|
Church Of San Gallo
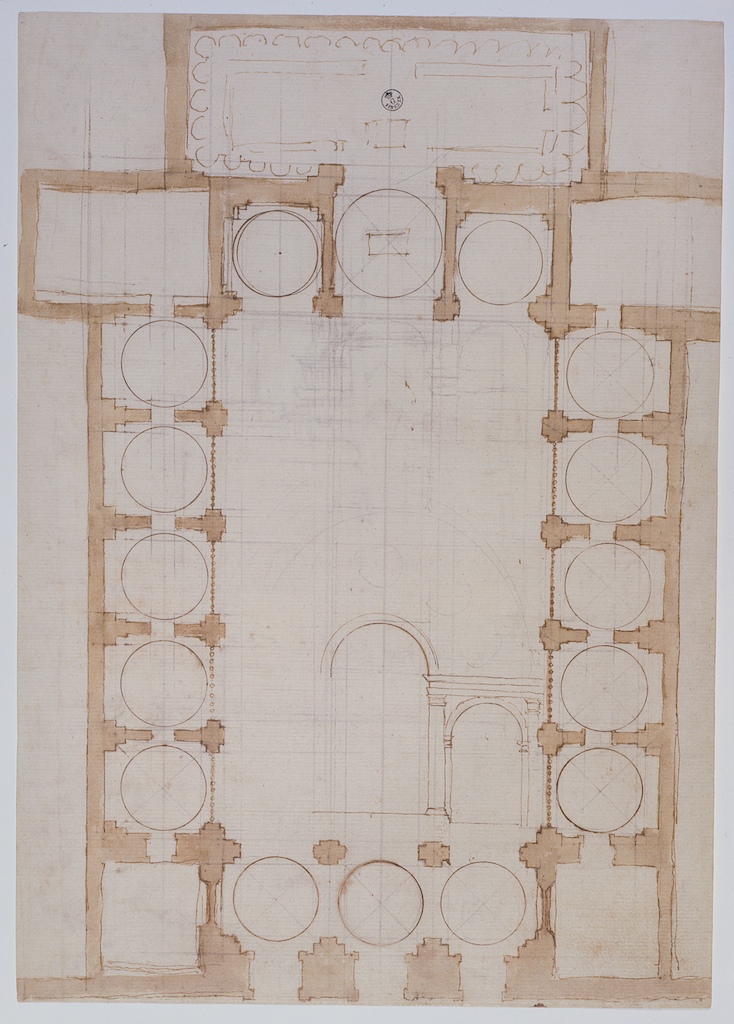
Church of San Gallo was a 15th-century church designed by architect Giuliano da Sangallo. The church was built outside of the city walls and it was destroyed during the Siege of Florence (1529–30). Background Lorenzo de' Medici commissioned Giuliano da Sangallo to design a monastery of Austin Friars outside the gate of San Gallo. One Architectural drawings for the building survived and it shows Architrave and Pilasters. This commission was meant to be used as an example of Medici family public patronage in Florence. History Based on correspondences during that time, historians have inferred that construction began on the church in 1488. The architect Giuliano got his name (San Gallo) from the church. In addition to the architect's last name, the gate in the Florence city wall closest to the church took on the San Gallo name: it was called Porta San Gallo. During the 1529 Siege of Florence, the Florentine army retreated within the walls of the city. The church was built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Of San Gallo Floor Plan
Church may refer to: Religion * Church (building), a building for Christian religious activities * Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination * Church service, a formalized period of Christian communal worship * Christian denomination, a Christian organization with distinct doctrine and practice * Christian Church, either the collective body of all Christian believers, or early Christianity Places United Kingdom * Church (Liverpool ward), a Liverpool City Council ward * Church (Reading ward), a Reading Borough Council ward * Church (Sefton ward), a Metropolitan Borough of Sefton ward * Church, Lancashire, England United States * Church, Iowa, an unincorporated community * Church Lake, a lake in Minnesota Arts, entertainment, and media * '' Church magazine'', a pastoral theology magazine published by the National Pastoral Life Center Fictional entities * Church (''Red vs. Blue''), a fictional character in the video web series ''Red vs. Blue'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giuliano Da Sangallo
Giuliano da Sangallo (c. 1445 – 1516) was an Italian sculptor, architect and military engineer active during the Italian Renaissance. He is known primarily for being the favored architect of Lorenzo de' Medici, his patron. In this role, Giuliano designed a villa for Lorenzo as well as a monastery for Augustinians and a church where a miracle was said to have taken place. Additionally, Giuliano was commissioned to build multiple structures for Pope Julius II and Pope Leo X. Leon Battista Alberti and Filippo Brunelleschi heavily influenced Sangallo and in turn, he influenced other important Renaissance figures such as Raphael, Leonardo da Vinci, his brother Antonio da Sangallo the Elder, and his sons, Antonio da Sangallo the Younger and Francesco da Sangallo. Early life Giuliano da Sangallo (né Giuliano Giamberti) was born c. 1445 in Florence. His father, Francesco Giamberti, was a woodworker and an architect who worked closely with Cosimo de' Medici. This proved to be hel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Florence (1529–1530)
The siege of Florence took place from 24 October 1529 to 10 August 1530, at the end of the War of the League of Cognac. At the Congress of Bologna, the Medici Pope Clement VII and Emperor Charles V agreed to restore the Medici family in Florence. A large Imperial and Spanish army under Philibert of Châlon, Prince of Orange and Pier Maria III de' Rossi surrounded the city, and, after a siege of nearly ten months, captured it, overthrowing the Republic of Florence and installing Alessandro de' Medici as the ruler of the city. The Florentines had thrown off Medici rule and established a republic after the Sack of Rome in 1527; the Florentine Republic had continued to participate in the war on the side of the French. The French defeats at Naples in 1528 and Landriano in 1529, however, led to Francis I of France concluding the Treaty of Cambrai with the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V. When Pope Clement VII and the Republic of Venice also concluded treaties with the Emperor, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrea Del Sarto - The Annunciation - WGA00359
Andrea is a given name which is common worldwide for both males and females, cognate to Andreas, Andrej and Andrew. Origin of the name The name derives from the Greek word ἀνήρ (''anēr''), genitive ἀνδρός (''andrós''), that refers to man as opposed to woman (whereas ''man'' in the sense of ''human being'' is ἄνθρωπος, ''ánthropos''). The original male Greek name, ''Andréas'', represents the hypocoristic, with endearment functions, of male Greek names composed with the ''andr-'' prefix, like Androgeos (''man of the earth''), Androcles (''man of glory''), Andronikos (''man of victory''). In the year 2006, it was the third most popular name in Italy with 3.1% of newborns. It is one of the Italian male names ending in ''a'', with others being Elia (Elias), Enea (Aeneas), Luca ( Lucas), Mattia ( Matthias), Nicola ( Nicholas), Tobia (Tobias). In recent and past times it has also been used on occasion as a female name in Italy and in Spain, where it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorenzo De' Medici
Lorenzo di Piero de' Medici (; 1 January 1449 – 8 April 1492) was an Italian statesman, banker, ''de facto'' ruler of the Florentine Republic and the most powerful and enthusiastic patron of Renaissance culture in Italy. Also known as Lorenzo the Magnificent (''Lorenzo il Magnifico'' ) by contemporary Florentines, he was a magnate, diplomat, politician and patron of scholars, artists, and poets. As a patron, he is best known for his sponsorship of artists such as Botticelli and Michelangelo. He held the balance of power within the Italic League, an alliance of states that stabilized political conditions on the Italian peninsula for decades, and his life coincided with the mature phase of the Italian Renaissance and the Golden Age of Florence. On the foreign policy front, Lorenzo manifested a clear plan to stem the territorial ambitions of Pope Sixtus IV, in the name of the balance of the Italian League of 1454. For these reasons, Lorenzo was the subject of the Pazzi consp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Architrave
In classical architecture, an architrave (; from it, architrave "chief beam", also called an epistyle; from Greek ἐπίστυλον ''epistylon'' "door frame") is the lintel or beam that rests on the capitals of columns. The term can also apply to all sides, including the vertical members, of a frame with mouldings around a door or window. The word "architrave" has come to be used to refer more generally to a style of mouldings (or other elements) framing a door, window or other rectangular opening, where the horizontal "head" casing extends across the tops of the vertical side casings where the elements join (forming a butt joint, as opposed to a miter joint). Classical architecture In an entablature in classical architecture, it is the lowest part, below the frieze and cornice. The word is derived from the Greek and Latin words ''arche'' and ''trabs'' combined to mean "main beam". The architrave is different in the different Classical orders. In the Tuscan o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilaster
In classical architecture, a pilaster is an architectural element used to give the appearance of a supporting column and to articulate an extent of wall, with only an ornamental function. It consists of a flat surface raised from the main wall surface, usually treated as though it were a column, with a capital at the top, plinth (base) at the bottom, and the various other column elements. In contrast to a pilaster, an engaged column or buttress can support the structure of a wall and roof above. In human anatomy, a pilaster is a ridge that extends vertically across the femur, which is unique to modern humans. Its structural function is unclear. Definition In discussing Leon Battista Alberti's use of pilasters, which Alberti reintroduced into wall-architecture, Rudolf Wittkower wrote: "The pilaster is the logical transformation of the column for the decoration of a wall. It may be defined as a flattened column which has lost its three-dimensional and tactile value." A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Gallo Gate
The San Gallo Gate ( it, Porta San Gallo) is part of the city walls of Florence and is located in Piazza della Libertà, opposite the Triumphal Arch. History The San Gallo Gate was begun according to the plans of Arnolfo di Cambio in 1284, but was not completed until 1327. In the 13th century, it was one of the most heavily trafficked gates in the city, as it was the most northerly, connected to the road to Bologna. On the gate, whose keys are still kept in the local history section of Palazzo Vecchio, an inscription recalls the foundation of the building in 1285 by the captain of the Guelph party Rolandino da Canossa, while another, later, celebrates the passage of King Frederick IV of Denmark in 1708, on his journey to Venice. The exterior is decorated with '' Marzocco'' while the interior lunette contains traces of a fresco depicting the Madonna and saints. Just outside the door was the complex of the convent of San Gallo, the work of Giuliano da Sangallo, who got his nickname " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
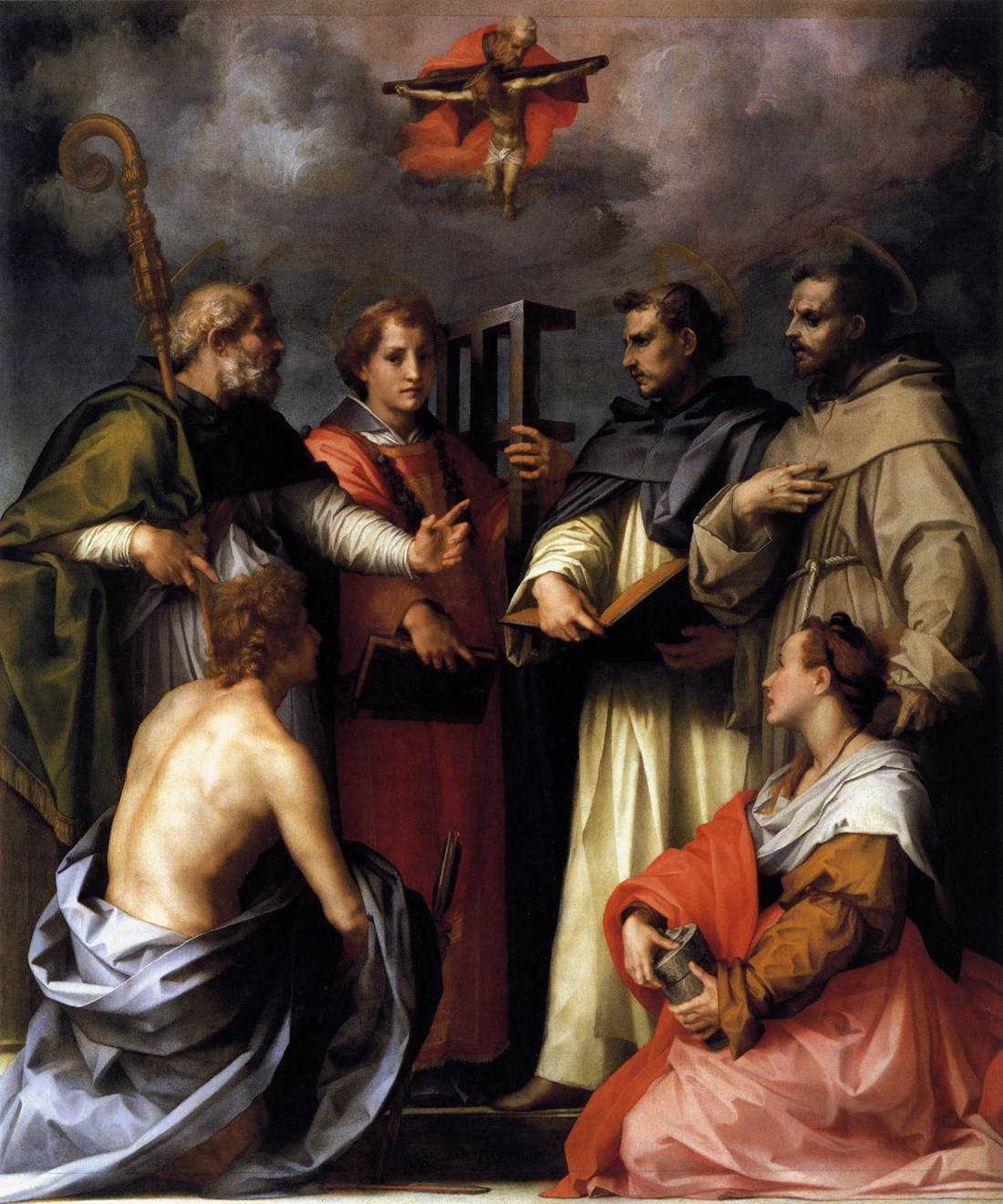
The Disputation On The Trinity
''The Disputation on the Trinity'' is an oil-on-canvas painting by the Italian Renaissance artist Andrea del Sarto, created ''c.'' 1517, now in the Galleria Palatina in Florence. At the top of the painting is a vision of the Holy Trinity. Seated in the foreground are Saint Sebastian and Mary Magdalene, the latter modelled on the artist's wife Lucrezia del Fede. Behind them stand four male saints, from left to right Augustine of Hippo (with his bishop's staff), Saint Lawrence (with the gridiron of his martyrdom), Peter Martyr (holding a book, wearing a Dominican habit and with a sword in his head) and Francis of Assisi (in his order's habit and bearing the stigmata). History Some art historians argue the work was commissioned by the Peri family due to its inclusion of saints linked to that family. It was the third painting Sarto produced for the Augustinian Church of San Gallo in Florence – the others were the ''San Gallo Annunciation'' and a '' Noli me tangere''. All th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Gallo Annunciation
The San Gallo Annunciation is an oil on panel painting by Andrea del Sarto, executed ''c.'' 1513–1514, now in the Palatine Gallery in Florence. It was the middle of three works the artist produced for the Augustinian monastery the Church of San Gallo in Florence, between '' Noli me tangere'' and '' The Disputation on the Trinity'', as recorded in the Anonimo Magliabechiano manuscript and in Vasari's ''Lives of the Artists''. When Florence was besieged, that monastery's goods were moved to San Jacopo tra i Fossi within the city walls and its buildings razed in 1531 by Charles V's troops. The monastery rebuilt all its chapels at its new site in their former form. About a third of the painting was submerged in the 1557 flood, probably leading to the loss of the predella, though in 1986 (Serena?) Padovani theorised that that predella wholly or partly survived and is now divided up between the National Gallery of Ireland and Warwick Castle. Stylistically its monumental figures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrea Del Sarto
Andrea del Sarto (, , ; 16 July 1486 – 29 September 1530) was an Italian painter from Florence, whose career flourished during the High Renaissance and early Mannerism. He was known as an outstanding fresco decorator, painter of altar-pieces, portraitist, draughtsman, and colorist. Although highly regarded during his lifetime as an artist ("without errors"), his renown was eclipsed after his death by that of his contemporaries Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael. Early life and training Andrea del Sarto was born Andrea d'Agnolo di Francesco di Luca in Florence on 16 July 1486. Since his father, Agnolo, was a tailor (Italian: '' sarto''), he became known as "del Sarto" (meaning "tailor's son"). Since 1677 some have attributed the surname Vannucchi with little documentation. By 1494 Andrea was apprenticed to a goldsmith, and then to a woodcarver and painter named Gian Barile, with whom he remained until 1498. According to his late biographer Vasari, he then app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
15th-century Churches
The 15th century was the century which spans the Julian dates from 1 January 1401 ( MCDI) to 31 December 1500 ( MD). In Europe, the 15th century includes parts of the Late Middle Ages, the Early Renaissance, and the early modern period. Many technological, social and cultural developments of the 15th century can in retrospect be seen as heralding the "European miracle" of the following centuries. The architectural perspective, and the modern fields which are known today as banking and accounting were founded in Italy. The Hundred Years' War ended with a decisive French victory over the English in the Battle of Castillon. Financial troubles in England following the conflict resulted in the Wars of the Roses, a series of dynastic wars for the throne of England. The conflicts ended with the defeat of Richard III by Henry VII at the Battle of Bosworth Field, establishing the Tudor dynasty in the later part of the century. Constantinople, known as the capital of the wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |