|
Chumbi
Chumbi (; ) is a historic village in the Chumbi Valley or the Yadong County of the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. It is in the valley of Amo Chu river, where the route from Sikkim's Cho La pass meets the Amo Chu valley. The "Chumbi Valley" of the European nomenclature derives its name from the village of Chumbi. It was the administrative center of the lower Chumbi Valley until the Chinese take-over of Tibet in 1950, after which Yatung became its headquarters. Chumbi is also associated with the Sikkim's royal family, which had a summer palace in the village. History The Chumbi Valley was originally part of the Lepcha territory. In the 13th or 14th century, it began to be colonised by Khampas from the Kham region of Tibet. A Minyak prince called Khye Bumsa () is said to have settled in Chumbi and established a small kingdom. He later built an alliance with the Lepchas in present-day Sikkim and expanded into that region. The ruins of the house built by Khye Bumsa were report ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chumbi Valley
The Chumbi Valley, called Dromo or Tromo in Tibetan, is a valley in the Himalayas that projects southwards from the Tibetan plateau, intervening between Sikkim and Bhutan. It is coextensive with the administrative unit Yadong County in the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. The Chumbi Valley is connected to Sikkim to the southwest via the mountain passes of Nathu La and Jelep La. The valley is at an altitude of , and being on the south side of the Himalayas, enjoys a wetter and more temperate climate than most of Tibet. The valley supports some vegetation in the form of the Eastern Himalayan broadleaf forests and transitions to the Eastern Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows in the north. The plant ''Pedicularis chumbica'' ( 春丕马先蒿) is named after the valley. The 1904 Younghusband Expedition of British India passed through the Chumbi Vally on its way to Lhasa. At the end of the expedition, the British took control of the Chumbi Valley in lieu of a war indemnity. Chin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yatung
Yatung or Yadong, also known as Shasima (, ), is the principal town in the Chumbi Valley or Yadong County in the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. It is also its administrative headquarters. Name The village is known locally as Shasima (''Sharsingma'') to the Tibetans, believed to be a Lepcha name. During the British Raj era, it was called Yatung, the name having been transferred from another location called "Yatung" in the valley between the Jelep La and Rinchengang. The original location later came to be called Old Yatung. The Chinese administration of Tibet uses the name Yatung (often transliterated "Yadong" in Chinese pinyin) for the county, and the name Shasima for the town. Geography Yatung is at the confluence of the Khambu Chu () and Tromo Chu (or Machu, ) rivers, which join here to form the Amo Chu river before it flows into Bhutan. Downstream along Amo Chu are further villages of Chumbi, Pipitang and Chema, within four miles distance. A further village afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nathu La
Nathu La (, ) is a mountain pass in the Dongkya Range of the Himalayas between China's Yadong County in Tibet, and the Indian states of Sikkim and West Bengal in Bengal, South Asia. The pass, at , connects the towns of Kalimpong and Gangtok to the villages and towns of the lower Chumbi Valley. The pass was surveyed by J. W. Edgar in 1873, who described the pass as being used for trade by Tibetans. Francis Younghusband used the pass in 1903-1904, a diplomatic British delegation to Lhasa in 1936-37, and Ernst Schäfer in 1938–1939. In the 1950s, trade in the Kingdom of Sikkim utilized this pass. Diplomatically sealed by China and India after the 1962 Sino-Indian War, the pass saw skirmishes between the two countries in coming years, including the clashes in 1967 which resulted in fatalities on both sides. Nathu La has often been compared to Jelep La, a mountain pass situated at a distance of 3 miles (4.8 km). The next few decades saw an improvement in ties leading to the re- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rinchengang
Rinchengang : "By order of Military Control Commission freedom of movement is not being permitted to our Trade Agents even in the vicinity where the Trade Agencies are located. For example the I.T.A. Yatung was not permitted to go to Rinchengang, only six miles from Yatung..." : "Renqinggang, also known as Rinchengang, is located south of Sharsingma in Yadong counrty." () or Renqinggang () is a town in the Chumbi Valley and the headquarters of the Xia Yadong Township of Yadong County, Tibet region of China. It is in the valley of Amo Chu where the route from Sikkim's Jelep La pass meets Amo Chu. It is also close to the Bhutan–China border (Doklam area), which is currently in dispute. In December 2018, Rinchengang village had a population of around 550 people. The inhabitants are engaged in animal grazing or work as forest rangers. Some also carry supplies to Chinese border troops. In 2003, the governments of India and China agreed to use Rinchengang as a border trade ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pipitang
Chema or Phema (; ), is a village in the Chumbi Valley or Yadong County in the Tibet region of China. It is in the valley of Amo Chu where the route from Sikkim's Nathu La pass meets the Amo Chu valley. Chema is in the Xiayadong Township. Across the river, on its eastern bank is the settlement of Pipitang (), which was described as a flourishing Chinese village in the 19th century. The village got emptied during the period of Tibet's independence (1912–1951). It is now repopulated. Geography Chema and Pipitang are four miles to the south of Yatung (Shasima). The track from the Nathu La pass met the Amo Chu valley here, while the track from the Jelep La pass also joined here via Rinchengang. At the present time, the Yanai Road () runs along this route to Nathu La. In December 1903, British travel writer Laurence Waddell passed through Chema on his way to Lhasa and described it as follows: His description continued with that of Pipitang: During the period 1894–1903, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chema, Tibet
Chema or Phema (; ), is a village in the Chumbi Valley or Yadong County in the Tibet Autonomous Region, Tibet region of China. It is in the valley of Amo Chu where the route from Sikkim's Nathu La pass meets the Amo Chu valley. Chema is in the Xiayadong Township. Across the river, on its eastern bank is the settlement of Pipitang (), which was described as a flourishing Chinese village in the 19th century. The village got emptied during the period of Tibet (1912–1951), Tibet's independence (1912–1951). It is now repopulated. Geography Chema and Pipitang are four miles to the south of Shasima, Yatung (Shasima). The track from the Nathu La pass met the Amo Chu valley here, while the track from the Jelep La pass also joined here via Rinchengang. At the present time, the Yanai Road () runs along this route to Nathu La. In December 1903, British travel writer Laurence Waddell passed through Chema on his way to Lhasa and described it as follows: His description continued with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
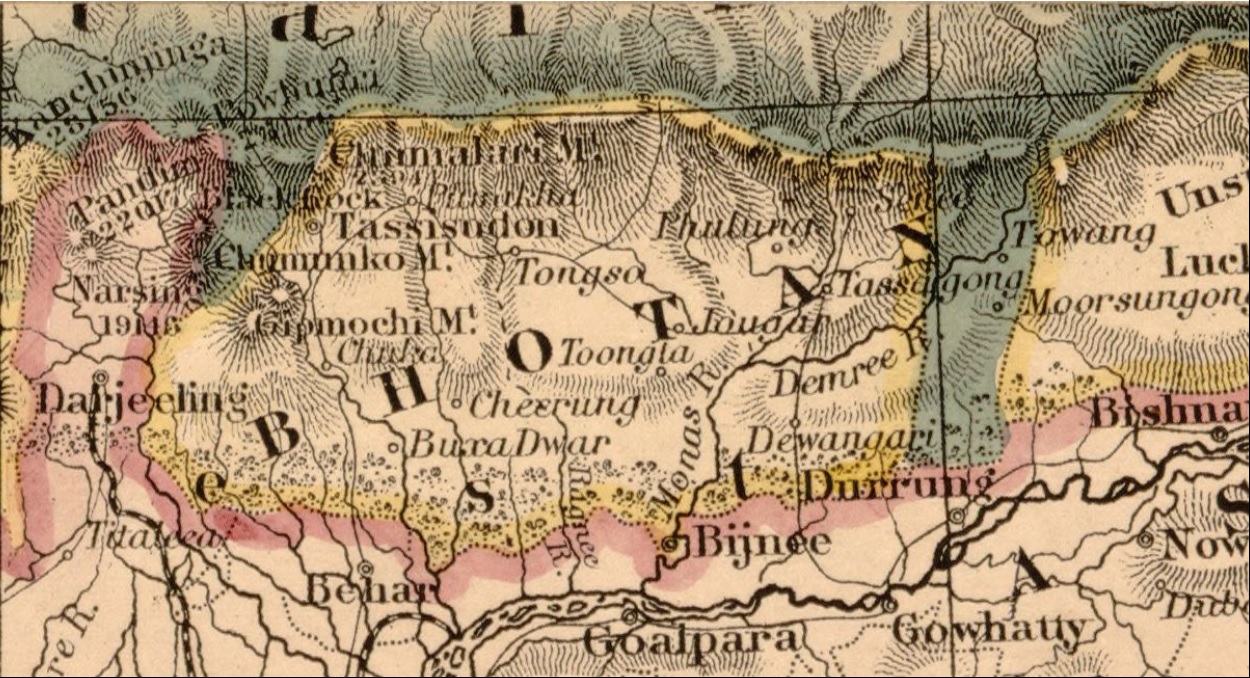
Gaeboo Achyok
Gaeboo Achyok ()B'day bash for Lepcha king The Telegraph (Kolkata), 18 December 2006. or Gyalpo Ajok () was a Lepcha chieftain of a principality based at , presently in the of , India. Achyok faced active threats from an expansionist Bhutan and formed an alliance with Tibet under the |
Cho La (Sikkim And Tibet)
Cho La or Cho-la () is a mountain pass in the Chola range of the Himalayas. It connects the Indian state of Sikkim with China's Tibet Autonomous Region. It is situated around four miles to the north-west of Nathu La. Cho La used to be the main mountain pass between Sikkim and the Chumbi Valley (Yadong County), connecting the Sikkimese capital of Tumlong with the Chumbi town. Towards the end of the 19th century, the British developed Jelep La, and later Nathu La, as they were accessible from British India, and Cho La fell into relative disuse. History The Cho La pass was in regular used by the Sikkim royal family, which had a summer palace at Chumbi and used to spend summers there. The road between Tumlong and Chumbi via Cho La was kept in good condition. The route was also the main trading route between Sikkim and Tibet. The first Europeans to visit the Chola Pass were Archibald Campbell (Darjeeling superintendent) and Joseph Dalton Hooker (botanist) in 1849, who attempted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yadong County
Yadong County (), also known by its Tibetan name Dromo/Tromo County () is a frontier county and trade-market of the Tibet region of China, part of its Shigatse Prefecture. Yadong County is coextensive with the Chumbi valley that extends south into the Himalayas between Sikkim and Bhutan. It shares boundaries with both India and Bhutan. It covers about 4,306 square kilometers with a population of 10,000. Its headquarters is Yatung (also called Shasima). Geography The Yadong County mainly consists of the Chumbi Valley, called Dromo/Tromo in Tibetan. The valley is bordered by Dongkya Range in the west and Massong-Chungdung range in the east. (See map.) Two rivers Khambu Machu and Tromo Chu arise within the valley and join together at the town of Yatung. The joint river is known in English by its Bhutanese name Amo Chu. (Tibetans continue to call it Khambu Machu.) The town of Yatung (also called Shasima), is the headquarers of the county. It is close to the borders of both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jelep La
Jelep La (; ) elevation , is a high mountain pass between Sikkim, India and Tibet Autonomous Region, China. It is on a route that connects Lhasa to India. The pass is about south of Nathu La and is slightly higher. It was frequently used for trade between Tibet and India during the British Raj, with Kalimpong serving as the contact point. The Menmecho Lake lies below the Jelep La. Name According to the ''Bengal District Gazetteer'', Jelep-la, a Tibetan name, means "The lovely level pass, so called because it is the easiest and most level of all the passes between Tibet and Sikkim." According to scholar Alex Mckay, the Tibetan name is actually , which would mean a "shepherd's bronze pass". Geography On the Indian side there are two routes to Jelep La, one through Gangtok and the other through Kalimpong. The Kalimpong route boosted the local economies due to the trading of wool and furs during the 20th century. It passes through the towns of Rongli, Rhenock, Pedong, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumlong
Tumlong is a village in the Indian state of Sikkim in northeastern India. It is located in the Mangan sub division of North Sikkim district. it is on the bank of the Dik Chu river, a tributary of the Teesta River. Tumlong was the capital of the Kingdom of Sikkim between 1793 and 1861. The Sikkim Chogyals had a palace here, and a summer palace in Chumbi in the Lower Chumbi Valley. There was route between the two locations via the Cho La pass. In 1861, the capital was moved to Gangtok in order to be closer to the Darjeeling district, which was under the administration of the British Raj. History Tumlong was the third capital after Yuksom and Rabdentse close to Nepal. After repeated raids, the capital was shifted to Tumlong, further inland, in 1793 by Tshudpud Namgyal. The Treaty of Tumlong was signed here in 1861 between the British and the Sikkim Rajah. In 1894, Thutob Namgyal shifted the capital of Sikkim from Tumlong to the current capital of Gangtok. Geography Tumlong is lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region or Xizang Autonomous Region, often shortened to Tibet or Xizang, is a Provinces of China, province-level Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China in Southwest China. It was overlayed on the traditional Tibetan regions of Ü-Tsang and Kham. It was formally established in 1965 to replace the Tibet Area (administrative division), Tibet Area, the former Administrative divisions of China, administrative division of the People's Republic of China (PRC) established after the annexation of Tibet by the People's Republic of China, annexation of Tibet. The establishment was about five years after the 1959 Tibetan uprising and the dismissal of the Kashag, and about 13 years after the original annexation. The current borders of the Tibet Autonomous Region were generally established in the 18th century and include about half of historic Tibet, or the Tibet, ethno-cultural Tibet. The Tibet Autonomous Region spans ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

