|
Choga (architecture)
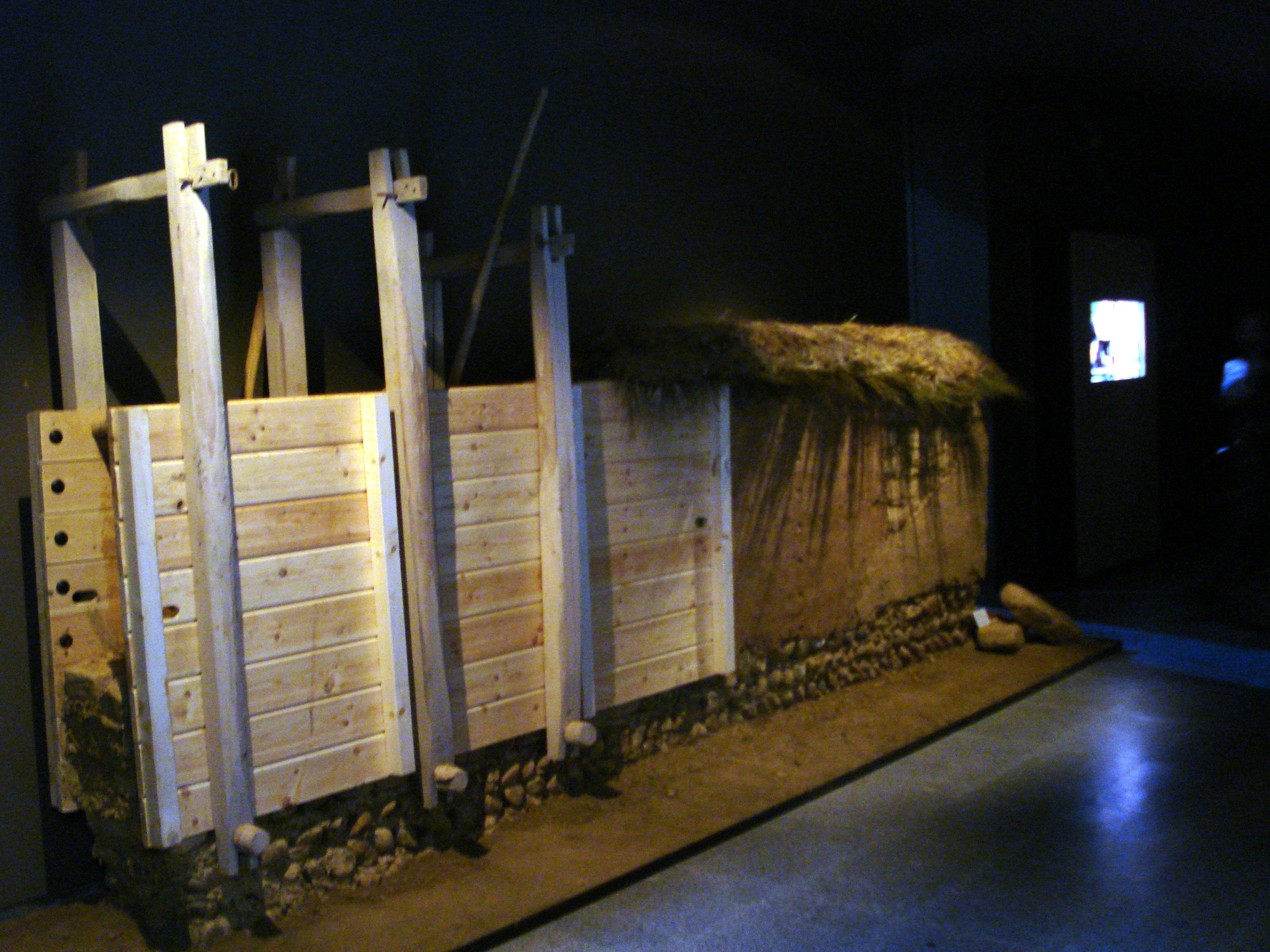
''Choga'' () is a term for traditional Korean houses ('' hanok'') with thatched roofing. The main building materials used to build these houses are straw, wood and soil. Thatched-roofing was especially popular among farmers and low-income classes in traditional Korean society. Certain plants, such as gourds and pumpkins, could be grown on top of ''choga'' roofs. One of the major disadvantages of the materials used, in particular rice straw, was that it could rot quickly when exposed to the elements. ''Choga'' is one of the two classifications of traditional Korean housing. ''Choga'' is named after and characterised by its straw thatched-roof; to be distinguished from ''giwa'', its tiled-roof counterpart. ''Choga'' was the representative housing for the working class in Korea from prehistoric times until mid 20th century. Due to urbanisation and ''choga’s'' nondurable nature, this type of dwelling has been almost entirely replaced in Korea. History The origin of ''choga'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanok
A ''hanok'' () is a traditional Korean house. ''Hanok'' were first designed and built in the 14th century during the Joseon dynasty. Korean architecture considers the positioning of the house in relation to its surroundings, with thought given to the land and seasons. The interior of the house is also planned accordingly. This principle is called ''baesanimsu'' (, ), meaning that the ideal house is built with a mountain in the back and a river in the front. ''Hanok'' shapes differ by region. In the cold northern regions of Korea, ''hanok'' are built in a square with a courtyard in the middle in order to retain heat better. In the south, ''hanok'' are more open and L-shaped. History A ''hanok'' is a Korean house which was developed in Korea, Korean Peninsula and Manchuria. Early Time Paleolithic people in the Korean Peninsula may have occupied caves or made temporary houses. In the Neolithic era, the temporary house developed into a dugout hut. They dug into the ground with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kim Suro
Kim Soo-ro (born Kim Sang-joong on May 7, 1970) is a South Korean actor. Career Early career Kim Soo-ro studied Theater at the Seoul Institute of the Arts and Dongguk University, then joined the Mokwha Repertory Company. In 1993, he made his cinematic debut with a minor role in ''Two Cops'', and became known for being a scene-stealing supporting actor, especially in comedies such as '' The Foul King'', ''Hi! Dharma!'', ''Fun Movie'' and ''S Diary''. With '' Vampire Cop Ricky'' in 2006, Kim began starring in leading roles, and this was followed by the films ''A Bold Family'', '' Our School's E.T.'', '' Death Bell 2: Bloody Camp'', ''The Quiz Show Scandal'', '' Romantic Heaven'', and ''Ghost Sweepers''. He also appeared in the television series ''Master of Study'' and ''A Gentleman's Dignity''. Kim Soo-ro’s Project In 2009, it was ''The Lower Depths'', a play by Maxim Gorky considered to be one of the most important works of Russian Socialist realism Socialist real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hahoe Folk Village
The Hahoe Folk Village (Korean: 안동하회마을) is a traditional village from the Joseon Dynasty, located in Andong, Gyeongsangbuk-do, South Korea. The 'Ha' is short for river and 'hoe' means to 'turn around, return, come back. The village is a valuable part of Korean culture because it preserves Joseon period-style architecture, folk traditions, valuable books, and an old tradition of clan-based villages. It is listed by the South Korean government with UNESCO as a World Heritage Site with Yangdong Folk Village in 2010 and attract around 1 million visitors every year. Overview Founded in the 14th-15th century, Hahoe is one of the most representative historic clan village in South Korea, together with Yangdong. The settlement include residences of head families and clan members, pavilions, Confucian academies and study pavilions that reflect the aristocratic Confuncian culture of the early Joseon. Within the village, six houses out of 124 have been designated as National ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hahoe Folk Village - Panoramio
The Hahoe Folk Village (Korean: 안동하회마을) is a traditional village from the Joseon Dynasty, located in Andong, Gyeongsangbuk-do, South Korea. The 'Ha' is short for river and 'hoe' means to 'turn around, return, come back. The village is a valuable part of Korean culture because it preserves Joseon period-style architecture, folk traditions, valuable books, and an old tradition of clan-based villages. It is listed by the South Korean government with UNESCO as a World Heritage Site with Yangdong Folk Village in 2010 and attract around 1 million visitors every year. Overview Founded in the 14th-15th century, Hahoe is one of the most representative historic clan village in South Korea, together with Yangdong. The settlement include residences of head families and clan members, pavilions, Confucian academies and study pavilions that reflect the aristocratic Confuncian culture of the early Joseon. Within the village, six houses out of 124 have been designated as Nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanok
A ''hanok'' () is a traditional Korean house. ''Hanok'' were first designed and built in the 14th century during the Joseon dynasty. Korean architecture considers the positioning of the house in relation to its surroundings, with thought given to the land and seasons. The interior of the house is also planned accordingly. This principle is called ''baesanimsu'' (, ), meaning that the ideal house is built with a mountain in the back and a river in the front. ''Hanok'' shapes differ by region. In the cold northern regions of Korea, ''hanok'' are built in a square with a courtyard in the middle in order to retain heat better. In the south, ''hanok'' are more open and L-shaped. History A ''hanok'' is a Korean house which was developed in Korea, Korean Peninsula and Manchuria. Early Time Paleolithic people in the Korean Peninsula may have occupied caves or made temporary houses. In the Neolithic era, the temporary house developed into a dugout hut. They dug into the ground with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
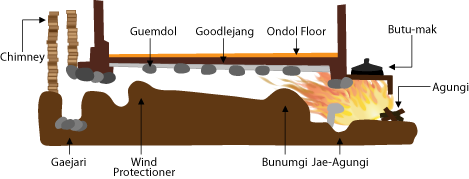
Ondol
Ondol (; , Hangul: 온돌, 溫堗, ) or gudeul (Hangul: 구들, ) in Korean traditional architecture, is underfloor heating that uses direct heat transfer from wood smoke to heat the underside of a thick masonry floor. In modern usage it refers to any type of underfloor heating, or to a hotel or a sleeping room in Korean (as opposed to Western) style. The main components of the traditional ''ondol'' are an ''agungi'' (firebox or stove) accessible from an adjoining room (typically kitchen or master bedroom), a raised masonry floor underlain by horizontal smoke passages, and a vertical, freestanding chimney on the opposite exterior wall providing a draft. The heated floor, supported by stone piers or baffles to distribute the smoke, is covered by stone slabs, clay and an impervious layer such as oiled paper. History Origin Use of the ''ondol'' has been found at archaeological sites in present-day North Korea. A Neolithic Age archaeological site, circa 5000 BC, discovered in Unggi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rammed Earth
Rammed earth is a technique for constructing foundations, floors, and walls using compacted natural raw materials such as earth, chalk, lime, or gravel. It is an ancient method that has been revived recently as a sustainable building method. Under its French name of pisé it is also a material for sculptures, usually small and made in molds. It has been especially used in Central Asia and Tibetan art, and sometimes in China. Edifices formed of rammed earth are on every continent except Antarctica, in a range of environments including temperate, wet, semiarid desert, montane, and tropical regions. The availability of suitable soil and a building design appropriate for local climatic conditions are the factors that favour its use. The French term "pisé de terre" or "terre pisé" was sometimes used in English for architectural uses, especially in the 19th century. The process Making rammed earth involves compacting a damp mixture of subsoil that has suitable proportions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wattle And Daub
Wattle and daub is a composite building method used for making walls and buildings, in which a woven lattice of wooden strips called wattle is daubed with a sticky material usually made of some combination of wet soil, clay, sand, animal dung and straw. Wattle and daub has been used for at least 6,000 years and is still an important construction method in many parts of the world. Many historic buildings include wattle and daub construction. History The wattle and daub technique was used already in the Neolithic period. It was common for houses of Linear pottery and Rössen cultures of middle Europe, but is also found in Western Asia (Çatalhöyük, Shillourokambos) as well as in North America (Mississippian culture) and South America (Brazil). In Africa it is common in the architecture of traditional houses such as those of the Ashanti people. Its usage dates back at least 6,000 years. There are suggestions that construction techniques such as lath and plaster and even cob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korea South Traditional House
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic of Korea) comprising its southern half. Korea consists of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and several minor islands near the peninsula. The peninsula is bordered by China to the northwest and Russia to the northeast. It is separated from Japan to the east by the Korea Strait and the Sea of Japan (East Sea). During the first half of the 1st millennium, Korea was divided between three states, Goguryeo, Baekje, and Silla, together known as the Three Kingdoms of Korea. In the second half of the 1st millennium, Silla defeated and conquered Baekje and Goguryeo, leading to the " Unified Silla" period. Meanwhile, Balhae formed in the north, superseding former Goguryeo. Unified Silla eventually collapsed into three separate states due to civil w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms () from 220 to 280 AD was the tripartite division of China among the dynastic states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. The Three Kingdoms period was preceded by the Han dynasty#Eastern Han, Eastern Han dynasty and was followed by the Jin dynasty (266–420), Western Jin dynasty. The short-lived state of Yan (Three Kingdoms), Yan on the Liaodong Peninsula, which lasted from 237 to 238, is sometimes considered as a "4th kingdom". Academically, the period of the Three Kingdoms refers to the period between the establishment of Cao Wei in 220 and the Conquest of Wu by Jin, conquest of the Eastern Wu by the Western Jin in 280. The earlier, "unofficial" part of the period, from 184 to 220, was marked by chaotic infighting between warlords in various parts of China during the end of the Han dynasty, downfall of the Eastern Han dynasty. The middle part of the period, from 220 to 263, was marked by a more militarily stable arrangement between three rival states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thatching
Thatching is the craft of building a roof with dry vegetation such as straw, water reed, sedge (''Cladium mariscus''), rushes, heather, or palm branches, layering the vegetation so as to shed water away from the inner roof. Since the bulk of the vegetation stays dry and is densely packed—trapping air—thatching also functions as insulation. It is a very old roofing method and has been used in both tropical and temperate climates. Thatch is still employed by builders in developing countries, usually with low-cost local vegetation. By contrast, in some developed countries it is the choice of some affluent people who desire a rustic look for their home, would like a more ecologically friendly roof, or who have purchased an originally thatched abode. History Thatching methods have traditionally been passed down from generation to generation, and numerous descriptions of the materials and methods used in Europe over the past three centuries survive in archives and early publica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic Architecture
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)


