|
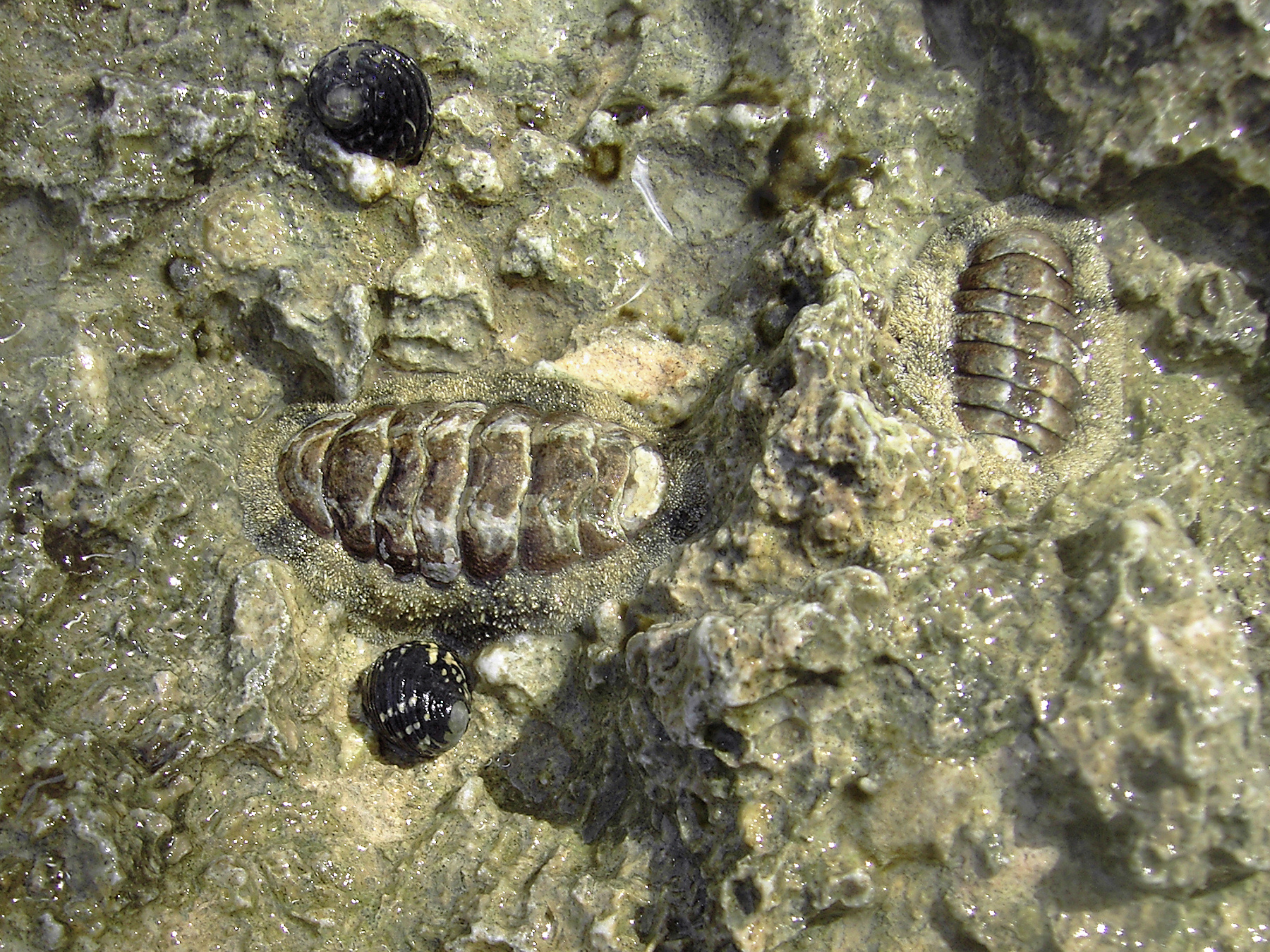
Chitons Described In 1835
Chitons () are marine molluscs of varying size in the class Polyplacophora (), formerly known as Amphineura. About 940 extant and 430 fossil species are recognized. They are also sometimes known as gumboots or sea cradles or coat-of-mail shells or suck-rocks, or more formally as loricates, polyplacophorans, and occasionally as polyplacophores. Chitons have a shell composed of eight separate shell plates or valves. These plates overlap slightly at the front and back edges, and yet articulate well with one another. Because of this, the shell provides protection at the same time as permitting the chiton to flex upward when needed for locomotion over uneven surfaces, and even allows the animal to curl up into a ball when dislodged from rocks. The shell plates are encircled by a skirt known as a girdle. Habitat Chitons live worldwide, from cold waters through to the tropics. They live on hard surfaces, such as on or under rocks, or in rock crevices. Some species live quite hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonicella Lineata
''Tonicella lineata'', commonly known as the lined chiton, is a species of chiton from the North Pacific. Size and description ''Tonicella lineata'' is a very colorful chiton, having blue, purple or black straight or zig-zag lines on each of the eight valves. The background color of the valves is often brown or red, but can also be bright blue or yellow to orange. The girdle is hairless and brown to red or pink, often with regular yellow or white patches. This species grows to 5 cm in length. Similar species ''Tonicella lokii'' is extremely similar but has radiating bands on the girdle. ''Tonicella undocaerulea'' is very similar but lacks a dark border to the concentric blue lines on the anterior plate. ''Mopalia spectabilis'' looks superficially similar due to its bright blue wavy lines on the valves, but has a hairy girdle.Baldwin, A. (2007). Illustrated Keys to the chitons (Polyplacophora). Accessed from: It can also be confused with ''Tonicella insignis'' ( Reeve, 184 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsum (biology)
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek language, Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axis, anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
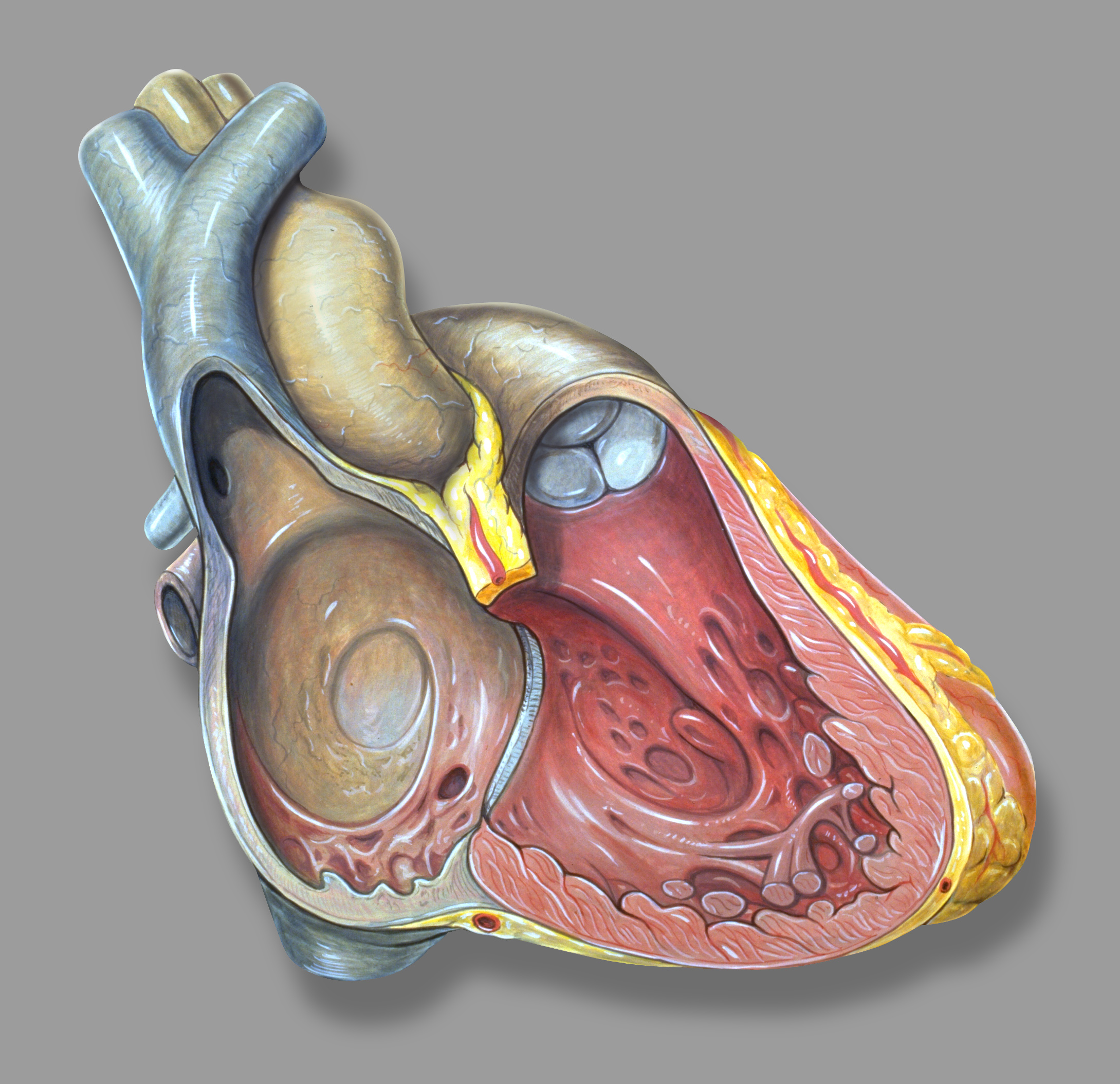
Atrium (heart)
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves. There are two atria in the human heart – the left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary circulation, and the right atrium receives blood from the venae cavae of the systemic circulation. During the cardiac cycle the atria receive blood while relaxed in diastole, then contract in systole to move blood to the ventricles. Each atrium is roughly cube-shaped except for an ear-shaped projection called an atrial appendage, sometimes known as an auricle. All animals with a closed circulatory system have at least one atrium. The atrium was formerly called the 'auricle'. That term is still used to describe this chamber in some other animals, such as the ''Mollusca''. They have thicker muscular walls than the atria do. Structure Humans have a four-chambered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
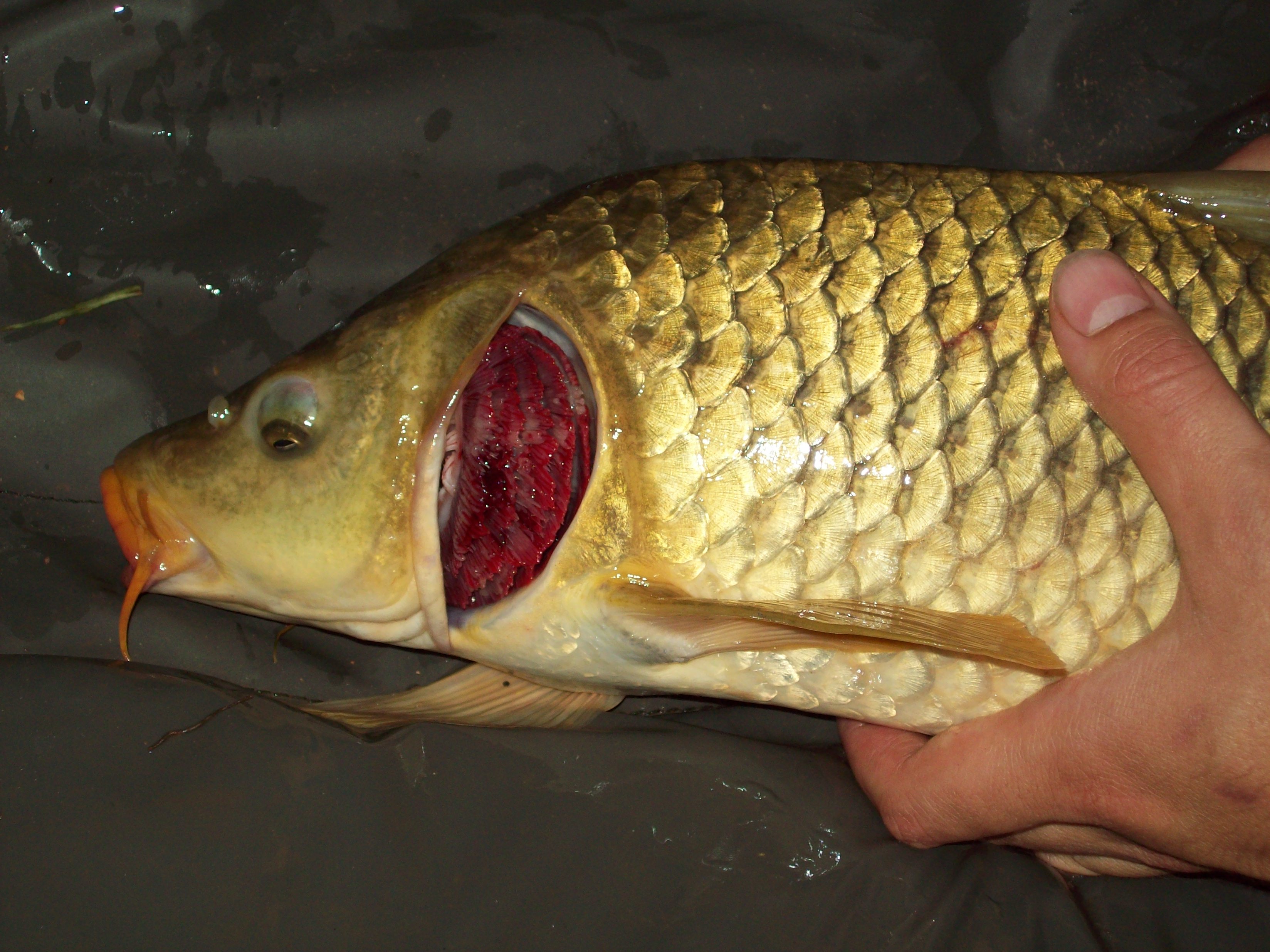
Gill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are kept moist. The microscopic structure of a gill presents a large surface area to the external environment. Branchia (pl. branchiae) is the zoologists' name for gills (from Ancient Greek ). With the exception of some aquatic insects, the filaments and lamellae (folds) contain blood or coelomic fluid, from which gases are exchanged through the thin walls. The blood carries oxygen to other parts of the body. Carbon dioxide passes from the blood through the thin gill tissue into the water. Gills or gill-like organs, located in different parts of the body, are found in various groups of aquatic animals, including mollusks, crustaceans, insects, fish, and amphibians. Semiterrestrial marine animals such as crabs and mudskippers have gill cham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anus
The anus (Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is an opening at the opposite end of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to control the expulsion of feces, the residual semi-solid waste that remains after food digestion, which, depending on the type of animal, includes: matter which the animal cannot digest, such as bones; Summary at food material after the nutrients have been extracted, for example cellulose or lignin; ingested matter which would be toxic if it remained in the digestive tract; and dead or excess gut bacteria and other endosymbionts. Amphibians, reptiles, and birds use the same orifice (known as the cloaca) for excreting liquid and solid wastes, for copulation and egg-laying. Monotreme mammals also have a cloaca, which is thought to be a feature inherited from the earliest amniotes via the therapsids. Marsupials have a single orifice for excreting both solids and liquids and, in females, a separate vagina for reproduction. Female placental mamm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantle (mollusc)
The mantle (also known by the Latin word pallium meaning mantle, robe or cloak, adjective pallial) is a significant part of the anatomy of molluscs: it is the dorsal body wall which covers the visceral mass and usually protrudes in the form of flaps well beyond the visceral mass itself. In many species of molluscs the epidermis of the mantle secretes calcium carbonate and conchiolin, and creates a shell. In sea slugs there is a progressive loss of the shell and the mantle becomes the dorsal surface of the animal. The words mantle and pallium both originally meant cloak or cape, see mantle (vesture). This anatomical structure in molluscs often resembles a cloak because in many groups the edges of the mantle, usually referred to as the ''mantle margin'', extend far beyond the main part of the body, forming flaps, double-layered structures which have been adapted for many different uses, including for example, the siphon. Mantle cavity The ''mantle cavity'' is a central fea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snail
A snail is, in loose terms, a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name ''snail'' is also used for most of the members of the molluscan class Gastropoda that have a coiled shell that is large enough for the animal to retract completely into. When the word "snail" is used in this most general sense, it includes not just land snails but also numerous species of sea snails and freshwater snails. Gastropods that naturally lack a shell, or have only an internal shell, are mostly called '' slugs'', and land snails that have only a very small shell (that they cannot retract into) are often called ''semi-slugs''. Snails have considerable human relevance, including as food items, as pests, and as vectors of disease, and their shells are used as decorative objects and are incorporated into jewelry. The snail has also had some cultural significance, tending to be associated with lethargy. The sn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanleya
''Hanleya'' is a genus of polyplacophoran molluscs known from Oligocene and Miocene The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ... fossils; it is represented today by a number of species including '' H. sinica'' Xu 1990 (China), '' H. brachyplax'' (Brazil) and ''H. hanleyi'' Bean in Thorpe, 1844 (Chile), which feeds on sponges. References Prehistoric chiton genera Chiton genera Oligocene genus first appearances Miocene genus extinctions {{paleo-mollusc-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engrailed (gene)
''engrailed'' is a homeodomain transcription factor involved in many aspects of multicellular development. First known for its role in arthropod embryological development, working in consort with the Hox genes, ''engrailed'' has been found to be important in other areas of development. It has been identified in many bilaterians, including the arthropods, vertebrates, echinoderms, molluscs, nematodes, brachiopods, and polychaetes. It acts as a "selector" gene, conferring a specific identity to defined areas of the body, and co-ordinating the expression of downstream genes. Protein ''engrailed (en)'' encodes the homeodomain-containing transcription factor protein Engrailed. Homologous Engrailed proteins are found in a diversity of organisms. When expressed in the ectoderm, ''engrailed'' is involved in the production of skeletal material. ''engrailed'', or genes with very similar sequences, are found in all bilaterian animals. ''engrailed'' plays a number of crucial roles in brai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthochitona Garnoti
''Acanthochitona garnoti'', the spiny chiton, is a medium-sized polyplacophoran mollusc in the family Acanthochitonidae, found on the coast of southern Africa. Description This species is conspicuous for the nine paired tufts or rosettes of long glassy spines that decorate its girdle. Between the tufts, the girdle bears many smaller spicules. The spicules are sharp, and if carelessly handled, easily penetrate the human skin, where they detach and remain, becoming painfully irritating. The valves are of a dull brown color and marked with oblique pale stripes. They are largely concealed by the girdle. Adult size is 30–45 mm. Distribution and habitat ''A. garnoti'' occurs along the south coast of Africa, from Cape Columbine in Namibia to the south coast of KwaZulu-Natal in South Africa South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with water (hydrolysis) using amylase enzymes as catalyst, which produces constituent sugars (monosaccharides, or oligosaccharides). They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Examples include storage polysaccharides such as starch, glycogen and galactogen and structural polysaccharides such as cellulose and chitin. Polysaccharides are often quite heterogeneous, containing slight modifications of the repeating unit. Depending on the structure, these macromolecules can have distinct properties from their monosaccharide building blocks. They may be amorphous or even insoluble in water. When all the monosaccharides in a polysaccharide are the same type, the polysaccharide is called a homopolysaccharide or homoglycan, but when more t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiton Shell
Chitons () are marine molluscs of varying size in the class Polyplacophora (), formerly known as Amphineura. About 940 extant and 430 fossil species are recognized. They are also sometimes known as gumboots or sea cradles or coat-of-mail shells or suck-rocks, or more formally as loricates, polyplacophorans, and occasionally as polyplacophores. Chitons have a shell composed of eight separate shell plates or valves. These plates overlap slightly at the front and back edges, and yet articulate well with one another. Because of this, the shell provides protection at the same time as permitting the chiton to flex upward when needed for locomotion over uneven surfaces, and even allows the animal to curl up into a ball when dislodged from rocks. The shell plates are encircled by a skirt known as a girdle. Habitat Chitons live worldwide, from cold waters through to the tropics. They live on hard surfaces, such as on or under rocks, or in rock crevices. Some species live quite hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |