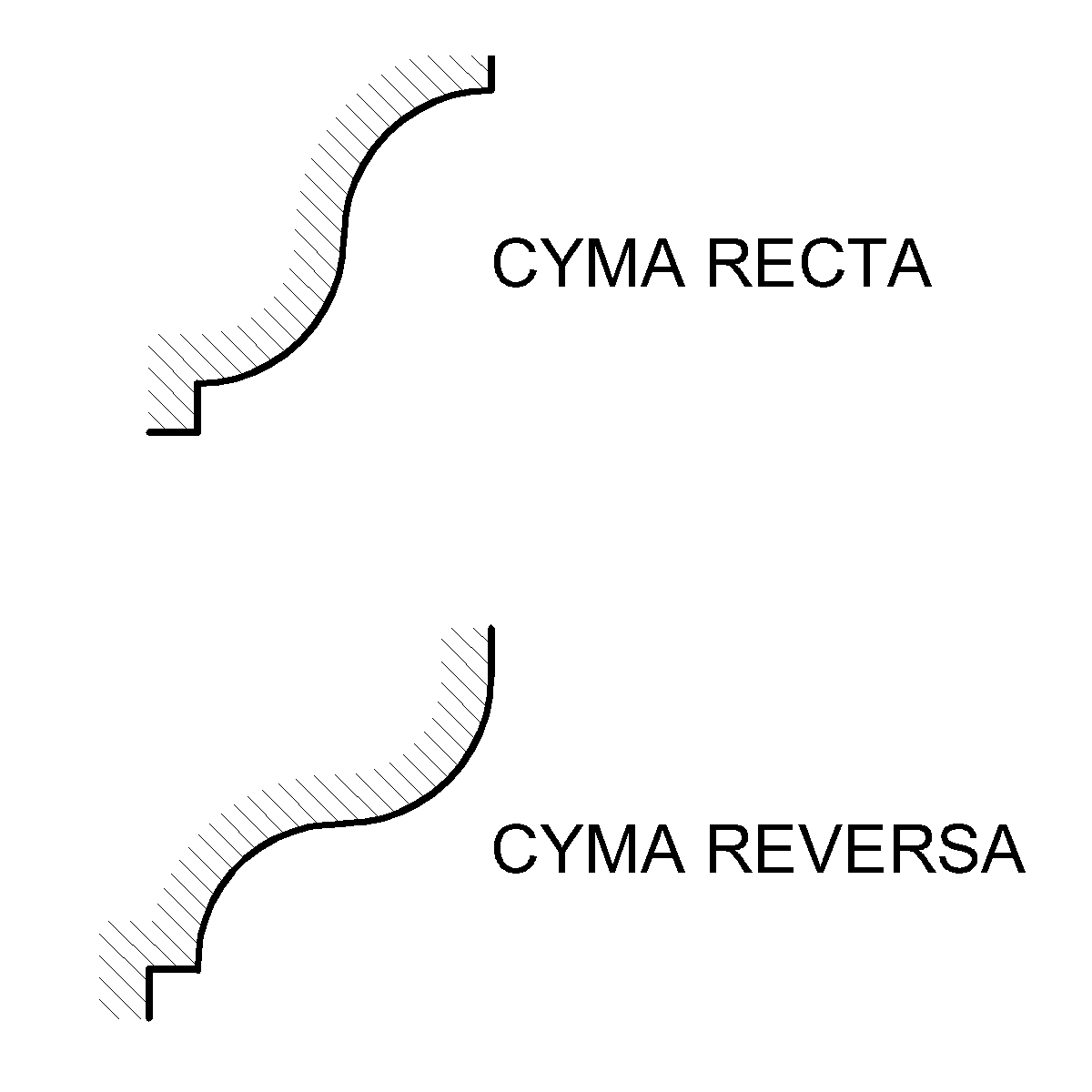
Ogee
An ogee ( ) is the name given to objects, elements, and curves—often seen in architecture and building trades—that have been variously described as serpentine-, extended S-, or sigmoid-shaped. Ogees consist of a "double curve", the combination of two semicircular curves or arcs that, as a result of a point of inflection from concave to convex or ''vice versa'', have ends of the overall curve that point in opposite directions (and have tangents that are approximately parallel). First seen in textiles in the 12th century, the use of ogee elements—in particular, in the design of arches—has been said to characterise various Gothic and Gothic Revival architectural styles. The shape has many such uses in architecture from those periods to the present day, including in the ogee arch in these architectural styles, where two ogees oriented as mirror images compose the sides of the arch, and in decorative molding designs, where single ogees are common profiles (see opening image) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Churches Mansion Decorative Panel
Church may refer to: Religion * Church (building), a building for Christian religious activities * Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination * Church service, a formalized period of Christian communal worship * Christian denomination, a Christian organization with distinct doctrine and practice * Christian Church, either the collective body of all Christian believers, or early Christianity Places United Kingdom * Church (Liverpool ward), a Liverpool City Council ward * Church (Reading ward), a Reading Borough Council ward * Church (Sefton ward), a Metropolitan Borough of Sefton ward * Church, Lancashire, England United States * Church, Iowa, an unincorporated community * Church Lake, a lake in Minnesota Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Church magazine'', a pastoral theology magazine published by the National Pastoral Life Center Fictional entities * Church (''Red vs. Blue''), a fictional character in the video web series ''Red vs. Blue'' * Churc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jettying
Jettying (jetty, jutty, from Old French ''getee, jette'') is a building technique used in medieval timber-frame buildings in which an upper floor projects beyond the dimensions of the floor below. This has the advantage of increasing the available space in the building without obstructing the street. Jettied floors are also termed ''jetties''. In the U.S., the most common surviving colonial version of this is the garrison house. Most jetties are external, but some early medieval houses were built with internal jetties. Structure A jetty is an upper floor that depends on a cantilever system in which a horizontal beam, the jetty bressummer, supports the wall above and projects forward beyond the floor below (a technique also called ''oversailing''). The bressummer (or breastsummer) itself rests on the ends of a row of jetty beams or joists which are supported by jetty plates. Jetty joists in their turn were slotted sideways into the diagonal dragon beams at angle of 45° by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_cropped_2.jpg)



.jpg)
.jpg)