|
Checkpoint Inhibition
Checkpoint inhibitor therapy is a form of cancer immunotherapy. The therapy targets immune checkpoints, key regulators of the immune system that when stimulated can dampen the immune response to an immunologic stimulus. Some cancers can protect themselves from attack by stimulating immune checkpoint targets. Checkpoint therapy can block inhibitory checkpoints, restoring immune system function. The first anti-cancer drug targeting an immune checkpoint was ipilimumab, a CTLA4 blocker approved in the United States in 2011. Currently approved checkpoint inhibitors target the molecules CTLA4, PD-1, and PD-L1. PD-1 is the transmembrane programmed cell death 1 protein (also called PDCD1 and CD279), which interacts with PD-L1 ( PD-1 ligand 1, or CD274). PD-L1 on the cell surface binds to PD-1 on an immune cell surface, which inhibits immune cell activity. Among PD-L1 functions is a key regulatory role on T cell activities. It appears that (cancer-mediated) upregulation of PD-L1 on the cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treatment Of Cancer
Cancer can be treated by surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy, targeted therapy (including immunotherapy such as monoclonal antibody therapy) and synthetic lethality, most commonly as a series of separate treatments (e.g. chemotherapy before surgery). The choice of therapy depends upon the location and grade of the tumor and the stage of the disease, as well as the general state of the patient (performance status). Cancer genome sequencing helps in determining which cancer the patient exactly has for determining the best therapy for the cancer. A number of experimental cancer treatments are also under development. Under current estimates, two in five people will have cancer at some point in their lifetime. Complete removal of the cancer without damage to the rest of the body (that is, achieving cure with near-zero adverse effects) is the ideal, if rarely achieved, goal of treatment and is often the goal in practice. Sometimes this can be accomplished by s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Cell Carcinoma
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a kidney cancer that originates in the lining of the proximal convoluted tubule, a part of the very small tubes in the kidney that transport primary urine. RCC is the most common type of kidney cancer in adults, responsible for approximately 90–95% of cases. RCC occurrence shows a male predominance over women with a ratio of 1.5:1. RCC most commonly occurs between 6th and 7th decade of life. Initial treatment is most commonly either partial or complete removal of the affected kidney(s). Where the cancer has not metastasised (spread to other organs) or burrowed deeper into the tissues of the kidney, the five-year survival rate is 65–90%, but this is lowered considerably when the cancer has spread. The body is remarkably good at hiding the symptoms and as a result people with RCC often have advanced disease by the time it is discovered. The initial symptoms of RCC often include blood in the urine (occurring in 40% of affected persons at the time th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is a cancer arising from the cervix. It is due to the abnormal growth of cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. Early on, typically no symptoms are seen. Later symptoms may include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain or pain during sexual intercourse. While bleeding after sex may not be serious, it may also indicate the presence of cervical cancer. Human papillomavirus infection (HPV) causes more than 90% of cases; most women who have had HPV infections, however, do not develop cervical cancer. HPV 16 and 18 strains are responsible for nearly 50% of high grade cervical pre-cancers. Other risk factors include smoking, a weak immune system, birth control pills, starting sex at a young age, and having many sexual partners, but these are less important. Genetic factors also contribute to cervical cancer risk. Cervical cancer typically develops from precancerous changes over 10 to 20 years. About 90% of cervical cancer cas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastric Cancer
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a cancer that develops from the lining of the stomach. Most cases of stomach cancers are gastric carcinomas, which can be divided into a number of subtypes, including gastric adenocarcinomas. Lymphomas and mesenchymal tumors may also develop in the stomach. Early symptoms may include heartburn, upper abdominal pain, nausea, and loss of appetite. Later signs and symptoms may include weight loss, yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, vomiting, difficulty swallowing, and blood in the stool, among others. The cancer may spread from the stomach to other parts of the body, particularly the liver, lungs, bones, lining of the abdomen, and lymph nodes. The most common cause is infection by the bacterium ''Helicobacter pylori'', which accounts for more than 60% of cases. Certain types of ''H. pylori'' have greater risks than others. Smoking, dietary factors such as pickled vegetables and obesity are other risk factors. About 10% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pembrolizumab
Pembrolizumab, sold under the brand name Keytruda, is a humanized antibody used in cancer immunotherapy that treats melanoma, lung cancer, head and neck cancer, Hodgkin lymphoma, stomach cancer, cervical cancer, and certain types of breast cancer. It is given by slow injection into a vein. Common side effects include fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, decreased appetite, itchy skin (pruritus), diarrhea, nausea, rash, fever (pyrexia), cough, difficulty breathing (dyspnea), constipation, pain, and abdominal pain. It is an IgG4 isotype antibody that blocks a protective mechanism of cancer cells and thereby, allows the immune system to destroy them. It targets the programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) receptor of lymphocytes. It works by targeting the cellular pathway of proteins found on the body's immune cells and some cancer cells, known as PD-1/PD-L1. Pembrolizumab was approved for medical use in the United States in 2014. In 2017, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esophageal Carcinoma
Esophageal cancer is cancer arising from the esophagus—the food pipe that runs between the throat and the stomach. Symptoms often include difficulty in swallowing and weight loss. Other symptoms may include pain when swallowing, a hoarse voice, enlarged lymph nodes ("glands") around the collarbone, a dry cough, and possibly coughing up or vomiting blood. The two main sub-types of the disease are esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma (often abbreviated to ESCC), which is more common in the developing world, and esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC), which is more common in the developed world. A number of less common types also occur. Squamous-cell carcinoma arises from the epithelial cells that line the esophagus. Adenocarcinoma arises from glandular cells present in the lower third of the esophagus, often where they have already transformed to intestinal cell type (a condition known as Barrett's esophagus). Causes of the squamous-cell type include tobacco, alcohol, very hot drin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
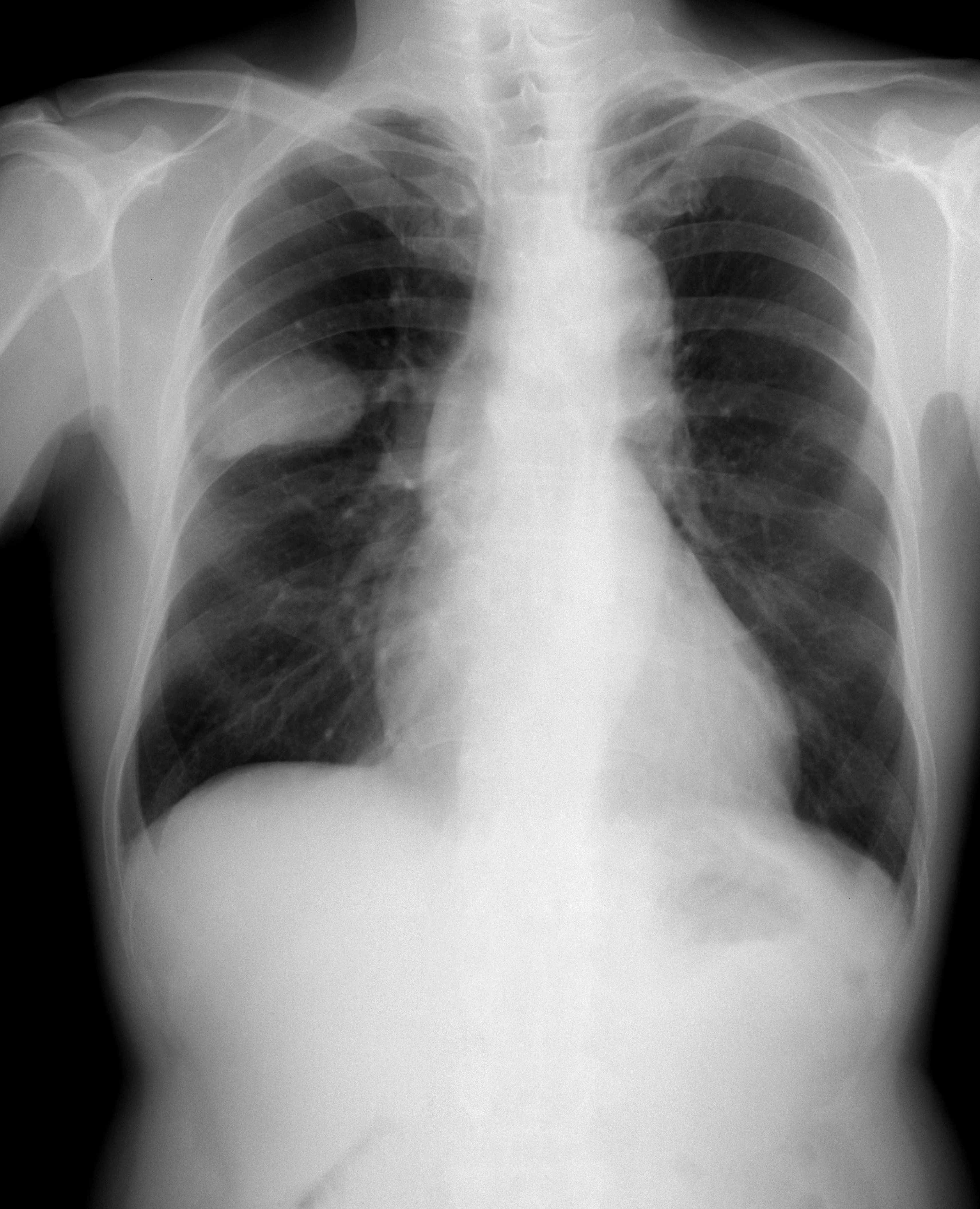
Small Cell Lung Cancer
Small-cell carcinoma is a type of highly malignant cancer that most commonly arises within the lung, although it can occasionally arise in other body sites, such as the cervix, prostate, and gastrointestinal tract. Compared to non-small cell carcinoma, small cell carcinoma has a shorter doubling time, higher growth fraction, and earlier development of metastases. Extensive stage small cell lung cancer is classified as a rare disorder. Ten-year relative survival rate is 3.5%; however, women have a higher survival rate, 4.3%, and men lower, 2.8%. Survival can be higher or lower based on a combination of factors including stage, age, gender and race. Types of SCLC Small-cell lung carcinoma has long been divided into two clinicopathological stages, termed ''limited stage'' (LS) and ''extensive stage'' (ES). The stage is generally determined by the presence or absence of metastases, whether or not the tumor appears limited to the thorax, and whether or not the entire tumor burden wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urothelial Carcinoma
Transitional epithelium also known as urothelium is a type of stratified epithelium. Transitional epithelium is a type of tissue that changes shape in response to stretching (stretchable epithelium). The transitional epithelium usually appears cuboidal when relaxed and squamous when stretched. This tissue consists of multiple layers of epithelial cells which can contract and expand in order to adapt to the degree of distension needed. Transitional epithelium lines the organs of the urinary system and is known here as urothelium. The bladder for example has a need for great distension. Structure The appearance of transitional epithelium differs according to its cell layer. Cells of the basal layer are cuboidal (cube-shaped), or columnar (column-shaped), while the cells of the superficial layer vary in appearance depending on the degree of distension. These cells appear to be cuboidal with a domed apex when the organ or the tube in which they reside is not stretched. When the orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head And Neck Cancer
Head and neck cancer develops from tissues in the lip and oral cavity (mouth), larynx (throat), salivary glands, nose, sinuses or the skin of the face. The most common types of head and neck cancers occur in the lip, mouth, and larynx. Symptoms predominantly include a sore that does not heal or a change in the voice. Some may experience a sore throat that does not go away. In those with advanced disease, there may be unusual bleeding, facial pain, numbness or swelling, and visible lumps on the outside of the neck or oral cavity. Given the location of these cancers, trouble breathing may also be present. The majority of head and neck cancer is caused by the use of alcohol or tobacco, including smokeless tobacco, with increasing cases linked to the human papillomavirus (HPV). Other risk factors include Epstein-Barr virus, betel quid, radiation exposure, certain workplace exposures. About 90% are pathologically classified as squamous cell cancers. The diagnosis is confirmed by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma, in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the patient's lymph nodes. The condition was named after the English physician Thomas Hodgkin, who first described it in 1832. Symptoms may include fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Often, nonpainful enlarged lymph nodes occur in the neck, under the arm, or in the groin. Those affected may feel tired or be itchy. The two major types of Hodgkin lymphoma are classic Hodgkin lymphoma and nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. About half of cases of Hodgkin lymphoma are due to Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) and these are generally the classic form. Other risk factors include a family history of the condition and having HIV/AIDS. Diagnosis is conducted by confirming the presence of cancer and identifying RS cells in lymph node biopsies. The virus-positive cases are classified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nivolumab
Nivolumab, sold under the brand name Opdivo, is a medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes melanoma, lung cancer, malignant pleural mesothelioma, renal cell carcinoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, head and neck cancer, urothelial carcinoma, colon cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, liver cancer, gastric cancer, and esophageal or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) cancer. It is used by slow injection into a vein. The most common side effects include fatigue, rash, musculoskeletal pain, pruritus, diarrhea, nausea, asthenia, cough, dyspnea, constipation, decreased appetite, back pain, arthralgia, upper respiratory tract infection, pyrexia, headache, abdominal pain, and vomiting. Use during pregnancy may harm the baby and use when breastfeeding is not recommended. Nivolumab is a human IgG4 monoclonal antibody that blocks PD-1. It is a type of immunotherapy and works as a checkpoint inhibitor, blocking a signal that prevents activation of T cells from attackin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
Mesothelioma is a type of cancer that develops from the thin layer of tissue that covers many of the internal organs (known as the mesothelium). The most common area affected is the lining of the lungs and chest wall. Less commonly the lining of the abdomen and rarely the sac surrounding the heart, or the sac surrounding the testis may be affected. Signs and symptoms of mesothelioma may include shortness of breath due to fluid around the lung, a swollen abdomen, chest wall pain, cough, feeling tired, and weight loss. These symptoms typically come on slowly. More than 80% of mesothelioma cases are caused by exposure to asbestos. The greater the exposure the greater the risk. As of 2013, about 125 million people worldwide have been exposed to asbestos at work. High rates of disease occur in people who mine asbestos, produce products from asbestos, work with asbestos products, live with asbestos workers, or work in buildings containing asbestos. Asbestos exposure and the onset ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
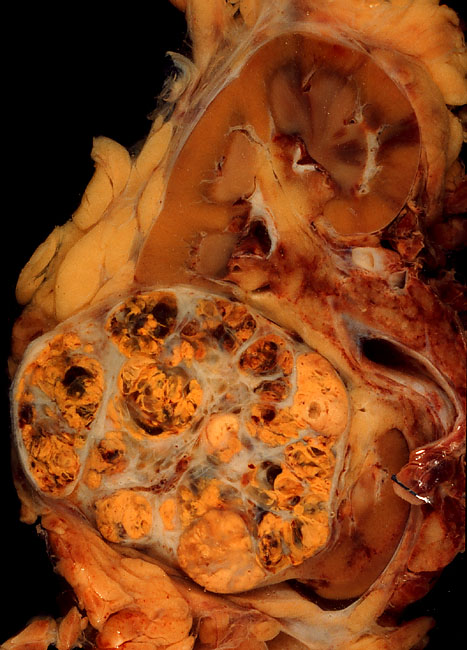
_Nephrectomy.jpg)



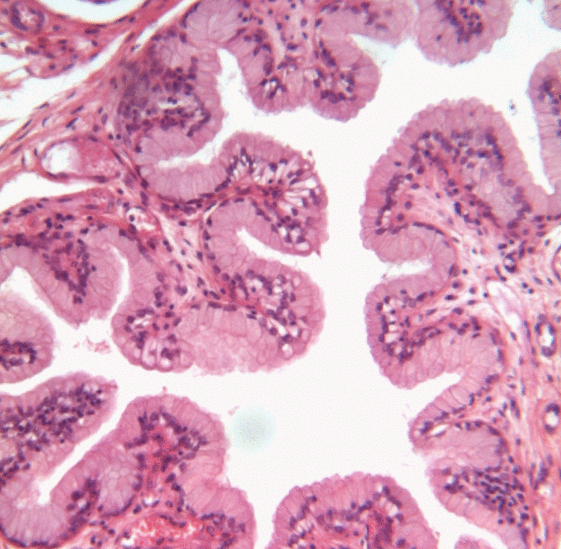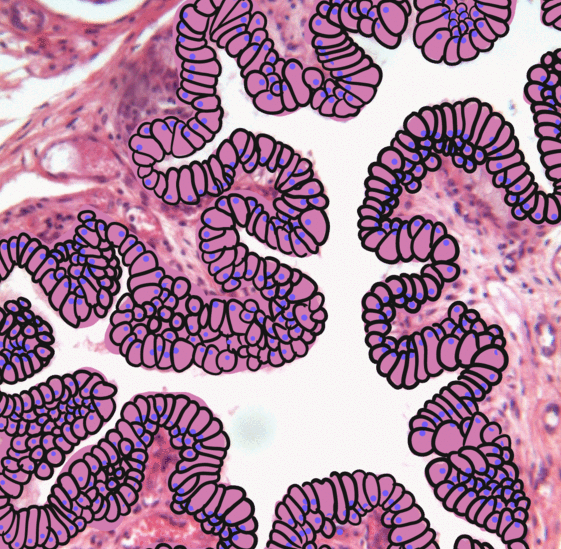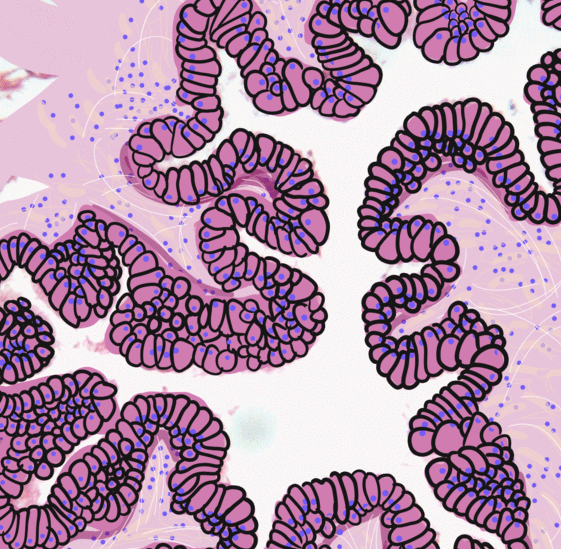
_squamous_cell_carcinoma_histopathology.jpg)
_mixed_cellulary_type.jpg)
