|
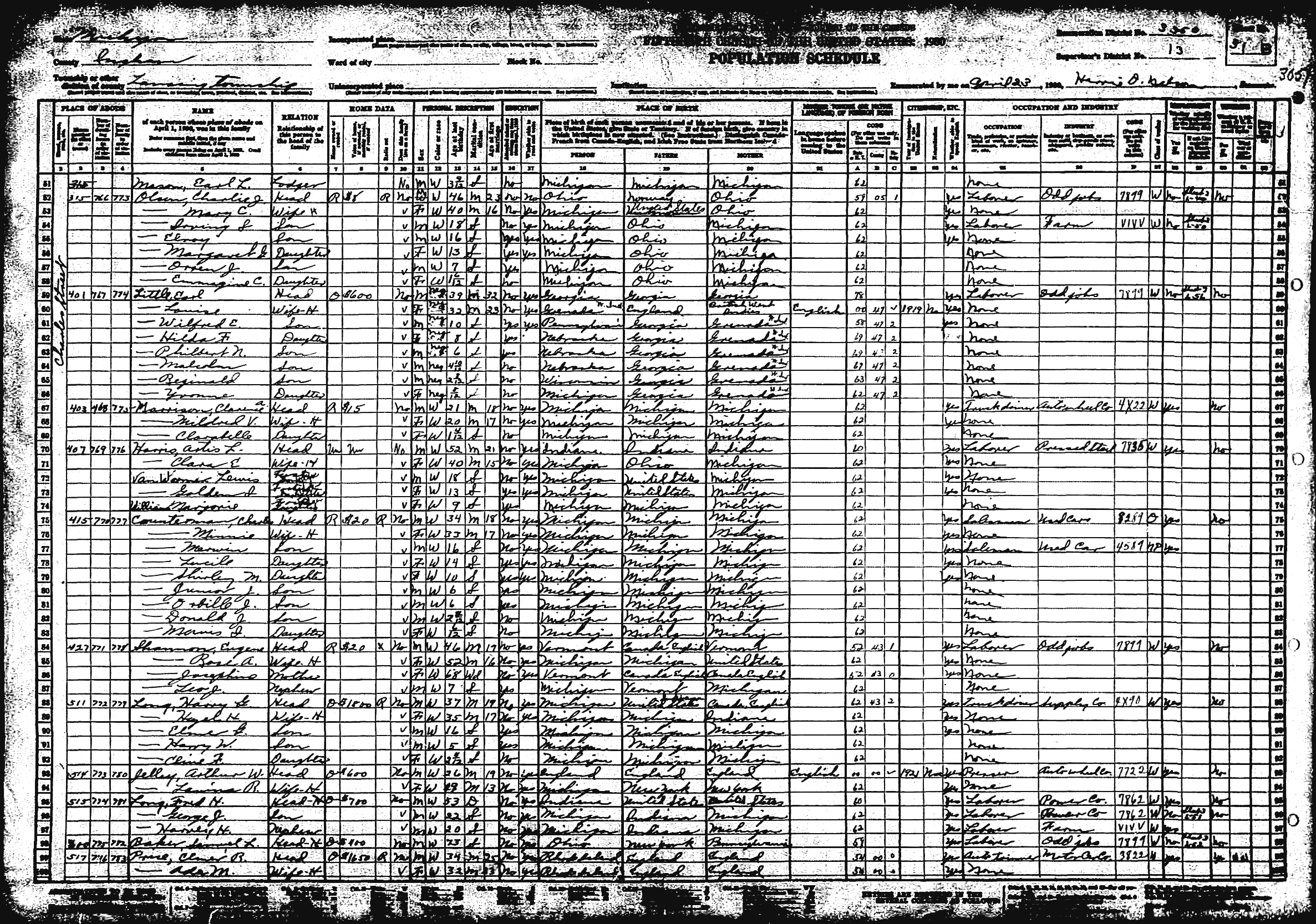
Chokwe Lumumba
Chokwe Lumumba (; August 2, 1947 – February 25, 2014) was an American attorney, activist, and politician, who was affiliated with the black nationalist organization Republic of New Afrika and served as its second vice president. He served as a human rights lawyer in Michigan and Mississippi. In 2013, after serving on the City Council, he was elected as Mayor of Jackson, Mississippi. He was born in Detroit, Michigan, as Edwin Finley Taliaferro, and was raised there. He changed his name in 1969 after joining the Republic of New Afrika. Early life and education He was born in Detroit, Michigan, as Edwin Finley Taliaferro, the second of eight children of Lucien Taliaferro, from Kansas, and Priscilla, from Alabama. Some of his forebears were said to be Cherokee. His parents had each moved to Detroit in the Great Migration of the early 20th century. Raised Catholic, Lumumba attended local Catholic schools. He graduated from St. Theresa High School in Detroit, where he served a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mayors Of Jackson, Mississippi
The post of Mayor of Jackson, Mississippi, was begun in 1834 and was originally referred to as "President of Selectmen" before being changed to "Mayor". The following individuals have held the office: President of Selectmen Mayors See also * Timeline of Jackson, Mississippi References Additional sources *Brinson, Carroll. ''Jackson/A Special Kind of Place.'' Jackson, MS: City of Jackson, 1977. LCCN 77-081145. External linksJackson, MS Mayor's Office - official website {{Mayors of Jackson, Mississippi Mayors of Jackson, Mississippi, Lists of mayors of places in Mississippi, Jackson, Mississippi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
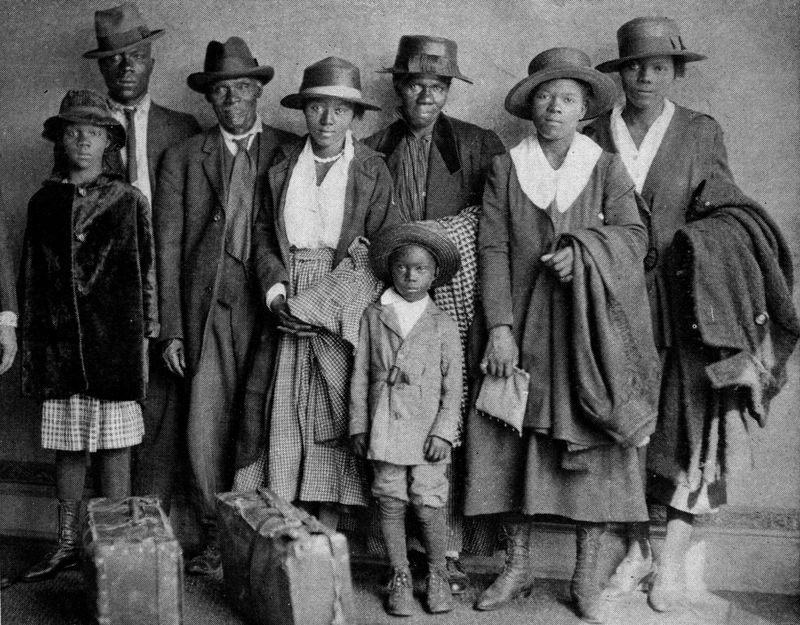
Great Migration (African American)
The Great Migration, sometimes known as the Great Northward Migration or the Black Migration, was the movement of six million African Americans out of the rural Southern United States to the urban Northeast, Midwest, and West between 1910 and 1970. It was caused primarily by the poor economic conditions for African American people, as well as the prevalent racial segregation and discrimination in the Southern states where Jim Crow laws were upheld. In particular, continued lynchings motivated a portion of the migrants, as African Americans searched for social reprieve. The historic change brought by the migration was amplified because the migrants, for the most part, moved to the then-largest cities in the United States (New York City, Chicago, Detroit, Los Angeles, Philadelphia, Cleveland, and Washington, D.C.) at a time when those cities had a central cultural, social, political, and economic influence over the United States. (with excepts from, Gregory, James. The Southe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pontiac, Illinois
Pontiac is a city in Livingston County, Illinois, United States. The population was 11,931 at the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Livingston County. The town is also the setting of the 1984 movie ''Grandview, U.S.A.'' Geography Location Pontiac is located at . According to the 2010 census, Pontiac has a total area of , of which (or 98.22%) is land and (or 1.78%) is water. Most of the land adjacent to Pontiac is farm ground. Pontiac lies on the Vermilion River. On December 4, 1982, Pontiac had the worst flood in the town's history, cresting at 19.16 feet. The most recent flooding occurred on January 9, 2008, cresting at 18.85 feet, the second worst in the town history. Climate History Slow beginnings Pontiac was laid out on 27 July 1837 by Henry Weed and brothers Lucius Young and Seth M. Young. A small group of people gathered at the cabin of Andrew McMillan on the banks of the Vermilion River. Their plan was to create a seat for the newly established county of L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pontiac Correctional Center
Pontiac Correctional Center, established in June 1871, is an Illinois Department of Corrections maximum security prison (Level 1) for adult males in Pontiac, Illinois. The prison also has a medium security unit that houses medium to minimum security inmates and is classified as Level 3. Until the 2011 abolition of the death penalty in Illinois, the prison housed male death row inmates, but had no execution chamber. Inmates were executed at the Tamms Correctional Center. Although the capacity of the prison is 2172, it has an average daily population of approximately 2000 inmates. In May 2008, Governor Rod Blagojevich proposed to shut down the Pontiac facility, with a phase-out plan to take place from January through February 2009. The inmate population would be transferred to the Thomson facility, a newly built maximum security prison, which is also equipped to house segregated inmates. Illinois has since sold Thomson to the Federal Bureau of Prisons. The Pontiac facility is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malcolm X
Malcolm X (born Malcolm Little, later Malik el-Shabazz; May 19, 1925 – February 21, 1965) was an American Muslim minister and human rights activist who was a prominent figure during the civil rights movement. A spokesman for the Nation of Islam until 1964, he was a vocal advocate for Black empowerment and the promotion of Islam within the Black community. A posthumous autobiography, on which he collaborated with Alex Haley, was published in 1965. Malcolm spent his adolescence living in a series of foster homes or with relatives after his father's death and his mother's hospitalization. He committed various crimes, being sentenced to 10 years in prison in 1946 for larceny and burglary. In prison he joined the Nation of Islam (adopting the name MalcolmX to symbolize his unknown African ancestral surname while discarding "the White slavemaster name of 'Little'"), and after his parole in 1952 quickly became one of the organization's most influential leaders. He was the public ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wayne State University Law School
Wayne State University Law School (Wayne Law) is the law school of Wayne State University in Detroit. Wayne Law is located in Midtown, Detroit's Cultural Center. Founded in 1927, the law school offers juris doctor (J.D.), master of laws (LL.M.), online master of studies in law, and minors in law degree programs. Wayne Law's more than 12,000 alumni include judges, justices, law firm partners and government officials working in every major market in the United States and at least 17 countries. History The Law School was founded in 1927 and originally named the Detroit City Law School as part of the City Colleges of Detroit. Allan Campbell served as the Law School's founding dean, which graduated its first class with the bachelor of laws (LL.B.) degree in 1928. The City Colleges of Detroit were renamed Wayne University in 1933. In 1956, the university joined Michigan State University and the University of Michigan as one of the state's three major public research institutions and wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fannie Lou Hamer
Fannie Lou Hamer (; Townsend; October 6, 1917 – March 14, 1977) was an American voting rights, voting and women's rights activist, Community organizing, community organizer, and a leader in the civil rights movement. She was the co-founder and vice-chair of the Mississippi Freedom Democratic Party, Freedom Democratic Party, which she represented at the 1964 Democratic National Convention. Hamer also organized Mississippi's Freedom Summer along with the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC). She was also a co-founder of the National Women's Political Caucus, an organization created to recruit, train, and support women of all races who wish to seek election to government office. Hamer began civil rights activism in 1962, continuing until her health declined nine years later. She was known for her use of spiritual hymnal, hymns and quotes and her resilience in leading the civil rights movement for black women in Mississippi. She was extorted, threatened, harassed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinds County, Mississippi
Hinds County is a county located in the U.S. state of Mississippi. With its county seats (Raymond and the state's capital, Jackson), Hinds is the most populous county in Mississippi with a 2020 census population of 227,742 residents. Hinds County is a central part of the Jackson metropolitan statistical area. It is a professional, educational, business and industrial hub in the state. It is bordered on the northwest by the Big Black River and on the east by the Pearl River. It is one county width away from the Yazoo River and the southern border of the Mississippi Delta. In the 19th century, the rural areas of the county were devoted to cotton plantations worked by enslaved African Americans and depended on agriculture well into the 20th century; from 1877 to 1950, this county had 22 lynchings, the highest number in the state. Mississippi has the highest total number of lynchings of any state. * Clinton Public School District * Hinds County School District (Raymond) * Jackso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of The Congo (Léopoldville)
The Republic of the Congo (french: République du Congo) was a sovereign state in Central Africa, created with the independence of the Belgian Congo in 1960. From 1960 to 1966, the country was also known as Congo-Léopoldville (after its capital) to distinguish it from its northwestern neighbor, which is also called the Republic of the Congo, alternatively known as "Congo-Brazzaville". In 1964, the state's official name was changed to the ''Democratic Republic of the Congo,''"Zaire: Post-Independence Political Development" ''Library of Congress'' but the two countries continued to be distinguished by their capitals; with the renaming of Léopoldville as Kinshasa in 1966, it became also known as Congo-Kinshasa. After Joseph Désiré Mobutu, renamed Mobutu Sese Seko in 1972, com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrice Lumumba
Patrice Émery Lumumba (; 2 July 1925 – 17 January 1961) was a Congolese politician and independence leader who served as the first prime minister of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (then known as the Republic of the Congo) from June until September 1960. A member of the Congolese National Movement (MNC), he led the MNC from 1958 until his execution in January 1961. Ideologically an African nationalist and pan-Africanist, he played a significant role in the transformation of the Congo from a colony of Belgium into an independent republic. Shortly after Congolese independence in 1960, a mutiny broke out in the army, marking the beginning of the Congo Crisis. Lumumba appealed to the United States and the United Nations for help to suppress the Belgian-supported Katangan secessionists led by Moïse Tshombe. Both refused, due to suspicions among the Western world that Lumumba secretly held pro-communist views. These suspicions deepened when Lumumba turned to the Soviet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chokwe People
__NOTOC__ The Chokwe people, known by many other names (including Kioko, Bajokwe, Chibokwe, Kibokwe, Ciokwe, Cokwe or Badjok), are an ethnic group of Central and Southern Africa. They are found primarily in Angola, southwestern parts of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (Kinshasa to Lualaba), and northwestern parts of Zambia.Chowke people , Encyclopædia Britannica Demographics and language Estimated to be about 1.3 million, their language is usually referred to as Chokwe (or Kichokwe, Tshokwe), a |
Western Michigan University
Western Michigan University (Western Michigan, Western or WMU) is a public research university in Kalamazoo, Michigan. It was initially established as Western State Normal School in 1903 by Governor Aaron T. Bliss for the training of teachers. In 1957, G. Mennen Williams signed a bill into law that made Western a university and gave the school its current name of Western Michigan University. Western is one of the eight research universities in the State of Michigan and is classified among "R2: Doctoral Universities – High research activity". The university has seven degree-granting colleges, offering 147 undergraduate degree programs, 73 master's degree programs, 30 doctoral programs, and one specialist degree program. It is governed by an eight-member board of regents whose members are appointed by the governor of Michigan and confirmed by the Michigan Senate for eight-year terms. The university's athletic teams compete in Division I of the National Collegiate Athleti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |