|
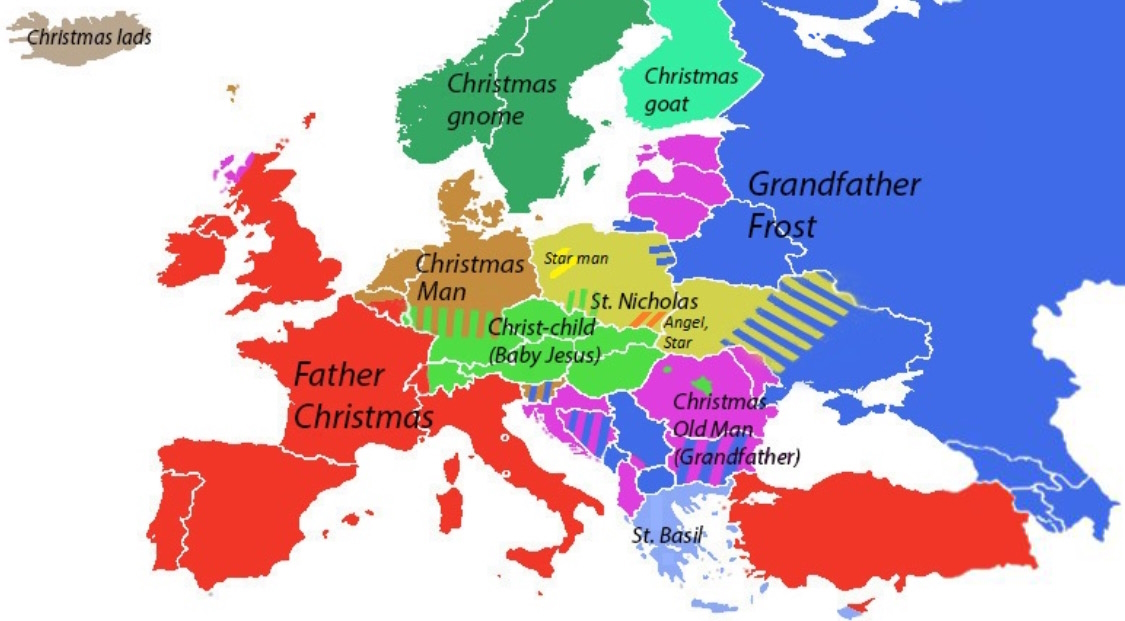
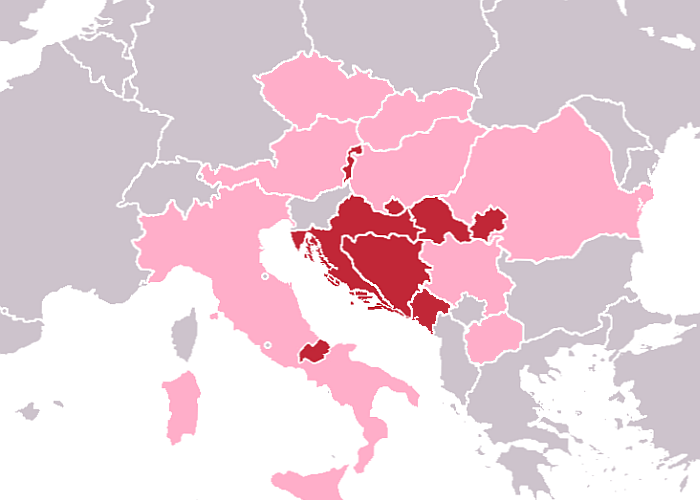
Christkind
The Christkind (; ), also called ''Christkindl'', is the traditional Christmas gift-bringer in Austria, Switzerland, southern and western Germany, the Czech Republic, Croatia, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, the eastern part of Belgium, Portugal, Slovakia, Hungary, parts of northeastern France, Upper Silesia in Poland, parts of Latin America, in certain areas of southern Brazil, and in the Acadiana region of Louisiana. Christkind is called in Portuguese ("Boy Jesus"), in Hungarian ("Little Jesus"), in Slovak ("Little Jesus"), in Czech ("Little Jesus"), in Latin America ("Child God") or ("Child Jesus") and in Croatian or ("Little Jesus"), in Polish ("Little baby"). In some parts of Italy, the analogous figure of the Christkind is known as ("Child Jesus"). History Promulgated by Martin Luther at the Protestant Reformation in 16th–17th-century Europe, many Protestants adopted this gift bringer, the Christ Child or ''Christkindl'', and the date of giving gifts change ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christkind
The Christkind (; ), also called ''Christkindl'', is the traditional Christmas gift-bringer in Austria, Switzerland, southern and western Germany, the Czech Republic, Croatia, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, the eastern part of Belgium, Portugal, Slovakia, Hungary, parts of northeastern France, Upper Silesia in Poland, parts of Latin America, in certain areas of southern Brazil, and in the Acadiana region of Louisiana. Christkind is called in Portuguese ("Boy Jesus"), in Hungarian ("Little Jesus"), in Slovak ("Little Jesus"), in Czech ("Little Jesus"), in Latin America ("Child God") or ("Child Jesus") and in Croatian or ("Little Jesus"), in Polish ("Little baby"). In some parts of Italy, the analogous figure of the Christkind is known as ("Child Jesus"). History Promulgated by Martin Luther at the Protestant Reformation in 16th–17th-century Europe, many Protestants adopted this gift bringer, the Christ Child or ''Christkindl'', and the date of giving gifts change ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christ Child
The Christ Child, also known as Divine Infant, Baby Jesus, Infant Jesus, the Divine Child, Child Jesus, the Holy Child, Santo Niño, and to some as Señor Noemi refers to Jesus Christ from his nativity to age 12. The four canonical gospels, accepted by most Christians today, lack any narration of the years between Jesus' infancy and the Finding in the Temple when he was 12. Liturgical feasts Liturgical feasts relating to Christ's infancy and childhood include: * The Feast of the Nativity of Jesus Christ (25 December); * The Feast of the Circumcision of Christ (1 January – Eastern Orthodox Church, Latin Rite-Extraordinary Form); * The Feast of the Holy Name of Jesus (3 January – Latin Rite; others – various); * The Feast of the Epiphany (6 January or 19 January in the Gregorian equivalent of the Julian calendar) * The Feast of the Presentation of the Lord (2 February) Depictions in art From about the third or fourth century onwards, the child Jesus is frequently shown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christmas Gift-bringer
A number of Midwinter or Christmas traditions in European folklore involve gift-bringers. Mostly involving the figure of a bearded old man, the traditions have mutually influenced one another, and have adopted aspects from Christian hagiography, even before the modern period. In Eastern Slavic countries, the figure is Father Frost. In Scandinavia, it is an elf-like figure or tomten who comes at Yule (and who sometimes also takes the form of a goat). In German-speaking Europe and Latin Europe, it became associated with the Christian Saint Nicholas. In some parts of Central Europe, there is a separate tradition of a young child or fairy-like being bringing presents, known as Christkind. Early modern England had Father Christmas, a character initially associated with feasting and good cheer, though he was not originally a gift bringer. From these European traditions, the North American figure of Santa Claus developed, beginning in the 1820s. The American figure in turn had consider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical region. Italy is also considered part of Western Europe, and shares land borders with France, Switzerland, Austria, Slovenia and the enclaved microstates of Vatican City and San Marino. It has a territorial exclave in Switzerland, Campione. Italy covers an area of , with a population of over 60 million. It is the third-most populous member state of the European Union, the sixth-most populous country in Europe, and the tenth-largest country in the continent by land area. Italy's capital and largest city is Rome. Italy was the native place of many civilizations such as the Italic peoples and the Etruscans, while due to its central geographic location in Southern Europe and the Mediterranean, the country has also historically been home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Language
Polish (Polish: ''język polski'', , ''polszczyzna'' or simply ''polski'', ) is a West Slavic language of the Lechitic group written in the Latin script. It is spoken primarily in Poland and serves as the native language of the Poles. In addition to being the official language of Poland, it is also used by the Polish diaspora. There are over 50 million Polish speakers around the world. It ranks as the sixth most-spoken among languages of the European Union. Polish is subdivided into regional dialects and maintains strict T–V distinction pronouns, honorifics, and various forms of formalities when addressing individuals. The traditional 32-letter Polish alphabet has nine additions (''ą'', ''ć'', ''ę'', ''ł'', ''ń'', ''ó'', ''ś'', ''ź'', ''ż'') to the letters of the basic 26-letter Latin alphabet, while removing three (x, q, v). Those three letters are at times included in an extended 35-letter alphabet, although they are not used in native words. The traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croatian Language
Croatian (; ' ) is the standardized variety of the Serbo-Croatian pluricentric language used by Croats, principally in Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Serbian province of Vojvodina, and other neighboring countries. It is the official and literary standard of Croatia and one of the official languages of the European Union. Croatian is also one of the official languages of Bosnia and Herzegovina and a recognized minority language in Serbia and neighboring countries. Standard Croatian is based on the most widespread dialect of Serbo-Croatian, Shtokavian, more specifically on Eastern Herzegovinian, which is also the basis of Standard Serbian, Bosnian, and Montenegrin. In the mid-18th century, the first attempts to provide a Croatian literary standard began on the basis of the Neo-Shtokavian dialect that served as a supraregional ''lingua franca'' pushing back regional Chakavian, Kajkavian, and Shtokavian vernaculars. The decisive role was played by Croatian Vukovians, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czech Language
Czech (; Czech ), historically also Bohemian (; ''lingua Bohemica'' in Latin), is a West Slavic language of the Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script. Spoken by over 10 million people, it serves as the official language of the Czech Republic. Czech is closely related to Slovak, to the point of high mutual intelligibility, as well as to Polish to a lesser degree. Czech is a fusional language with a rich system of morphology and relatively flexible word order. Its vocabulary has been extensively influenced by Latin and German. The Czech–Slovak group developed within West Slavic in the high medieval period, and the standardization of Czech and Slovak within the Czech–Slovak dialect continuum emerged in the early modern period. In the later 18th to mid-19th century, the modern written standard became codified in the context of the Czech National Revival. The main non-standard variety, known as Common Czech, is based on the vernacular of Prague, but is now spoken as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovak Language
Slovak () , is a West Slavic language of the Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script. It is part of the Indo-European language family, and is one of the Slavic languages, which are part of the larger Balto-Slavic branch. Spoken by approximately 5 million people as a native language, primarily ethnic Slovaks, it serves as the official language of Slovakia and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Slovak is closely related to Czech, to the point of mutual intelligibility to a very high degree, as well as Polish. Like other Slavic languages, Slovak is a fusional language with a complex system of morphology and relatively flexible word order. Its vocabulary has been extensively influenced by Latin and German and other Slavic languages. The Czech–Slovak group developed within West Slavic in the high medieval period, and the standardization of Czech and Slovak within the Czech–Slovak dialect continuum emerged in the early modern period. In the later mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Language
Hungarian () is an Uralic language spoken in Hungary and parts of several neighbouring countries. It is the official language of Hungary and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Outside Hungary, it is also spoken by Hungarian communities in southern Slovakia, western Ukraine ( Subcarpathia), central and western Romania (Transylvania), northern Serbia (Vojvodina), northern Croatia, northeastern Slovenia (Prekmurje), and eastern Austria. It is also spoken by Hungarian diaspora communities worldwide, especially in North America (particularly the United States and Canada) and Israel. With 17 million speakers, it is the Uralic family's largest member by number of speakers. Classification Hungarian is a member of the Uralic language family. Linguistic connections between Hungarian and other Uralic languages were noticed in the 1670s, and the family itself (then called Finno-Ugric) was established in 1717. Hungarian has traditionally been assigned to the Ugric alo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesus In Christianity
Jesus is called the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God in the Bible's New Testament, and in mainstream Christianity, mainstream Christian denominations he is God the Son, the second Person in the Trinity. He is believed to be the messiah in Judaism, Jewish messiah (the Christ (title), Christ) who is prophesied in the Hebrew Bible, which is called the Old Testament in Christianity. Through Crucifixion of Jesus, his crucifixion and Resurrection of Jesus, subsequent resurrection, God in Christianity, God offered humans Salvation (Christianity), salvation and Eternal life (Christianity), eternal life, that Jesus died to Salvation in Christianity#Atonement, atone for Christian views on sin, sin to make humanity right with God. These teachings emphasize that as the Lamb of God, Jesus chose to suffer nailed to the cross at Calvary as a sign of his obedience to the will of God, as an "agent and servant of God".''The Christology of Anselm of Canterbury'' by Dániel Deme 2004 pages 199- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Language
Portuguese ( or, in full, ) is a western Romance language of the Indo-European language family, originating in the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. It is an official language of Portugal, Brazil, Cape Verde, Angola, Mozambique, Guinea-Bissau and São Tomé and Príncipe, while having co-official language status in East Timor, Equatorial Guinea, and Macau. A Portuguese-speaking person or nation is referred to as " Lusophone" (). As the result of expansion during colonial times, a cultural presence of Portuguese speakers is also found around the world. Portuguese is part of the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia and the County of Portugal, and has kept some Celtic phonology in its lexicon. With approximately 250 million native speakers and 24 million L2 (second language) speakers, Portuguese has approximately 274 million total speakers. It is usually listed as the sixth-most spoken language, the third-most sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)