|
Cheche Disaster
The Cheche Disaster (Portuguese: ''Desastre do Cheche'') was an incident during the Portuguese Colonial War in Portuguese Guinea (now Guinea-Bissau) in which almost fifty Portuguese soldiers died on 6 February 1969 while crossing the Corubal River. Background When Brigadier António de Spínola came to Guinea in 1968 as Governor and Commander in Chief, he decided to evacuate the Portuguese troops in the east of the country, which was thinly populated and of no strategic value. The camp at Madina do Boé was surrounded and was suffering constant attacks by the PAIGC guerillas of Amílcar Cabral. The position was untenable. It was occupied by PAIGC forces the same day that the Portuguese evacuated it. The retreating force included ''Caçadores'' ("Hunters") company 1790, commanded by Captain José Aparício, more troops from company 2405 and Guinean militia. Moving the troops, vehicles and equipment over to Chéché, on the south bank of the Corubal River, was a difficult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chéché
Chéché or Ché Ché is a village in the Gabú Region of north-eastern Guinea-Bissau. It lies on the south of the Corubal River, to the south of Canjadude. The river crossing was the site of the Cheche Disaster of 6 February 1969, in which about 50 Portuguese soldiers drowned in an accident when their ferry tipped over. References Populated places in Guinea-Bissau Gabu Region {{GuineaBissau-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rearguard
A rearguard is a part of a military force that protects it from attack from the rear, either during an advance or withdrawal. The term can also be used to describe forces protecting lines, such as communication lines, behind an army. Even more generally, a rearguard action may refer idiomatically to an attempt at preventing something though it is likely too late to be prevented; this idiomatic meaning may apply in either a military- or in a non-military, perhaps-figurative context. Origins The term rearguard (also ''rereward'', ''rearward'') originates from the medieval custom of dividing an army into three ''battles'' or ''wards''; Van, Main (or Middle) and Rear. The Rear Ward usually followed the other wards on the march and during a battle usually formed the rearmost of the three if deployed in column or the left-hand ward if deployed in line. Original usage The commonly accepted definition of a rearguard in military tactics was largely established in the battles of the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shipwrecks In Rivers
A shipwreck is the wreckage of a ship that is located either beached on land or sunken to the bottom of a body of water. Shipwrecking may be intentional or unintentional. Angela Croome reported in January 1999 that there were approximately three million shipwrecks worldwide (an estimate rapidly endorsed by UNESCO and other organizations). When a ship's crew has died or abandoned the ship, and the ship has remained adrift but unsunk, they are instead referred to as ghost ships. Types Historic wrecks are attractive to maritime archaeologists because they preserve historical information: for example, studying the wreck of revealed information about seafaring, warfare, and life in the 16th century. Military wrecks, caused by a skirmish at sea, are studied to find details about the historic event; they reveal much about the battle that occurred. Discoveries of treasure ships, often from the period of European colonisation, which sank in remote locations leaving few livin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau was claimed by Portugal from the 1450s to the 1970s. However, Portuguese control of the region was limited to forts along the coast. Portugal gained full control of the mainland after the pacification campaigns of 1912-15, the offshore Bijago islands weren't colonised until 1936 establishing total control of Guinea-Bissau. Since independence in 1974, the country was controlled by a single-party system until 1991. Following the introduction of multi-party politics in 1991, the first multi-party elections were held in 1994. Pre-European Contact Empires and Kingdoms Kaabu Province of Imperial Mali (1200-1537) - Kaabu Empire (1537-1867) Origins Kaabu was established as a province of Mali Empire, Mali through the conquest of the Senegambia by the one of the generals of Sundiata Keita called Tiramakhan Traore, Tiramakhan Troare. According to oral tradition Tiramakhan went to the region in retaliation for an insult given to Sundiata by the Wolof King, resulting in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Man-made Disasters In Guinea-Bissau
Artificiality (the state of being artificial or manmade) is the state of being the product of intentional human manufacture, rather than occurring naturally through processes not involving or requiring human activity. Connotations Artificiality often carries with it the implication of being false, counterfeit, or deceptive. The philosopher Aristotle wrote in his ''Rhetoric'': However, artificiality does not necessarily have a negative connotation, as it may also reflect the ability of humans to replicate forms or functions arising in nature, as with an artificial heart or artificial intelligence. Political scientist and artificial intelligence expert Herbert A. Simon observes that "some artificial things are imitations of things in nature, and the imitation may use either the same basic materials as those in the natural object or quite different materials.Herbert A. Simon, ''The Sciences of the Artificial'' (1996), p. 4. Simon distinguishes between the artificial and the synthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Público (Portugal)
''Público'' (; English: ''Public'') is a Portuguese daily national newspaper of record published in Lisbon, Portugal. History and profile ''Público'' was first published on 5 March 1990. The paper was founded by Sonae and is owned by the Sonae group. In 1992 Italian media company Repubblica International Holding SA, a subsidiary of Gruppo Editoriale L'Espresso, acquired 16.75% of the paper. ''Público'' is published in tabloid format and has its headquarters in Lisbon. The paper is known as a publication of the French school with extensive texts and few illustrations. Its first editor-in-chief was Vicente Jorge Silva, formerly sub-editor-in-chief at ''Expresso''. José Manuel Fernandes also served as the editor-in-chief of the paper. Since 2009 Bárbara Reis has served as the editor-in-chief. ''Público'' is one of the first Portuguese mainstream newspapers to have an online edition which was started in 1995. Its online edition was free and included almost all the articles fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Grave
A mass grave is a grave containing multiple human corpses, which may or may not be identified prior to burial. The United Nations has defined a criminal mass grave as a burial site containing three or more victims of execution, although an exact definition is not unanimously agreed upon. Mass graves are usually created after many people die or are killed, and there is a desire to bury the corpses quickly for sanitation concerns. Although mass graves can be used during major conflicts such as war and crime, in modern times they may be used after a famine, epidemic, or natural disaster. In disasters, mass graves are used for infection and disease control. In such cases, there is often a breakdown of the social infrastructure that would enable proper identification and disposal of individual bodies. History Mass or communal burial was a common practice before the development of a dependable crematory chamber by Ludovico Brunetti in 1873. In ancient Rome waste and dead bodies of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Coimbra
The University of Coimbra (UC; pt, Universidade de Coimbra, ) is a Public university, public research university in Coimbra, Portugal. First established in Lisbon in 1290, it went through a number of relocations until moving permanently to Coimbra in 1537. The university is among the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, oldest universities in continuous operation in the world, the oldest in Portugal, and played an influential role in the development of higher education in the Lusophone, Portuguese-speaking world. In 2013, UNESCO declared the university a World Heritage Site, noting its architecture, unique culture and traditions, and historical role. The contemporary university is organized into eight faculty (division), faculties, granting bachelor's (''licenciado''), master's (''mestre'') and doctorate (''doutor'') degrees in nearly all major fields. It lends its name to the Coimbra Group of European research universities founded in 1985, of which it was a fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Diving
Underwater divers may be employed in any branch of an armed force, including the navy, army, marines, air force and coast guard. Scope of operations includes: search and recovery, search and rescue, hydrographic survey, explosive ordnance disposal, demolition , underwater engineering, salvage, ships husbandry, reconnaissance, infiltration, sabotage, counterifiltration, underwater combat and security. History of military diving Military divers are essential to many missions and campaigns. Combat and demolition work, underwater and coastal reconnaissance, ordnance disposal, search and rescue, salvage operations, construction, ship maintenance and underwater engineering. Every branch of the U.S. military employs divers, and more than 40 nations have military diving units. Military diving is an occupation that has risks and responsibilities beyond those of other professional diving. Research and development in military diving equipment and procedures often eventually contributes to r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
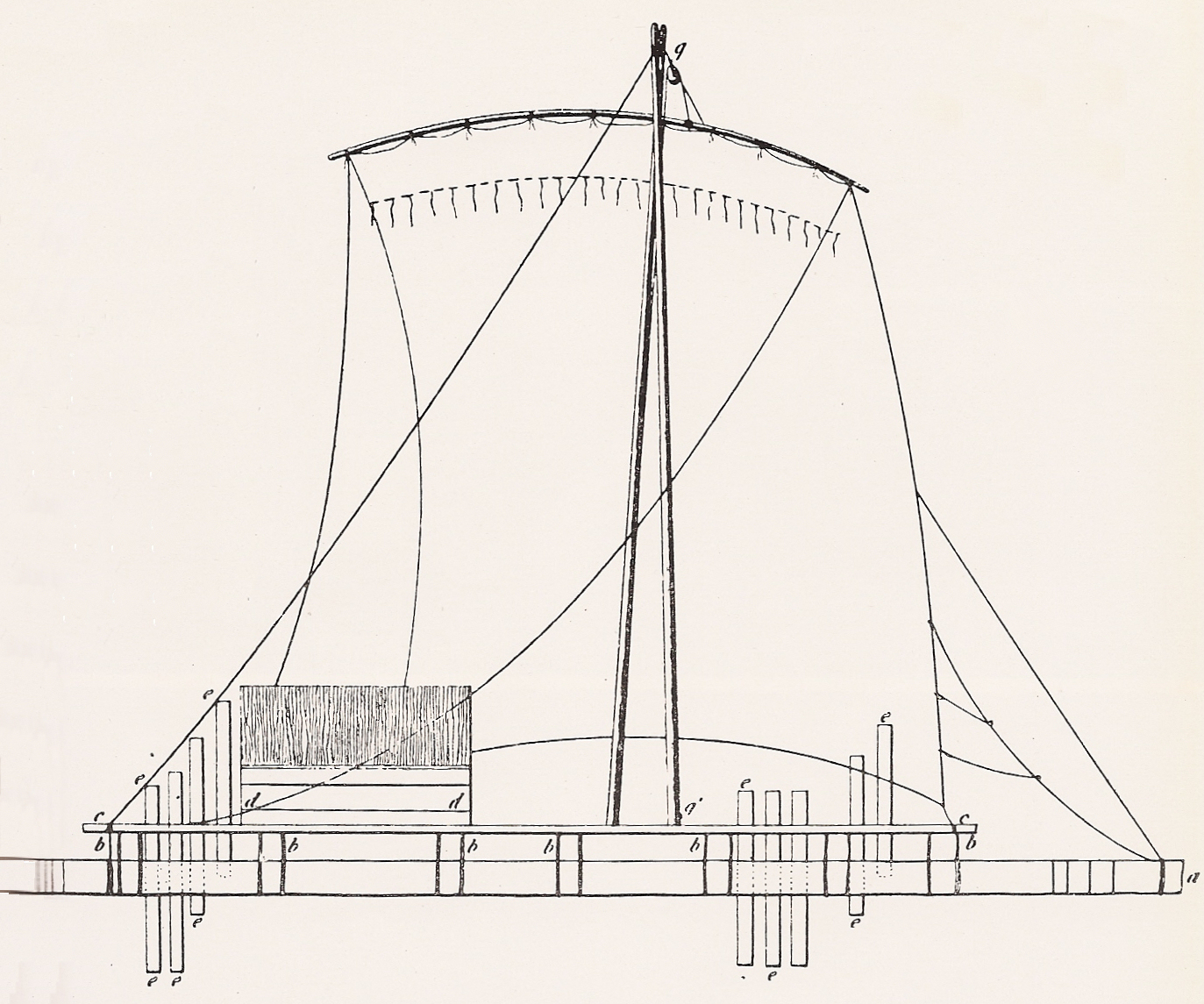
Raft
A raft is any flat structure for support or transportation over water. It is usually of basic design, characterized by the absence of a hull. Rafts are usually kept afloat by using any combination of buoyant materials such as wood, sealed barrels, or inflated air chambers (such as pontoons), and are typically not propelled by an engine. Rafts are an ancient mode of transport; naturally-occurring rafts such as entwined vegetation and pieces of wood have been used to traverse water since the dawn of humanity. Human-made rafts Traditional or primitive rafts were constructed of wood or reeds. Modern rafts may also use pontoons, drums, or extruded polystyrene Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a ... blocks. Inflatable rafts up to the 20th century used flotation chambers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
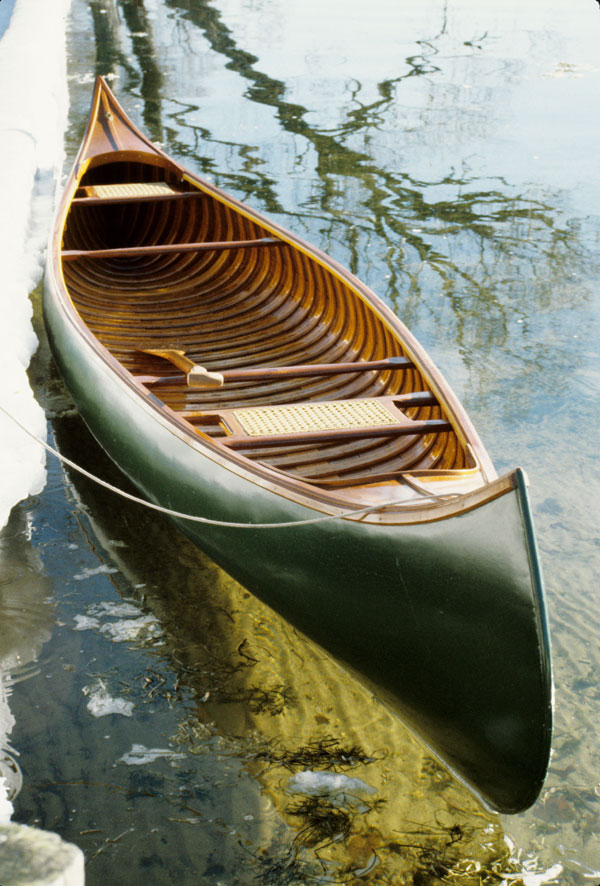
Canoes
A canoe is a lightweight narrow water vessel, typically pointed at both ends and open on top, propelled by one or more seated or kneeling paddlers facing the direction of travel and using a single-bladed paddle. In British English, the term ''canoe'' can also refer to a kayak, while canoes are called Canadian or open canoes to distinguish them from kayaks. Canoes were developed by cultures all over the world, including some designed for use with sails or outriggers. Until the mid-19th century, the canoe was an important means of transport for exploration and trade, and in some places is still used as such, sometimes with the addition of an outboard motor. Where the canoe played a key role in history, such as the Northern United States, Canada, and New Zealand, it remains an important theme in popular culture. Canoes are now widely used for competition and pleasure, such as racing, whitewater, touring and camping, freestyle and general recreation. Canoeing has been part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Guinea
Portuguese Guinea ( pt, Guiné), called the Overseas Province of Guinea from 1951 until 1972 and then State of Guinea from 1972 until 1974, was a West African colony of Portugal from 1588 until 10 September 1974, when it gained independence as Guinea-Bissau. Slave trade The Portuguese Crown commissioned its navigators to explore the Atlantic coast of West Africa in the 1430s, to find sources of gold. At that time the gold trade was controlled by Morocco. Muslim caravans across the Sahara also carried salt, kola, textiles, fish, grain, and slaves. The navigators first passed the obstruction of Cape Bojador in 1437 and were able to explore the West African coast as far as Sierra Leone by 1460 and colonize the Portuguese Cape Verde, Cape Verde islands beginning in 1456.C.R. Boxer, (1977). The Portuguese seaborne empire, 1415–1825, pp. 26–7, 30 London, Hutchinson & Co. The gold ultimately came from the upper reaches of the Niger and Volta Rivers and the Portuguese crown wanted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_1978%2C_MiNr_2293.jpg)