|
Fort Randolph (West Virginia)
Fort Randolph was an American Revolutionary War fort which stood at the confluence of the Ohio and Kanawha Rivers, on the site of present-day Point Pleasant, West Virginia, USA. Built in 1776 on the site of an earlier fort from Dunmore's War, Fort Randolph is best remembered as the place where the famous Shawnee Chief Cornstalk was murdered in 1777. The fort withstood attack by American Indians in 1778 but was abandoned the next year. It was rebuilt in the 1780s after the renewal of hostilities between the United States and American Indians, but saw little action and was eventually abandoned once again. Two centuries later, a replica of the fort has been built about a mile away. History Background The site where Fort Randolph was built emerged as a strategic location in the years before the American Revolution. In the Treaty of Fort Stanwix of 1768, the British Crown acquired the title to present-day West Virginia from the Iroquois. Thereafter, American colonists and land spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moravian Church
The Moravian Church ( cs, Moravská církev), or the Moravian Brethren, formally the (Latin: "Unity of the Brethren"), is one of the oldest Protestantism, Protestant Christian denomination, denominations in Christianity, dating back to the Bohemian Reformation of the 15th century and the History of the Moravian Church, Unity of the Brethren ( cs, Jednota bratrská, links=no) founded in the Kingdom of Bohemia, sixty years before Reformation, Luther's Reformation. The church's heritage can be traced to 1457 in Bohemian Crown territory, including its Lands of the Bohemian Crown, crown lands of Moravia and Silesia, which saw the emergence of the Hussite movement against several practices and doctrines of the Catholic Church. However, its name is derived from exiles who fled from Bohemia to Saxony in 1722 to escape the Counter-Reformation, establishing the Christian community of Herrnhut; hence it is also known in German language, German as the ("Unity of Brethren [of Herrnhut]"). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
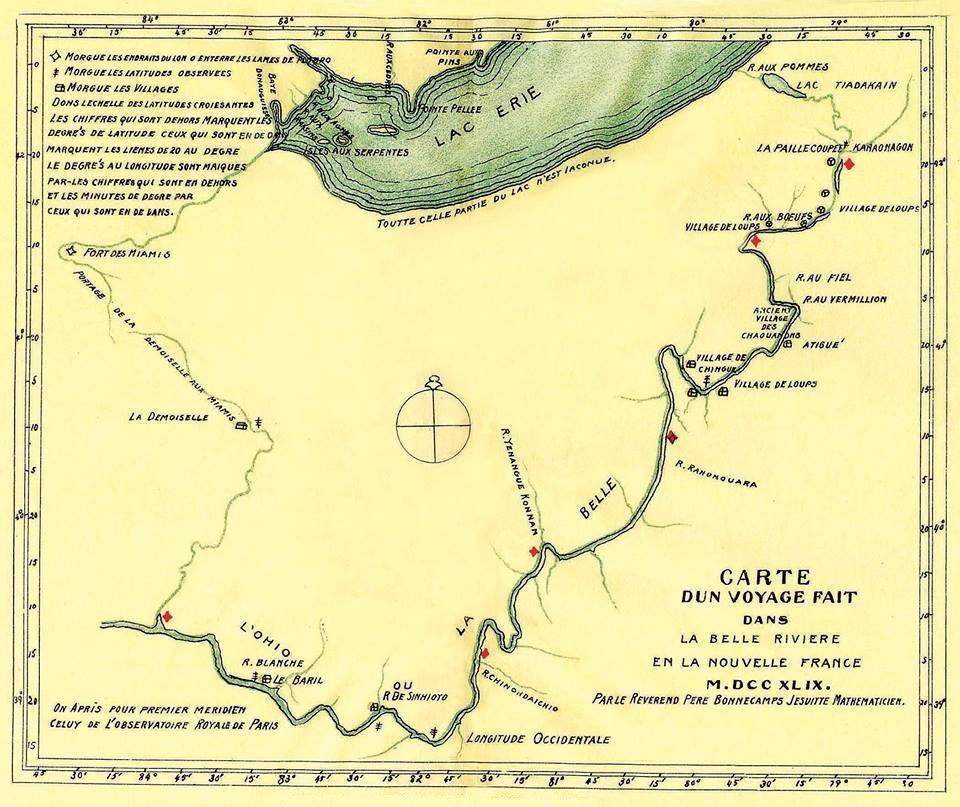
Scioto River
The Scioto River ( ) is a river in central and southern Ohio more than in length. It rises in Hardin County just north of Roundhead, Ohio, flows through Columbus, Ohio, where it collects its largest tributary, the Olentangy River, and meets the Ohio River at Portsmouth. Early settlers and Native Americans used the river for shipping,"Scioto River – Ohio History Central" but it is now too small for modern commercial craft. The primary economic importance for the river now is for recreation and drinking water. It is the longest river that is entirely within Ohio. Geography and geology The lower Scioto River valley is large compared to the width of the river and is extensively farmed. Meltwaters from retreating glaciers carved the valley exceptionally wide. Valley bottoms are smooth, and flood deposits created during and since the most recent Glacial period cause floodplain soils to be very productive. As a result, farms line much of the lower Scioto where it flows through lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohio River
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illinois. It is the third largest river by discharge volume in the United States and the largest tributary by volume of the north-south flowing Mississippi River that divides the eastern from western United States. It is also the 6th oldest river on the North American continent. The river flows through or along the border of six states, and its drainage basin includes parts of 14 states. Through its largest tributary, the Tennessee River, the basin includes several states of the southeastern U.S. It is the source of drinking water for five million people. The lower Ohio River just below Louisville is obstructed by rapids known as the Falls of the Ohio where the elevation falls in restricting larger commercial navigation, although in the 18th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Shawneetown
