|
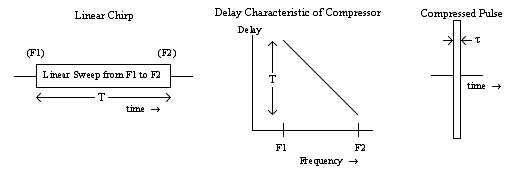
Chirp Compression
The chirp pulse compression process transforms a long duration frequency-coded pulse into a narrow pulse of greatly increased amplitude. It is a technique used in radar and sonar systems because it is a method whereby a narrow pulse with high peak power can be derived from a long duration pulse with low peak power. Furthermore, the process offers good range resolution because the half-power beam width of the compressed pulse is consistent with the system bandwidth. The basics of the method for radar applications were developed in the late 1940s and early 1950s, but it was not until 1960, following declassification of the subject matter, that a detailed article on the topic appeared the public domain.Klauder J. R., Price A. C., Darlington S. and Albersheim W. J., "The Theory and Design of Chirp Radars", BSTJ Vol. 39, July 1960, pp. 745–808 Thereafter, the number of published articles grew quickly, as demonstrated by the comprehensive selection of papers to be found in a compilati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse Compression
Pulse compression is a signal processing technique commonly used by radar, sonar and echography to increase the range resolution as well as the signal to noise ratio. This is achieved by modulating the transmitted pulse and then correlating the received signal with the transmitted pulse. Simple pulse Signal description The simplest signal a pulse radar can transmit is a sinusoidal-amplitude pulse, A and carrier frequency, f_0, truncated by a rectangular function of width, T. The pulse is transmitted periodically, but that is not the main topic of this article; we will consider only a single pulse, s. If we assume the pulse to start at time t=0, the signal can be written the following way, using the complex notation: :s(t) = \begin A e^ &\text \; 0 \leq t where it reaches its maximum 1, and it decreases linearly on ,\frac{1}{2}/math> until it reaches 0 again. Figures at the end of this paragraph show the shape of the intercorrelation for a sample signal (in red), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convolution
In mathematics (in particular, functional analysis), convolution is a operation (mathematics), mathematical operation on two function (mathematics), functions ( and ) that produces a third function (f*g) that expresses how the shape of one is modified by the other. The term ''convolution'' refers to both the result function and to the process of computing it. It is defined as the integral of the product of the two functions after one is reflected about the y-axis and shifted. The choice of which function is reflected and shifted before the integral does not change the integral result (see #Properties, commutativity). The integral is evaluated for all values of shift, producing the convolution function. Some features of convolution are similar to cross-correlation: for real-valued functions, of a continuous or discrete variable, convolution (f*g) differs from cross-correlation (f \star g) only in that either or is reflected about the y-axis in convolution; thus it is a cross-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compressed Pulses, TB=250,25, Far Out Slobes
Compression may refer to: Physical science *Compression (physics), size reduction due to forces *Compression member, a structural element such as a column *Compressibility, susceptibility to compression *Gas compression *Compression ratio, of a combustion engine *Compression (geology) *Compression or compressive strength Information science *Data compression, reducing the data required for information *Audio compression (data), reducing the data required for audio *Bandwidth compression *Compression artifact, defect in data due to compression *Image compression, of digital images *Video compression *One-way compression function, a cryptographic primitive *Dynamic range compression, reducing audio dynamic range Medicine *Brain compression, a medical condition * Compression bandage *Pressing on the lower abdominal area in an intravenous pyelogram *Cold compression therapy, for minor injuries Other *Amplifier gain compression, due to nonlinearity *Compression (dance), several techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse Width Versus Sidelobe Level For Several Weighting Functions
In medicine, a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle (heartbeat) by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the neck (carotid artery), wrist (radial artery), at the groin (femoral artery), behind the knee (popliteal artery), near the ankle joint (posterior tibial artery), and on foot (dorsalis pedis artery). Pulse (or the count of arterial pulse per minute) is equivalent to measuring the heart rate. The heart rate can also be measured by listening to the heart beat by auscultation, traditionally using a stethoscope and counting it for a minute. The radial pulse is commonly measured using three fingers. This has a reason: the finger closest to the heart is used to occlude the pulse pressure, the middle finger is used get a crude estimate of the blood pressure, and the finger most distal to the heart (usually the ring finger) is used to nullify the effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compressed Chirps, TB=250, Without & With Hamming, In Detail
Compression may refer to: Physical science *Compression (physics), size reduction due to forces *Compression member, a structural element such as a column *Compressibility, susceptibility to compression *Gas compression *Compression ratio, of a combustion engine *Compression (geology) *Compression or compressive strength Information science *Data compression, reducing the data required for information *Audio compression (data), reducing the data required for audio *Bandwidth compression *Compression artifact, defect in data due to compression *Image compression, of digital images *Video compression *One-way compression function, a cryptographic primitive *Dynamic range compression, reducing audio dynamic range Medicine *Brain compression, a medical condition * Compression bandage *Pressing on the lower abdominal area in an intravenous pyelogram *Cold compression therapy, for minor injuries Other *Amplifier gain compression, due to nonlinearity *Compression (dance), several techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compressed Pulse, TB=250, Without & With Hamming
Compression may refer to: Physical science *Compression (physics), size reduction due to forces *Compression member, a structural element such as a column *Compressibility, susceptibility to compression *Gas compression *Compression ratio, of a combustion engine *Compression (geology) *Compression or compressive strength Information science *Data compression, reducing the data required for information *Audio compression (data), reducing the data required for audio *Bandwidth compression *Compression artifact, defect in data due to compression *Image compression, of digital images *Video compression *One-way compression function, a cryptographic primitive *Dynamic range compression, reducing audio dynamic range Medicine *Brain compression, a medical condition * Compression bandage *Pressing on the lower abdominal area in an intravenous pyelogram *Cold compression therapy, for minor injuries Other *Amplifier gain compression, due to nonlinearity *Compression (dance), several techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chirp Spectra, TB=250, Without & With Weighting
A chirp is a signal in which the frequency increases (''up-chirp'') or decreases (''down-chirp'') with time. In some sources, the term ''chirp'' is used interchangeably with sweep signal. It is commonly applied to sonar, radar, and laser systems, and to other applications, such as in spread-spectrum communications (see chirp spread spectrum). This signal type is biologically inspired and occurs as a phenomenon due to dispersion (a non-linear dependence between frequency and the propagation speed of the wave components). It is usually compensated for by using a matched filter, which can be part of the propagation channel. Depending on the specific performance measure, however, there are better techniques both for radar and communication. Since it was used in radar and space, it has been adopted also for communication standards. For automotive radar applications, it is usually called linear frequency modulated waveform (LFMW). In spread-spectrum usage, surface acoustic wave (SAW) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Window Functions
A window is an opening in a wall, door, roof, or vehicle that allows the exchange of light and may also allow the passage of sound and sometimes air. Modern windows are usually glazed or covered in some other transparent or translucent material, a sash set in a frame in the opening; the sash and frame are also referred to as a window. Many glazed windows may be opened, to allow ventilation, or closed, to exclude inclement weather. Windows may have a latch or similar mechanism to lock the window shut or to hold it open by various amounts. In addition to this, many modern day windows may have a window screen or mesh, often made of aluminum or fibreglass, to keep bugs out when the window is opened. Types include the eyebrow window, fixed windows, hexagonal windows, single-hung, and double-hung sash windows, horizontal sliding sash windows, casement windows, awning windows, hopper windows, tilt, and slide windows (often door-sized), tilt and turn windows, transom windows, si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weighting Function
A weight function is a mathematical device used when performing a sum, integral, or average to give some elements more "weight" or influence on the result than other elements in the same set. The result of this application of a weight function is a weighted sum or weighted average. Weight functions occur frequently in statistics and analysis, and are closely related to the concept of a measure. Weight functions can be employed in both discrete and continuous settings. They can be used to construct systems of calculus called "weighted calculus" and "meta-calculus".Jane Grossma''Meta-Calculus: Differential and Integral'' , 1981. Discrete weights General definition In the discrete setting, a weight function w \colon A \to \R^+ is a positive function defined on a discrete set A, which is typically finite or countable. The weight function w(a) := 1 corresponds to the ''unweighted'' situation in which all elements have equal weight. One can then apply this weight to various con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compressed Pulses For TB=100,25
Compression may refer to: Physical science *Compression (physics), size reduction due to forces *Compression member, a structural element such as a column *Compressibility, susceptibility to compression *Gas compression *Compression ratio, of a combustion engine *Compression (geology) *Compression or compressive strength Information science *Data compression, reducing the data required for information *Audio compression (data), reducing the data required for audio *Bandwidth compression *Compression artifact, defect in data due to compression *Image compression, of digital images *Video compression *One-way compression function, a cryptographic primitive *Dynamic range compression, reducing audio dynamic range Medicine *Brain compression, a medical condition * Compression bandage *Pressing on the lower abdominal area in an intravenous pyelogram *Cold compression therapy, for minor injuries Other *Amplifier gain compression, due to nonlinearity *Compression (dance), several techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compressed Pulses For TB=1000,250
Compression may refer to: Physical science *Compression (physics), size reduction due to forces *Compression member, a structural element such as a column *Compressibility, susceptibility to compression *Gas compression *Compression ratio, of a combustion engine *Compression (geology) *Compression or compressive strength Information science *Data compression, reducing the data required for information *Audio compression (data), reducing the data required for audio *Bandwidth compression *Compression artifact, defect in data due to compression *Image compression, of digital images *Video compression *One-way compression function, a cryptographic primitive *Dynamic range compression, reducing audio dynamic range Medicine *Brain compression, a medical condition * Compression bandage *Pressing on the lower abdominal area in an intravenous pyelogram *Cold compression therapy, for minor injuries Other *Amplifier gain compression, due to nonlinearity *Compression (dance), several techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fast Fourier Transform
A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is an algorithm that computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of a sequence, or its inverse (IDFT). Fourier analysis converts a signal from its original domain (often time or space) to a representation in the frequency domain and vice versa. The DFT is obtained by decomposing a sequence of values into components of different frequencies. This operation is useful in many fields, but computing it directly from the definition is often too slow to be practical. An FFT rapidly computes such transformations by factorizing the DFT matrix into a product of sparse (mostly zero) factors. As a result, it manages to reduce the complexity of computing the DFT from O\left(N^2\right), which arises if one simply applies the definition of DFT, to O(N \log N), where N is the data size. The difference in speed can be enormous, especially for long data sets where ''N'' may be in the thousands or millions. In the presence of round-off error, many FFT algorithm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |