|
Chondroteuthis
''Chondroteuthis'' is a genus of belemnite, an extinct group of cephalopods. It was found in the Schistes bitumineux of Luxembourg.''Bode, A. (1933). ''Chondroteuthis wunnenbergi'' n.g. n.sp''.'', eine neue Belemnoideenform, in günstiger Erhaltung. ''Sonderabdruck Aus Dem 25 Jahresbericht Des Niedersächsischen Geologischen Vereins Zu Hannover (geologische Abteilung Der Naturhistorischen Gesellschaft Zu Hannover),'' ''25'', 33–66.'' See also * Belemnite * List of belemnites This list of belemnite genera is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the extinct subclass Belemnoidea, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, as we ... References Belemnites {{paleo-cephalopod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belemnite
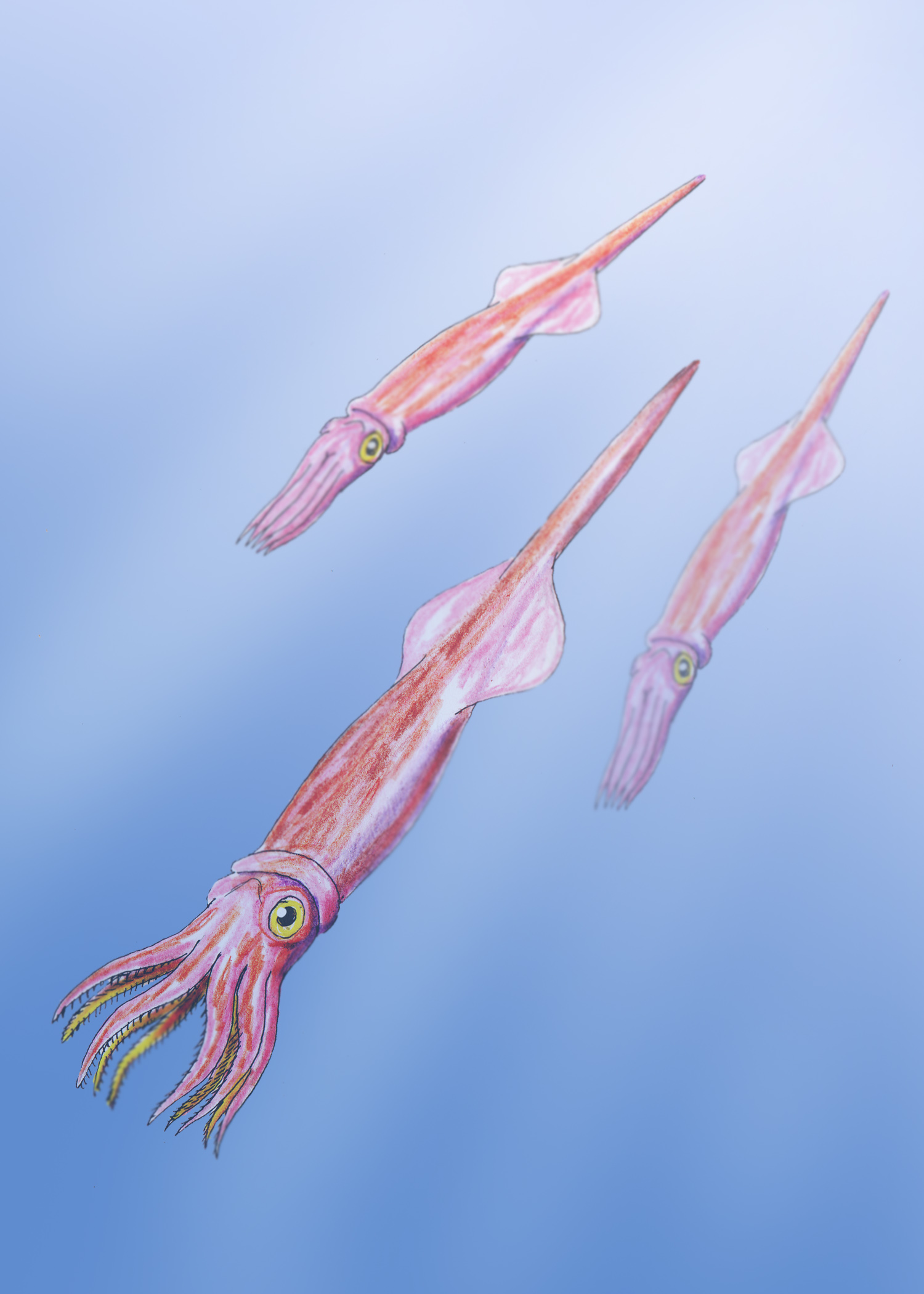
Belemnitida (or the belemnite) is an extinct order of squid-like cephalopods that existed from the Late Triassic to Late Cretaceous. Unlike squid, belemnites had an internal skeleton that made up the cone. The parts are, from the arms-most to the tip: the tongue-shaped pro-ostracum, the conical phragmocone, and the pointy guard. The calcitic guard is the most common belemnite remain. Belemnites, in life, are thought to have had 10 hooked arms and a pair of fins on the guard. The chitinous hooks were usually no bigger than , though a belemnite could have had between 100 and 800 hooks in total, using them to stab and hold onto prey. Belemnites were an important food source for many Mesozoic marine creatures, both the adults and the planktonic juveniles, and likely played an important role in restructuring marine ecosystems after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event. They may have laid between 100 and 1,000 eggs. Some species may have been adapted to speed and swam in the tur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belemnite
Belemnitida (or the belemnite) is an extinct order of squid-like cephalopods that existed from the Late Triassic to Late Cretaceous. Unlike squid, belemnites had an internal skeleton that made up the cone. The parts are, from the arms-most to the tip: the tongue-shaped pro-ostracum, the conical phragmocone, and the pointy guard. The calcitic guard is the most common belemnite remain. Belemnites, in life, are thought to have had 10 hooked arms and a pair of fins on the guard. The chitinous hooks were usually no bigger than , though a belemnite could have had between 100 and 800 hooks in total, using them to stab and hold onto prey. Belemnites were an important food source for many Mesozoic marine creatures, both the adults and the planktonic juveniles, and likely played an important role in restructuring marine ecosystems after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event. They may have laid between 100 and 1,000 eggs. Some species may have been adapted to speed and swam in the tur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Belemnites
This list of belemnite genera is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the extinct subclass Belemnoidea, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, as well as genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful (''nomina dubia''), or were not formally published (''nomina nuda''), as well as junior synonyms of more established names, and genera that are no longer considered belemites. Naming conventions and terminology follow the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature as indicated. The list currently contains 100 generic names. List of belemnites See also * Belemnoidea * List of ammonites * List of nautiloids This list of nautiloids is a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the subclass Nautiloidea, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered in ... References :''Unc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serpukhovian
The Serpukhovian is in the ICS geologic timescale the uppermost stage or youngest age of the Mississippian, the lower subsystem of the Carboniferous. The Serpukhovian age lasted from Ma to Ma. It is preceded by the Visean and is followed by the Bashkirian. The Serpukhovian correlates with the lower part of the Namurian Stage of European stratigraphy and the middle and upper parts of the Chesterian Stage of North American stratigraphy. Name and definition The Serpukhovian Stage was proposed in 1890 by Russian stratigrapher Sergei Nikitin and was introduced in the official stratigraphy of European Russia in 1974. It was named after the city of Serpukhov, near Moscow. The ICS later used the upper Russian subdivisions of the Carboniferous in its international geologic time scale. The base of the Serpukhovian is informally defined by the first appearance of the conodont '' Lochriea ziegleri'', though the utility and systematic stability of this species is not yet certain. N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda (Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of arms or tentacles (muscular hydrostats) modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology. Cephalopods became dominant during the Ordovician period, represented by primitive nautiloids. The class now contains two, only distantly related, extant subclasses: Coleoidea, which includes octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish; and Nautiloidea, represented by ''Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus''. In the Coleoidea, the molluscan shell has been internalized or is absent, whereas in the Nautiloidea, the external shell remains. About 800 living species of cephalopods have been ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schistes Bitumineux
The "Schistes bitumineux" (French for Oil shale/Bituminous shale) is an Early Jurassic geologic formation in Luxembourg that is located within an oil shale, hence the name.Weishampel, et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution." The machimosaurid teleosauroid ''Macrospondylus bollensis'' is known from this formation. This formation may be part of the larger Posidonia Shale The Posidonia Shale (german: Posidonienschiefer, also called Schistes Bitumineux in Luxembourg) geologically known as the Sachrang Formation, is an Early Jurassic (Toarcian) geological formation of southwestern and northeast Germany, northern Swit ...,HENROTAY, M., MARQUES, D., Paicheler, J. C., Gall, J. C., & NEL, A. (1998). Le Toarcien inférieur des régions de Bascharage et de Bettembourg (Grand-Duché du Luxembourg): évidences paléontologiques et sédimentologiques d'environnements restreints proches de l'émersion. ''Geodiversitas'', 20(2), 263-284. which also outcrops in Luxembourg, among other countries. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small landlocked country in Western Europe. It borders Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France to the south. Its capital and most populous city, Luxembourg, is one of the four institutional seats of the European Union (together with Brussels, Frankfurt, and Strasbourg) and the seat of several EU institutions, notably the Court of Justice of the European Union, the highest judicial authority. Luxembourg's culture, people, and languages are highly intertwined with its French and German neighbors; while Luxembourgish is legally the only national language of the Luxembourgish people, French and German are also used in administrative and judicial matters and all three are considered administrative languages of the cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)