Lower Shawneetown, also known as Shannoah or Sonnontio, was an 18th-century Shawnee village located within the Lower Shawneetown Archeological District, near South Portsmouth in Greenup County, Kentucky and Lewis County, Kentucky. The population eventually occupied areas on both sides of the Ohio River, and along both sides of the Scioto River in what is now Scioto County, Ohio. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places on 28 April, 1983. It is near the Bentley site, a Madisonville Horizon settlement inhabited between 1400 CE and 1625 CE. Nearby, to the east, there are also four groups of Hopewell tradition mounds, built between 100 BCE and 500 CE, known as the Portsmouth Earthworks. Extensive archaelogical work has provided a clear picture of the town's appearance and activities, particularly the nature of trade, social organization, agriculture, and relationships with other Native American communities. Well-known British traders William Trent and George Croghan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Bouquet
Henry Bouquet (born Henri Louis Bouquet; 1719 – 2 September 1765) was a Swiss mercenary who rose to prominence in British service during the French and Indian War and Pontiac's War. He is best known for his victory over a Native American force at the Battle of Bushy Run, lifting the siege of Fort Pitt during Pontiac's War. During the conflict Bouquet gained lasting infamy in an exchange of letters with his commanding officer, Jeffery Amherst, who suggested a form of biological warfare in the use of blankets infected with smallpox which were to be distributed to Native Americans. Despite this indictment historians have praised Bouquet for leading British forces in several demanding campaigns on the Western Frontier in which they "protected and rescued" settlers from increasingly frequent attacks. Early life Bouquet was born in Rolle, Switzerland, as the oldest of seven brothers. The son of a Swiss roadhouse owner and his well-to-do wife, he entered military service at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muskingum River
The Muskingum River (Shawnee: ') is a tributary of the Ohio River, approximately long, in southeastern Ohio in the United States. An important commercial route in the 19th century, it flows generally southward through the eastern hill country of Ohio. Via the Ohio, it is part of the Mississippi River watershed. The river is navigable for much of its length through a series of locks and dams. Course The Muskingum is formed at Coshocton in east-central Ohio by the confluence of the Walhonding and Tuscarawas rivers. It flows in a meandering course southward past Conesville and Dresden to Zanesville, and then southeastward past South Zanesville, Philo, Gaysport, Malta, McConnelsville, Beverly, Lowell, Stockport and Devola. It joins the Ohio at Marietta. Along its course the Muskingum collects Wills Creek near Conesville; Wakatomika Creek at Dresden; the Licking River at Zanesville; Moxahala Creek at South Zanesville; and Wolf Creek near Beverly. History The name '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wakatomika
Wakatomika was the name of two 18th century Shawnee villages in what is now the U.S. state of Ohio. The name was also spelled Wapatomica, Waketomika, Waketomica, and Waketameki, among other variations, but the similar name Wapakoneta was a different Shawnee village. Both Wakatomikas were destroyed in raids, the first by colonial Virginians in 1774, the second by Kentuckians in 1786. Wakatomika 1 The first Wakatomika was located along the Muskingum River, near present-day Dresden, Ohio, and was close to a number of Lenape towns. It was established around 1756 by Shawnees from Upper Shawneetown, which was located along the Ohio River. After the outbreak of the French and Indian War in 1754, the Shawnees were distancing themselves from raids by the colony of Virginia. For the same reason, in 1758 the Shawnee residents of Lower Shawneetown, also on the Ohio River, moved fifty miles upriver and established new towns on the Pickaway Plains, near modern Circleville, Ohio. In August 1774, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French And Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the start of the war, the French colonies had a population of roughly 60,000 settlers, compared with 2 million in the British colonies. The outnumbered French particularly depended on their native allies. Two years into the French and Indian War, in 1756, Great Britain declared war on France, beginning the worldwide Seven Years' War. Many view the French and Indian War as being merely the American theater of this conflict; however, in the United States the French and Indian War is viewed as a singular conflict which was not associated with any European war. French Canadians call it the ('War of the Conquest').: 1756–1763 The British colonists were supported at various times by the Iroquois, Catawba, and Cherokee tribes, and the French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hathawekela
Hathawekela (also spelled Oawikila, Thaawikila, Thawegila, Shawnee: ''θawikila'', French: ''Chalaqua'') was one of the five divisions (or bands) of the Shawnee, a Native American people during the 18th century. The other four divisions were the Chalahgawtha, Mekoche, Kispoko, and Pekowi. (All five division names have been spelled in a great variety of ways.) Together these divisions formed the loose confederacy that was the Shawnee tribe. Traditionally, Shawnee political leadership came from the Hathawekela patrilineal division. According to J.D. Lewis, "Tradition and the known linguistic connections of the Shawnee indicate that they had migrated to the Cumberland River Valley from the north not long previous to the historic period ... Shortly after 1674, the Hathawekela or that part of the Shawnee afterward so called, settled upon Savannah River, and in 1681 they proved of great assistance to the new colony of South Carolina by driving a tribe known as Westo, probably part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pekowi
Pekowi was the name of one of the five divisions (or bands) of the Shawnee, a Native American people, during the 18th century. The other four divisions were the Chalahgawtha, Mekoche, Kispoko, and Hathawekela. Together these divisions formed the loose confederacy that was the Shawnee tribe. All five Shawnee division names have been spelled in a great variety of ways. Variations of the name "Pekowi" are reflected in many place names in the United States, including Piqua, Pickawillany, Pickaway, and Pequea. Traditionally, Shawnee ritual leaders came from the Pekowi patrilineal division. From 1737 to about 1750 the Pekowi were led by Peter Chartier (born Pierre Chartier), a fur trader of Pekowi and French colonial parentage. He was recognized as a leader and rose to be chief of the band. Through his mother's line, Chartier was the grandson of chief Straight Tail Meaurroway Opessa. In 1710 he married his cousin, ''Blanceneige-Wapakonee'' Opessa and they had three children: two s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |