|
Chondrocalcinosis
Chondrocalcinosis or cartilage calcification is calcification (accumulation of calcium salts) in hyaline cartilage and/or fibrocartilage.Rothschild, Bruce M It can be seen on radiography. Causes Buildup of calcium phosphate in the ankle joints has been found in about 50% of the general population, and may be associated with osteoarthritis. Another common cause of chondrocalcinosis is calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease (CPPD). CPPD is estimated to affect 4% to 7% of the adult populations of Europe and the United States. This topic last updated: Jul 24, 2018. Previous studies have overestimated the prevalence by simply estimating the prevalence of chondrocalcinosis regardless of cause. A magnesium deficiency may cause chondrocalcinosis, and there is anecdotal evidence that magnesium supplementation may reduce or alleviate symptoms. In some cases, arthritis from injury can cause chondrocalcinosis. Other causes of chondrocalcinosis include: *Hypercalcaemia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
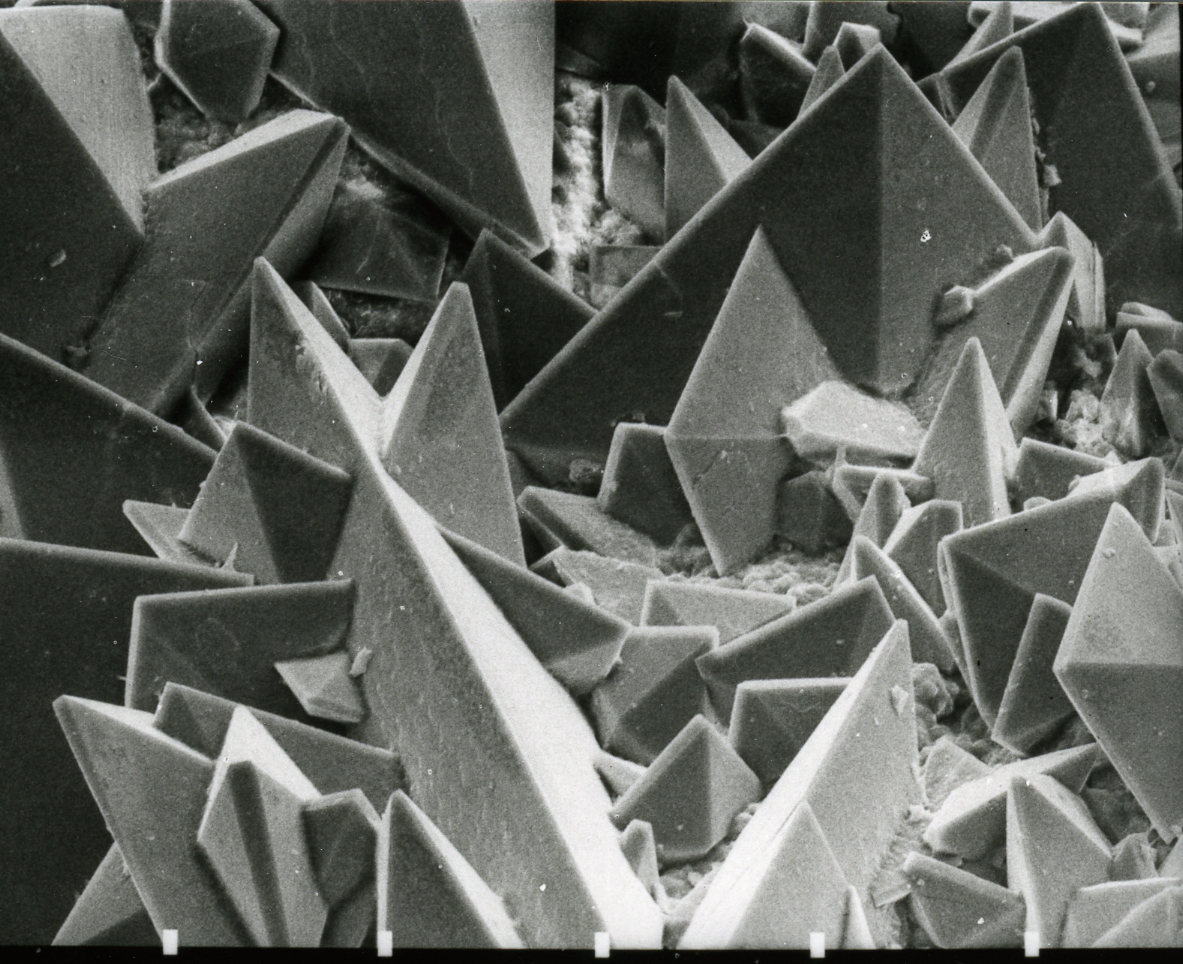
Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate Crystal Deposition Disease
Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate (CPPD) crystal deposition disease, also known as pseudogout and pyrophosphate arthropathy, is a rheumatologic disease which is thought to be secondary to abnormal accumulation of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals within joint soft tissues. The knee joint is most commonly affected. Signs and symptoms When symptomatic, the disease classically begins with symptoms that are similar to a gout attack (thus the moniker "pseudogout"). These include: * severe pain * warmth * swelling of one or more joints The symptoms can be monoarticular (involving a single joint) or polyarticular (involving several joints). Symptoms usually last for days to weeks, and often recur. Although any joint may be affected, the knees, wrists, and hips are most common. X-ray, CT, or other imaging usually shows accumulation of calcium within the joint cartilage, known as chondrocalcinosis. There can also be findings of osteoarthritis.Rothschild, Bruce M The white blood c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypophosphatasia
Hypophosphatasia (; also called deficiency of alkaline phosphatase, phosphoethanolaminuria, or Rathbun's syndrome; sometimes abbreviated HPP) is a rare, and sometimes fatal, inherited metabolic bone disease. Clinical symptoms are heterogeneous, ranging from the rapidly fatal, perinatal variant, with profound skeletal hypomineralization, respiratory compromise or vitamin B6 dependent seizures to a milder, progressive osteomalacia later in life. Tissue non-specific alkaline phosphatase (TNSALP) deficiency in osteoblasts and chondrocytes impairs bone mineralization, leading to rickets or osteomalacia. The pathognomonic finding is subnormal serum activity of the TNSALP enzyme, which is caused by one of 388 genetic mutations identified to date, in the gene encoding TNSALP. Genetic inheritance is autosomal recessive for the perinatal and infantile forms but either autosomal recessive or autosomal dominant in the milder forms. The prevalence of hypophosphatasia is not known; one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate Crystal Deposition Disease
Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate (CPPD) crystal deposition disease, also known as pseudogout and pyrophosphate arthropathy, is a rheumatologic disease which is thought to be secondary to abnormal accumulation of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals within joint soft tissues. The knee joint is most commonly affected. Signs and symptoms When symptomatic, the disease classically begins with symptoms that are similar to a gout attack (thus the moniker "pseudogout"). These include: * severe pain * warmth * swelling of one or more joints The symptoms can be monoarticular (involving a single joint) or polyarticular (involving several joints). Symptoms usually last for days to weeks, and often recur. Although any joint may be affected, the knees, wrists, and hips are most common. X-ray, CT, or other imaging usually shows accumulation of calcium within the joint cartilage, known as chondrocalcinosis. There can also be findings of osteoarthritis.Rothschild, Bruce M The white blood c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projectional Radiography
Projectional radiography, also known as conventional radiography, is a form of radiography and medical imaging that produces two-dimensional images by x-ray radiation. The image acquisition is generally performed by radiographers, and the images are often examined by radiologists. Both the procedure and any resultant images are often simply called "X-ray". Plain radiography or roentgenography generally refers to projectional radiography (without the use of more advanced techniques such as computed tomography that can generate 3D-images). ''Plain radiography'' can also refer to radiography without a radiocontrast agent or radiography that generates single static images, as contrasted to fluoroscopy, which are technically also projectional. Equipment X-ray generator Projectional radiographs generally use X-rays created by X-ray generators, which generate X-rays from X-ray tubes. Grid An anti-scatter grid may be placed between the patient and the detector to reduce the qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism is an increase in parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels in the blood. This occurs from a disorder either within the parathyroid glands ( primary hyperparathyroidism) or as response to external stimuli (secondary hyperparathyroidism). Symptoms of hyperparathyroidism are caused by inappropriately normal or elevated blood calcium leaving the bones and flowing into the blood stream in response to increased production of parathyroid hormone. In healthy people, when blood calcium levels are high, parathyroid hormone levels should be low. With long-standing hyperparathyroidism, the most common symptom is kidney stones. Other symptoms may include bone pain, weakness, depression, confusion, and increased urination. Both primary and secondary may result in osteoporosis (weakening of the bones). In 80% of cases, primary hyperparathyroidism is due to a single benign tumor known as a parathyroid adenoma. Most of the remainder are due to several of these adenomas. Very rar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, although "open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computed Tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry to measure X-ray attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, it can also be used to form images of non-living objects. The 1979 N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projectional Radiography
Projectional radiography, also known as conventional radiography, is a form of radiography and medical imaging that produces two-dimensional images by x-ray radiation. The image acquisition is generally performed by radiographers, and the images are often examined by radiologists. Both the procedure and any resultant images are often simply called "X-ray". Plain radiography or roentgenography generally refers to projectional radiography (without the use of more advanced techniques such as computed tomography that can generate 3D-images). ''Plain radiography'' can also refer to radiography without a radiocontrast agent or radiography that generates single static images, as contrasted to fluoroscopy, which are technically also projectional. Equipment X-ray generator Projectional radiographs generally use X-rays created by X-ray generators, which generate X-rays from X-ray tubes. Grid An anti-scatter grid may be placed between the patient and the detector to reduce the qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
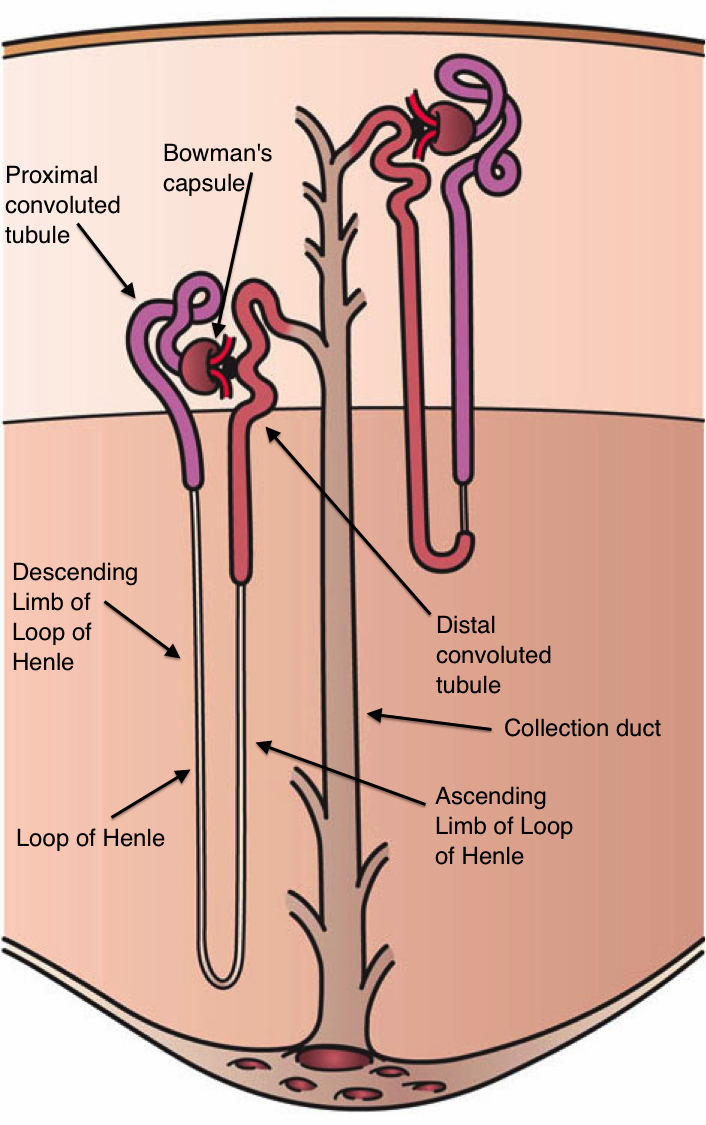
Gitelman Syndrome
Gitelman syndrome (GS) is an autosomal recessive kidney tubule disorder characterized by low blood levels of potassium and magnesium, decreased excretion of calcium in the urine, and elevated blood pH. The disorder is caused by disease-causing variants in both alleles of the ''SLC12A3'' gene''.'' The ''SLC12A3'' gene encodes the thiazide-sensitive sodium-chloride cotransporter (also known as NCC, NCCT, or TSC), which can be found in the distal convoluted tubule of the kidney. The distal convoluted tubule of the kidney plays an important homeostatic role in sodium and chloride absorption as well as of the reabsorption of magnesium and calcium. Genetic mutations of NCC, lead to loss of function and subsequently, reduced transport of sodium and chloride via NCC. Secondary derangement of calcium, magnesium, and potassium concentrations are caused by secondary effects in the distal tubule and collecting duct. The effect is an electrolyte imbalance similar to that seen with thiazide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acromegaly
Acromegaly is a disorder that results from excess growth hormone (GH) after the growth plates have closed. The initial symptom is typically enlargement of the hands and feet. There may also be an enlargement of the forehead, jaw, and nose. Other symptoms may include joint pain, thicker skin, deepening of the voice, headaches, and problems with vision. Complications of the disease may include type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and high blood pressure. Acromegaly is usually caused by the pituitary gland producing excess growth hormone. In more than 95% of cases the excess production is due to a benign tumor, known as a pituitary adenoma. The condition is not inherited from a person's parents. Acromegaly is rarely due to a tumor in another part of the body. Diagnosis is by measuring growth hormone after a person has consumed a glucose solution, or by measuring insulin-like growth factor I in the blood. After diagnosis, medical imaging of the pituitary is carried out to determine i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperoxalemia
Oxalate (IUPAC: ethanedioate) is an anion with the formula C2O42−. This dianion is colorless. It occurs naturally, including in some foods. It forms a variety of salts, for example sodium oxalate (Na2C2O4), and several esters such as dimethyl oxalate (C2O4(CH3)2). It is a conjugate base of oxalic acid. At neutral pH in aqueous solution, oxalic acid converts completely to oxalate. Relationship to oxalic acid The dissociation of protons from oxalic acid proceeds in a stepwise manner; as for other polyprotic acids, loss of a single proton results in the monovalent hydrogenoxalate anion . A salt with this anion is sometimes called an acid oxalate, monobasic oxalate, or hydrogen oxalate. The equilibrium constant ( ''K''a) for loss of the first proton is (p''K''a = 1.27). The loss of the second proton, which yields the oxalate ion, has an equilibrium constant of (p''K''a = 4.28). These values imply, in solutions with neutral pH, no oxalic acid and onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
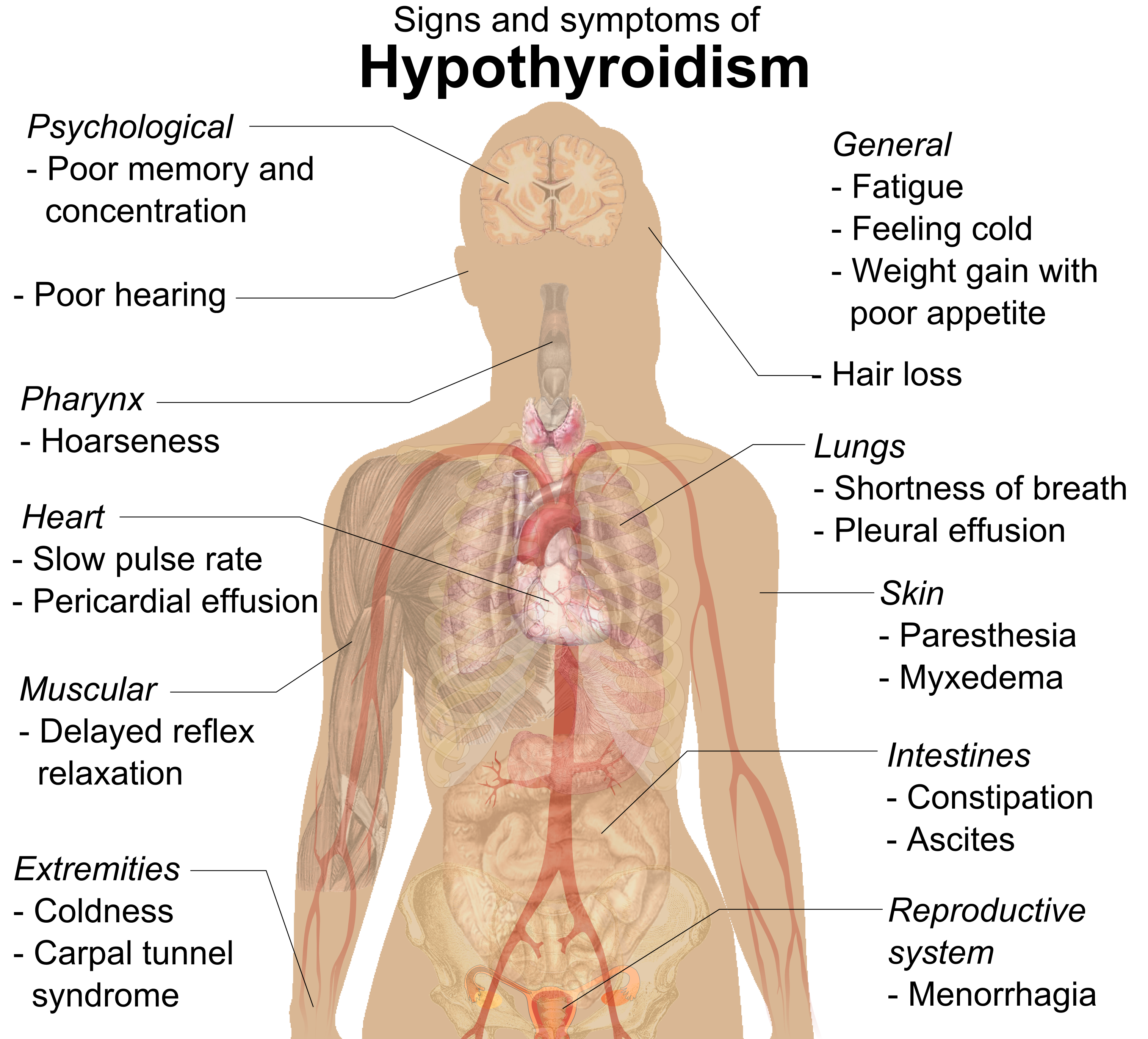
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as poor ability to tolerate cold, a feeling of tiredness, constipation, slow heart rate, depression, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling of the front part of the neck due to goiter. Untreated cases of hypothyroidism during pregnancy can lead to delays in growth and intellectual development in the baby or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome. Worldwide, too little iodine in the diet is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. Hashimoto's thyroiditis is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in countries with sufficient dietary iodine. Less common causes include previous treatment with radioactive iodine, injury to the hypothalamus or the anterior pituitary gland, certain medications, a lack of a functioning t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)