|
Chinese Skullcap
''Scutellaria baicalensis'', with the common name Baikal skullcap or Chinese skullcap, is a species of flowering plant in the family Lamiaceae. Distribution The plant is native to China, Korea, Mongolia, and Russia in the Russian Far East and Siberia. Medicinal plant Traditional Chinese medicine It is one of the 50 fundamental herbs used in traditional Chinese medicine, where it has the name ''huángqín'' (). As a Chinese traditional medicine, ''huang qin'' usually refers to the dried root of ''S. baicalensis'' Georgi, ''S. viscidula'' Bge., ''S. amoena'' C.H. Wright, and ''S. ikoninkovii'' Ju. Its use in TCM is for "the prophylaxis and treatment of hepatitis, atherosclerosis, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, type 2 diabetes, dysentery, ulcerative colitis, and respiratory disorders." Pharmacology Several chemical compounds have been isolated from the root; baicalein, baicalin, wogonin, norwogonin, oroxylin A and β-sitosterol are the major ones. Names It is impor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Gottlieb Georgi
Johann Gottlieb Georgi (31 December 1729 – 27 October 1802) was a German botanist, naturalist and geographer. A native of Pomerania, Georgi accompanied both Johan Peter Falk and Peter Simon Pallas on their respective journeys through Siberia. During 1770-1774 he travelled on its behalf to Astrakhan, the Urals, Bashkir, the Barabinsk steppe, the Kolyvanskoe silver mines (to assess the ore content), Altai, Tomsk, Irkutsk, Baikal, and Dauren. In 1783 he became an academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences in St Petersburg. Georgi was particularly interested in the Baikal region. Based on collections from far eastern Russia, in his 1775 publication ''Bemerkungen einer Reise im Russischen Reich im Jahre 1772'', Georgi provided the first botanical descriptions of many of the region's flowering plants, among them the Baikal skullcap (''Scutellaria baicalensis''). Many of these plants and herbs were later collected by European botanists in China, and thereafter became rare sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a long-term condition that results in inflammation and ulcers of the colon and rectum. The primary symptoms of active disease are abdominal pain and diarrhea mixed with blood (hematochezia). Weight loss, fever, and anemia may also occur. Often, symptoms come on slowly and can range from mild to severe. Symptoms typically occur intermittently with periods of no symptoms between flares. Complications may include abnormal dilation of the colon (megacolon), inflammation of the eye, joints, or liver, and colon cancer. The cause of UC is unknown. Theories involve immune system dysfunction, genetics, changes in the normal gut bacteria, and environmental factors. Rates tend to be higher in the developed world with some proposing this to be the result of less exposure to intestinal infections, or to a Western diet and lifestyle. The removal of the appendix at an early age may be protective. Diagnosis is typically by colonoscopy with tissue biopsies. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valeriana Officinalis
Valerian (''Valeriana officinalis'', Caprifoliaceae) is a perennial flowering plant native to Europe and Asia. In the summer when the mature plant may have a height of , it bears sweetly scented pink or white flowers that attract many fly species, especially hoverflies of the genus ''Eristalis''. It is consumed as food by the larvae of some Lepidoptera (butterfly and moth) species, including the grey pug. Crude extract of valerian root may have sedative and anxiolytic effects, and is commonly sold in dietary supplement capsules to promote sleep, but there is insufficient clinical evidence that it is effective for this purpose. Its roots and leaves cause a catnip-like response in cats. History Valerian has been used as a herb in traditional medicine since at least the time of ancient Greece and Rome. Hippocrates described its properties, and Galen later prescribed it as a remedy for insomnia. In medieval Sweden, it was sometimes placed in the wedding clothes of the groom to war ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GABAergic
In molecular biology and physiology, something is GABAergic or GABAnergic if it pertains to or affects the neurotransmitter GABA. For example, a synapse is GABAergic if it uses GABA as its neurotransmitter, and a GABAergic neuron produces GABA. A substance is GABAergic if it produces its effects via interactions with the GABA system, such as by stimulating or blocking neurotransmission. A GABAergic or GABAnergic agent is any chemical that modifies the effects of GABA in the body or brain. Some different classes of GABAergic drugs include agonists, antagonists, modulators, reuptake inhibitors and enzymes. See also * GABA reuptake inhibitor * Adenosinergic * Adrenergic * Cannabinoidergic * Cholinergic * Dopaminergic * Glycinergic * Histaminergic * Melatonergic * Monoaminergic * Opioidergic * Serotonergic Serotonergic () or serotoninergic () means "pertaining to or affecting serotonin". Serotonin is a neurotransmitter. A synapse is serotonergic if it uses serotonin as its neurotr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piper Methysticum
Kava or kava kava (''Piper (genus), Piper methysticum'': Latin 'pepper' and Latinized Ancient Greek, Greek 'intoxicating') is a crop of the Pacific Islands. The name ''kava'' is from Tongan language, Tongan and Marquesan language, Marquesan, meaning 'bitter'; other names for kava include ''ʻawa'' (Hawaii, Hawaiʻi), Samoa 'ava ceremony, ''ʻava'' (Samoa), ''yaqona'' or ''yagona'' (Fiji), ''sakau'' (Pohnpei), ''seka'' (Kosrae), and ''malok'' or ''malogu'' (parts of Vanuatu). Kava is consumed for its Sedation, sedating effects throughout the Pacific Ocean cultures of Polynesia, including Hawaii and Vanuatu, Melanesia, some parts of Micronesia, such as Pohnpei and Kosrae, and the Philippines. The root of the plant is used to produce a drink with sedative, anesthetic, and euphoriant properties. Its active ingredients are called kavalactones. A systematic review done by the British nonprofit Cochrane (organisation), Cochrane concluded it was likely to be more effective than placebo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States National Library Of Medicine
The United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), operated by the United States federal government, is the world's largest medical library. Located in Bethesda, Maryland, the NLM is an institute within the National Institutes of Health. Its collections include more than seven million books, journals, technical reports, manuscripts, microfilms, photographs, and images on medicine and related sciences, including some of the world's oldest and rarest works. The current director of the NLM is Patricia Flatley Brennan.National Library of Medicine Welcomes New Director Dr. Patricia Flatley Brennan . ''National Library of Medicine''. August 15, 2016. History The precursor o ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaundice
Jaundice, also known as icterus, is a yellowish or greenish pigmentation of the skin and sclera due to high bilirubin levels. Jaundice in adults is typically a sign indicating the presence of underlying diseases involving abnormal heme metabolism, liver dysfunction, or biliary-tract obstruction. The prevalence of jaundice in adults is rare, while jaundice in babies is common, with an estimated 80% affected during their first week of life. The most commonly associated symptoms of jaundice are itchiness, pale feces, and dark urine. Normal levels of bilirubin in blood are below 1.0 mg/ dl (17 μmol/ L), while levels over 2–3 mg/dl (34–51 μmol/L) typically result in jaundice. High blood bilirubin is divided into two types – unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin. Causes of jaundice vary from relatively benign to potentially fatal. High unconjugated bilirubin may be due to excess red blood cell breakdown, large bruises, genetic conditions s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
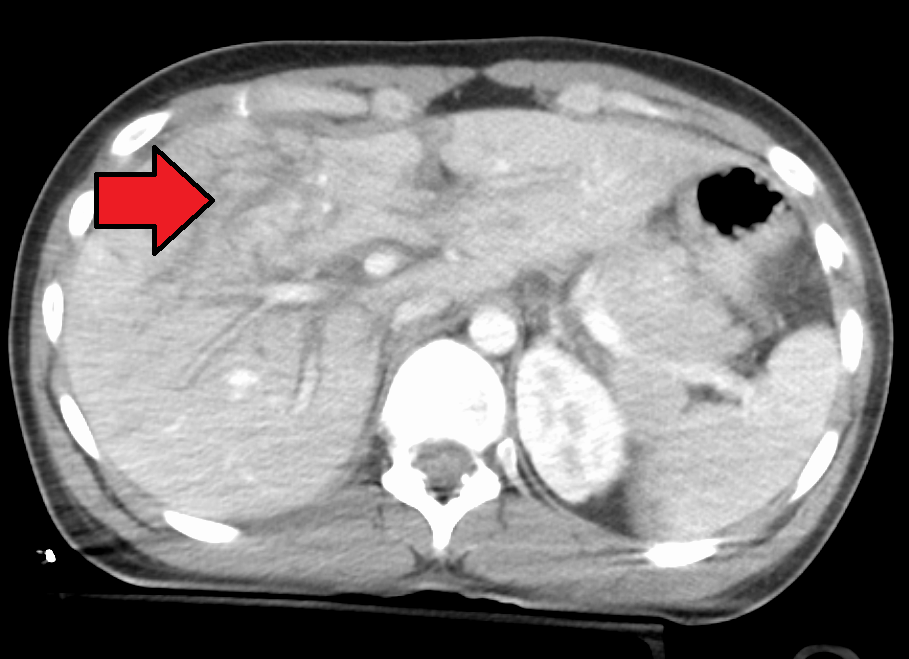
Liver Injury
A liver injury, also known as liver laceration, is some form of trauma sustained to the liver. This can occur through either a blunt force such as a car accident, or a penetrating foreign object such as a knife. Liver injuries constitute 5% of all traumas, making it the most common abdominal injury. Generally nonoperative management and observation is all that is required for a full recovery. Cause Given its anterior position in the abdominal cavity and its large size, the liver is prone to gun shot wounds and stab wounds. Its firm location under the diaphragm also makes it especially prone to shearing forces. Common causes of this type of injury are blunt force mechanisms such as motor vehicle accidents, falls, and sports injuries. Typically these blunt forces dissipate through and around the structure of the liver and causes irreparable damage to the internal microarchitecture of the tissue. With increasing velocity of the impact, the internal damage of the liver tissue als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scutellaria Lateriflora
''Scutellaria lateriflora'', (commonly "blue skullcap", "mad dog skullcap",''Scutellaria lateriflora''. NatureServe. 2012., "American skullcap", "side-flowering skullcap", etc.) is a hardy herb of the mint family, Lamiaceae, native to North America. It has an upright , growing in maximum height. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
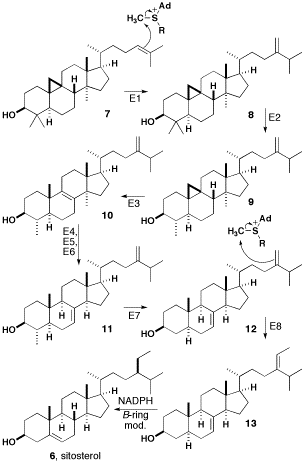
β-sitosterol
β-sitosterol (beta-sitosterol) is one of several phytosterols (plant sterols) with chemical structures similar to that of cholesterol. It is a white, waxy powder with a characteristic odor, and is one of the components of the food additive E499. Phytosterols are hydrophobic and soluble in alcohols. Natural occurrences and food β-sitosterol is widely distributed in the plant kingdom. It is found in vegetable oil, nuts, avocados, and derived prepared foods such as salad dressings. Human research β-sitosterol is being studied for its potential to reduce benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and blood cholesterol levels. Genetic disorder While plant sterols are usually beneficial, there is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder phytosterolemia which causes over-absorption of phytosterols. Precursor of anabolic steroid boldenone Being a steroid, β-sitosterol is a precursor of anabolic steroid boldenone. Boldenone undecylenate is commonly used in veterinary medicine to induce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oroxylin A
Oroxylin A is an O-methylated flavone, a chemical compound that can be found in the medicinal plants ''Scutellaria baicalensis'' and ''Scutellaria lateriflora'', and the ''Oroxylum indicum'' tree. It has demonstrated activity as a dopamine reuptake inhibitor, and is also a negative allosteric modulator of the benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor. Oroxylin A has been found to improve memory consolidation in mice by elevating brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in the hippocampus. See also * Baicalin * Baicalein * ''Chaenomeles speciosa ''Chaenomeles speciosa'', the flowering quince, Chinese quince, or Japanese quinceBailey, L.H.; Bailey, E.Z.; the staff of the Liberty Hyde Bailey Hortorium. 1976. ''Hortus third: A concise dictionary of plants cultivated in the United States ...'' References O-methylated flavones Resorcinols Dopamine reuptake inhibitors GABAA receptor negative allosteric modulators Nootropics {{Aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwogonin
Norwogonin, also known as 5,7,8-trihydroxyflavone (5,7,8-THF), is a flavone, a naturally occurring flavonoid-like chemical compound which is found in ''Scutellaria baicalensis'' (Baikal skullcap). It has been found to act as an agonist of the TrkB, the main signaling receptor of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and appears to possess roughly the same activity in this regard to that of the closely related but more well-known tropoflavin Tropoflavin, also known as 7,8-dihydroxyflavone, is a naturally occurring flavone found in '' Godmania aesculifolia'', '' Tridax procumbens'', and primula tree leaves. It has been found to act as a potent and selective small-molecule agonist of ... (7,8-DHF). See also * Tropomyosin receptor kinase B § Agonists References Flavones TrkB agonists {{aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |