|
Chinese Couplet
In Chinese poetry, a duilian () is a pair of lines of poetry which adhere to certain rules (see below). Outside of poems, they are usually seen on the sides of doors leading to people's homes or as hanging scrolls in an interior. Although often called Chinese couplet or antithetical couplet, they can better be described as a written form of counterpoint. The two lines have a one-to-one correspondence in their metrical length, and each pair of characters must have certain corresponding properties. A duilian is ideally profound yet concise, using one character per word in the style of Classical Chinese. A special, widely seen type of duilian is the chunlian (), used as a New Year's decoration that expresses happiness and hopeful thoughts for the coming year. Requirements A duilian must adhere to the following rules: #Both lines must have the same number of Chinese characters. #The lexical category of each character must be the same as its corresponding character. #The tone pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
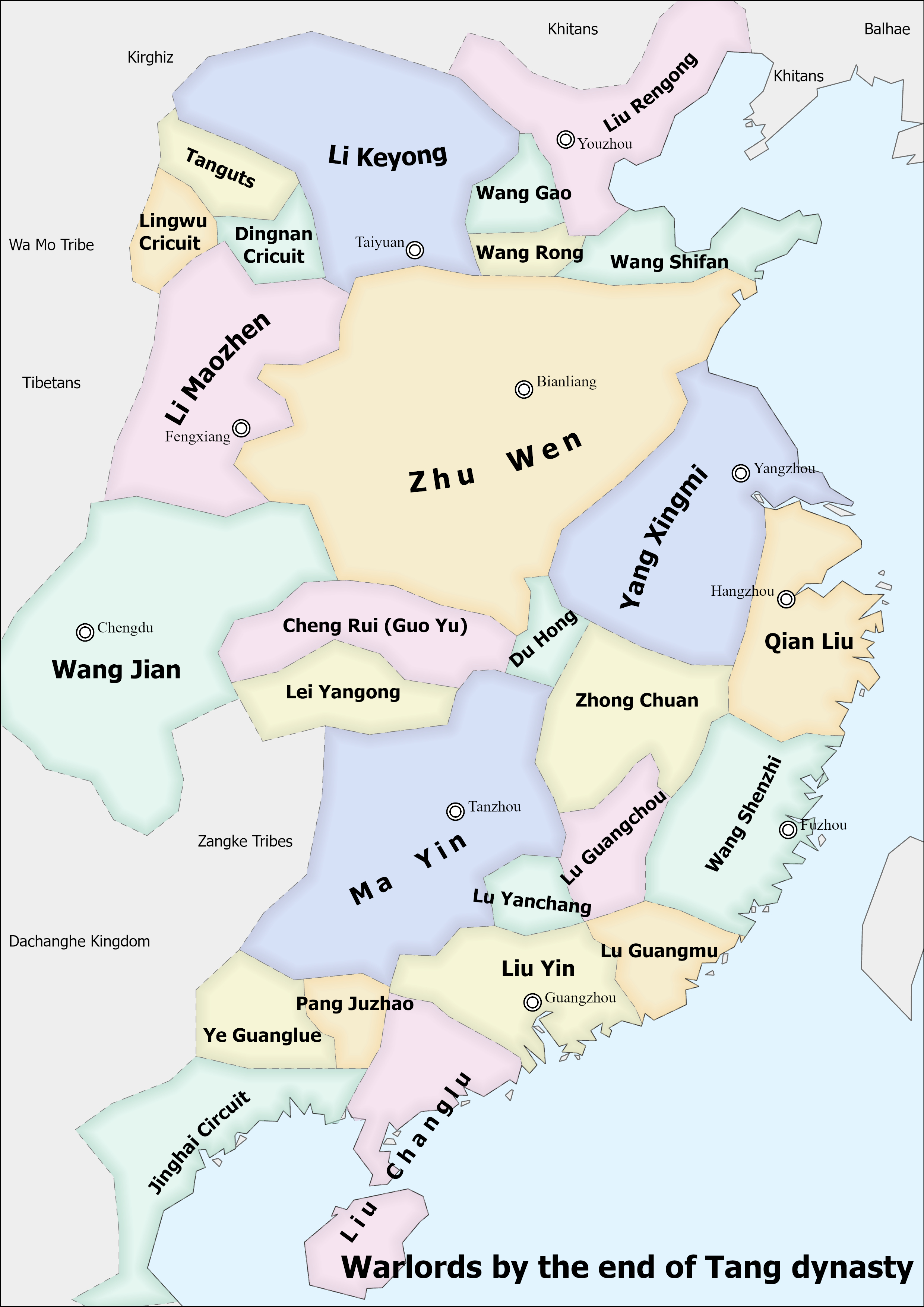
Five Dynasties
The Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (), from 907 to 979, was an era of political upheaval and division in 10th-century Imperial China. Five dynastic states quickly succeeded one another in the Central Plain, and more than a dozen concurrent dynastic states were established elsewhere, mainly in South China. It was a prolonged period of multiple political divisions in Chinese imperial history. Traditionally, the era is seen as beginning with the fall of the Tang dynasty in 907 and reaching its climax with the founding of the Song dynasty in 960. In the following 19 years, Song gradually subdued the remaining states in South China, but the Liao dynasty still remained in China's north (eventually succeeded by the Jin dynasty), and the Western Xia was eventually established in China's northwest. Many states had been ''de facto'' independent long before 907 as the Tang dynasty's control over its officials waned, but the key event was their recognition as sovereign by fore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Poetry Forms
Chinese can refer to: * Something related to China * Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity **''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation ** List of ethnic groups in China, people of various ethnicities in contemporary China ** Han Chinese, the largest ethnic group in the world and the majority ethnic group in Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan, and Singapore ** Ethnic minorities in China, people of non-Han Chinese ethnicities in modern China ** Ethnic groups in Chinese history, people of various ethnicities in historical China ** Nationals of the People's Republic of China ** Nationals of the Republic of China ** Overseas Chinese, Chinese people residing outside the territories of Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan * Sinitic languages, the major branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family ** Chinese language, a group of related languages spoken predominantly in China, sharing a written script (Chinese c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dongba Symbols
The Dongba, Tomba or Tompa or Mo-so symbols are a system of pictographic glyphs used by the '' ²dto¹mba'' (Bon priests) of the Naxi people in southern China. In the Naxi language it is called ''²ss ³dgyu'' 'wood records' or ''²lv ³dgyu'' 'stone records'.He, 292 "They were developed in approximately the seventh century." The glyphs may be used as rebuses for abstract words which do not have glyphs. Dongba is largely a mnemonic system, and cannot by itself represent the Naxi language; different authors may use the same glyphs with different meanings, and it may be supplemented with the ''geba'' syllabary for clarification. Origin and development The Dongba script appears to be an independent ancient writing system, though presumably it was created in the environment of older scripts. According to Dongba religious fables, the Dongba script was created by the founder of the Bön religious tradition of Tibet, Tönpa Shenrab (Tibetan: ''ston pa gshen rab)'' or Shenrab Miwo (T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Lore
Weather lore is the body of informal folklore related to the prediction of the weather and its greater meaning. Much like regular folklore, weather lore is passed down through speech and writing from normal people without the use of external measuring instruments. The origin of weather lore can be dated back to primeval men and their usage of star studying in navigation. However, more recently during the Late Middle Ages, the works of two Greek philosopher-poets, Theophrastus of Eresus on Lesbos and Aratus of Macedonia, are known for shaping the prediction of weather. Theophrastus and Aratus collated their works in two main collections for weather lore: ''On Weather Signs'' and ''On Winds.'' These were used for helping farmers with harvest, merchants for trade and determining the weather the next day. Astrology and weather lore have been closely interlinked for many years - with each planet often being associated with a weather state. For example, Mars is red and must therefore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakhi People
The Nakhi or Nashi (; Naxi: ; lit.: "Black people") are an East Asian ethnic group inhabiting the foothills of the Himalayas in the northwestern part of Yunnan Province, as well as the southwestern part of Sichuan Province in China. The Nakhi are thought to have come originally from northwestern China, migrating south toward Tibetan populated regions, and usually inhabiting the most fertile riverside land, driving the other competing tribes farther up the hillsides onto less fertile land. The Nakhi, along with the Bai and the Tibetans, traded over the dangerous overland trading links with Lhasa and India, on the so-called Tea and Horse Caravan routes. The Nakhi form one of the 56 ethnic groups officially recognized by the People's Republic of China. The official Chinese government classification includes the Mosuo as part of the Nakhi people. Although both groups are descendants of the Qiang people and notwithstanding very striking resemblances between their respective lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yunnan Nationalities Museum
The Yunnan Nationalities Museum () is located on the east bank of Dianchi Lake in Kunming, Yunnan, China, next to the Yunnan Ethnic Village. Completed in 1995, it is a comprehensive ethnology museum. Covering an area of over 200 mu, the museum has a building area of 130,000 square meters. It consists of various exhibition halls, office building, report hall, storage and workshops. The ecological environment, religious customs, culture and arts and relics of the ethnic groups of Yunnan are collected in it. The 120,000 items of objects fall into the 16 categories such as ethnic groups, dresses and personal adornment, technique, arts, ecology, ancient books, and strange stones etc. See also * List of museums in China , there are 3,589 museums in China, including 3,054 state-owned museums (museums run by national and local government or universities) and 535 private museums. With a total collection of over 20 million items, these museums hold more than 8,000 e ... References * http ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daguan Park
Daguan Park () is a lakeside park located in the southwestern suburb of Kunming, Yunnan, China. Today many locals come to sit, drink tea, fly kites, and go boating. Among shady walks and pools, Daguan's focal point is Daguan Lou, a square, three-storeyed pavilion built to better the Kangxi Emperor's enjoyment of the distant Western Hills and now a storehouse of calligraphy extolling the area's charms. The most famous poem here is a 118-character verse, carved into the gateposts by the Qing dynasty scholar Sun Ran, reputed to be the longest set of rhyming couplets in China. The park is set on Daguan Stream, which flows south into Lake Dian, and there are frequent hour-long cruises down the waterway, lined with willows, to points along Lake Dian's northern shore. Lake Dian, also known as the Kunming Lake, is the largest lake on the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau. At Longmen of the Western Hills, there is a panoramic view of the lake. History In 1696, Wang Jiwen, the governor of Yunnan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fai Chun
''Fai chun'' () is a traditional decoration that is frequently used during Chinese New Year. People put ''fai chun'' in the doorways to create a jubilant festive atmosphere since the phrases written on it means good luck and prosperity. Customarily, ''fai chun'' is written by hand but owing to convenience, printed versions are mass-produced nowadays. ''fai chun'' is in either square or rectangular shape. It can be hung vertically or horizontally. Not only does it exist in Greater China but also in Korea, Japan, and Vietnam. History ''Fai chun'' originated from ''taofu'' (桃符; peach wood charms) in ancient times. Peach wood charms are the long pieces of wood hung from peach trees. They are about seven to eight inches long and slightly more than one inch wide. According to the legend, there was a peach tree in the East China Sea that was the gate where the ghosts passed through between the underworld and the world of the living. Two gods, Shentu and Yulei, were responsible fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Couplet
A couplet is a pair of successive lines of metre in poetry. A couplet usually consists of two successive lines that rhyme and have the same metre. A couplet may be formal (closed) or run-on (open). In a formal (or closed) couplet, each of the two lines is end-stopped, implying that there is a grammatical pause at the end of a line of verse. In a run-on (or open) couplet, the meaning of the first line continues to the second. Background The word "couplet" comes from the French word meaning "two pieces of iron riveted or hinged together". The term "couplet" was first used to describe successive lines of verse in Sir P. Sidney's '' Arcadia '' in 1590: "In singing some short coplets, whereto the one halfe beginning, the other halfe should answere." While couplets traditionally rhyme, not all do. Poems may use white space to mark out couplets if they do not rhyme. Couplets in iambic pentameter are called ''heroic couplets''. John Dryden in the 17th century and Alexander Pope in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Dozens
The Dozens is a game played between two contestants in which the participants insult each other until one of them gives up. Common in African-American communities, the Dozens is almost exclusively played in front of an audience, who encourage the participants to reply with increasingly severe insults in order to heighten the tension and consequently make the contest more interesting to watch. Comments in the game may focus on the opposite player's intelligence, appearance, competency, social status, and financial situation. Disparaging remarks about the other player's family members are common, especially regarding their mother. Commentary is often related to sexual issues, and this version of the game is referred to as the "Dirty Dozens".Chimezie, Amuzie (June 1976). "The Dozens: An African-Heritage Theory", ''Journal of Black Studies'', Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 401–420. According to sociologist Harry Lefever and journalist John Leland, the game is played almost entirely by Afric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaking ethnic group who unified other Jurchen tribes to form a new "Manchu" ethnic identity. The dynasty was officially proclaimed in 1636 in Manchuria (modern-day Northeast China and Outer Manchuria). It seized control of Beijing in 1644, then later expanded its rule over the whole of China proper and Taiwan, and finally expanded into Inner Asia. The dynasty lasted until 1912 when it was overthrown in the Xinhai Revolution. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing dynasty lasted for almost three centuries and assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest imperial dynasty in the history of China and in 1790 the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |