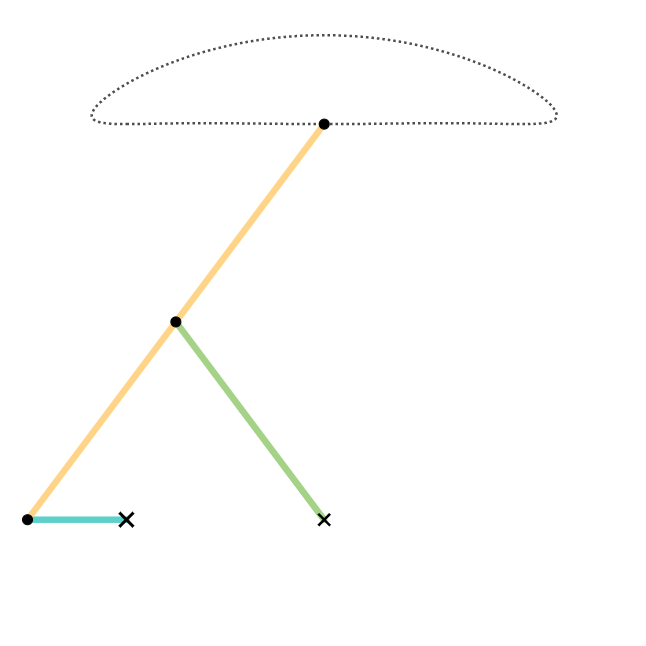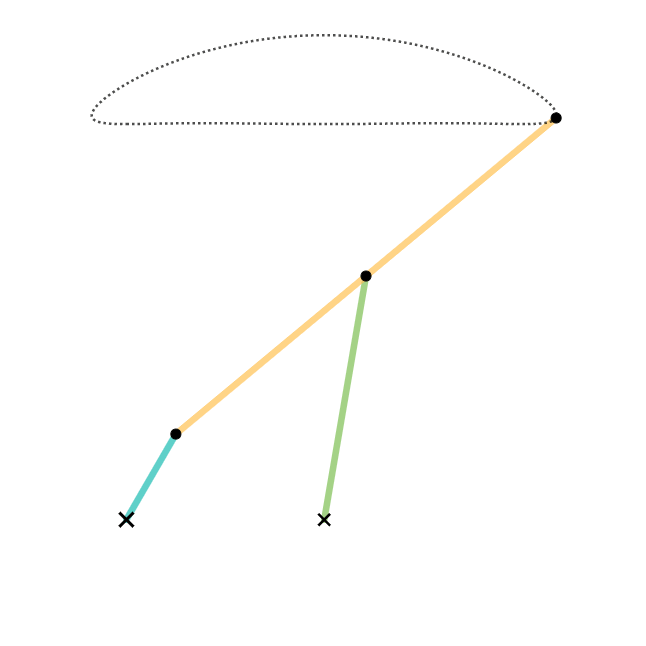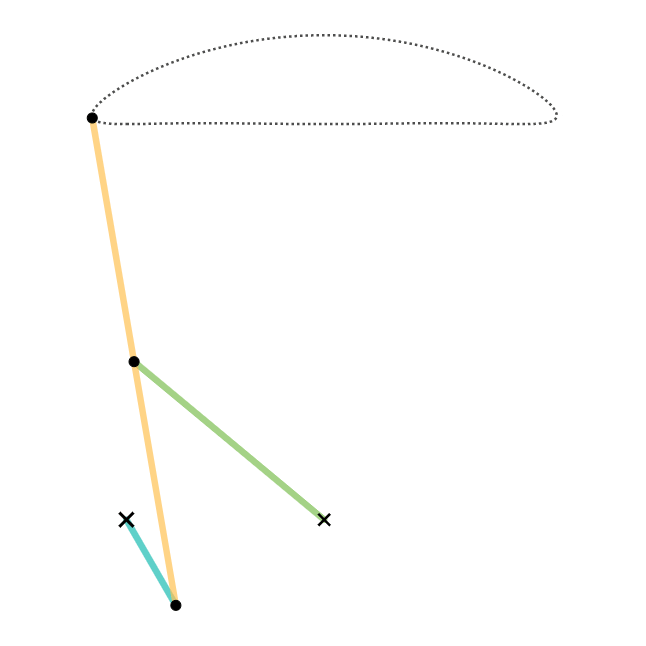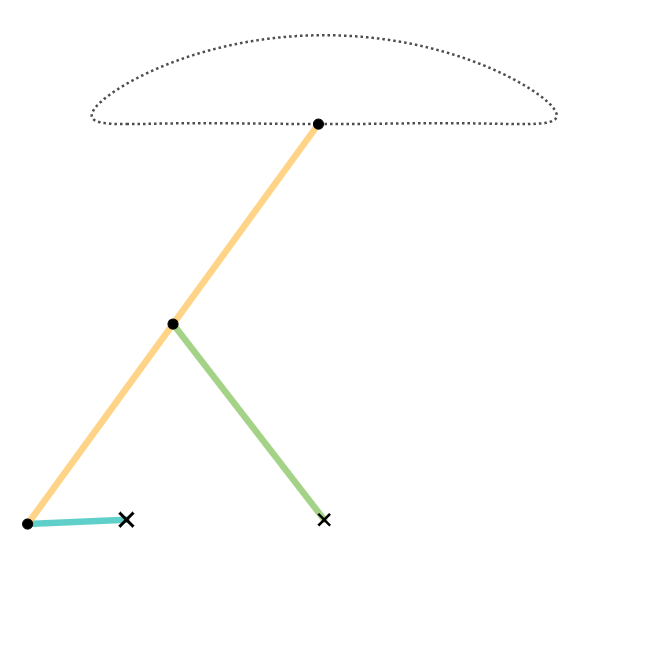|
Chebyshev Lambda Linkage
In kinematics, the Chebyshev Lambda Linkage is a four-bar linkage that converts rotational motion to approximate straight-line motion with approximate constant velocity. It is so-named because it looks like a lowercase Greek letter lambda (λ). The precise design trades off straightness, lack of acceleration, and the proportion of the driving rotation that is spent in the linear portion of the full curve. The example to the right spends over half of the cycle in the near straight portion. Coupler (link 3) point stays within 1% positional tolerance with intersecting the ideal straight line 6 times. The linkage was first shown in Paris on the Exposition Universelle (1878) as "The Plantigrade Machine". The Chebyshev Lambda Linkage is a cognate linkage of the Chebyshev linkage. The Chebyshev Lambda Linkage is used in vehicle suspension mechanisms, walking robots and rover wheel mechanisms. In 2004, a study completed as a Master of Science Thesis at Izmir Institute of Technology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chebyshev Lambda Linkage
In kinematics, the Chebyshev Lambda Linkage is a four-bar linkage that converts rotational motion to approximate straight-line motion with approximate constant velocity. It is so-named because it looks like a lowercase Greek letter lambda (λ). The precise design trades off straightness, lack of acceleration, and the proportion of the driving rotation that is spent in the linear portion of the full curve. The example to the right spends over half of the cycle in the near straight portion. Coupler (link 3) point stays within 1% positional tolerance with intersecting the ideal straight line 6 times. The linkage was first shown in Paris on the Exposition Universelle (1878) as "The Plantigrade Machine". The Chebyshev Lambda Linkage is a cognate linkage of the Chebyshev linkage. The Chebyshev Lambda Linkage is used in vehicle suspension mechanisms, walking robots and rover wheel mechanisms. In 2004, a study completed as a Master of Science Thesis at Izmir Institute of Technology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognate Linkage
In kinematics, cognate linkages are linkages that ensure the same coupler curve geometry or input-output relationship, while being dimensionally dissimilar. In case of four-bar linkage coupler cognates, the Roberts–Chebyshev Theorem, after Samuel Roberts and Pafnuty Chebyshev, Retrieved 2012-10-12 states that each coupler curve can be generated by three different four-bar linkages. These four-bar linkages can be constructed using similar triangles and parallelograms, and the Cayley diagram (named after Arthur Cayley). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straight Line Mechanism
A straight-line mechanism is a Mechanism (engineering), mechanism that converts any type of rotary or angular motion to perfect or near-perfect straight-line motion, or ''vice-versa''. Straight-line motion is linear motion of definite length or "stroke", every forward stroke being followed by a return stroke, giving reciprocating motion. The first such mechanism, patented in 1784 by James Watt, produced approximate straight-line motion, referred to by Watt as Watt's linkage, parallel motion. Straight-line mechanisms are used in a variety of applications, such as engines, vehicle suspensions, walking robots, and rover wheels. History In the late eighteenth century, before the development of the Planer (metalworking), planer and the milling machine, it was extremely difficult to machine straight, flat surfaces. During that era, much thought was given to the problem of attaining a straight-line motion, as this would allow the flat surfaces to be machined. To find a solution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leg Mechanism
A leg mechanism (walking mechanism) is a mechanical system designed to provide a propulsive force by intermittent frictional contact with the ground. This is in contrast with wheels or continuous tracks which are intended to maintain continuous frictional contact with the ground. Mechanical legs are linkages that can have one or more actuators, and can perform simple planar or complex motion. Compared to a wheel, a leg mechanism is potentially better fitted to uneven terrain, as it can step over obstacles. An early design for a leg mechanism called the ''Plantigrade Machine'' by Pafnuty Chebyshev was shown at the Exposition Universelle (1878). The original engravings for this leg mechanism are available. The design of the leg mechanism for the Ohio State Adaptive Suspension Vehicle (ASV) is presented in the 1988 book ''Machines that Walk''. In 1996, W-B. Shieh presented a design methodology for leg mechanisms. The artwork of Theo Jansen, see Jansen's linkage, has been pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoeckens Linkage
In kinematics, the Hoecken linkage (named for Karl Hoecken) is a four-bar linkage that converts rotational motion to approximate straight-line motion. The Hoecken linkage is a cognate linkage of the Chebyshev linkage and Chebyshev's Lambda Mechanism. The linkage was first published in 1926. A generalization of the Hoecken linkage is Wittgenstein's rod. See also *Chebyshev linkage and Chebyshev lambda linkage, linkages that produce a very similar locus without the need of a sliding joint. *Straight line mechanism *Four-bar linkage In the study of mechanisms, a four-bar linkage, also called a four-bar, is the simplest closed- chain movable linkage. It consists of four bodies, called ''bars'' or ''links'', connected in a loop by four joints. Generally, the joints are configu ... References External links Straight line mechanisms Linkages (mechanical) {{technology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognate Linkage
In kinematics, cognate linkages are linkages that ensure the same coupler curve geometry or input-output relationship, while being dimensionally dissimilar. In case of four-bar linkage coupler cognates, the Roberts–Chebyshev Theorem, after Samuel Roberts and Pafnuty Chebyshev, Retrieved 2012-10-12 states that each coupler curve can be generated by three different four-bar linkages. These four-bar linkages can be constructed using similar triangles and parallelograms, and the Cayley diagram (named after Arthur Cayley). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chebyshev Linkage
In kinematics, Chebyshev's linkage is a four-bar linkage that converts rotational motion to approximate linear motion. It was invented by the 19th-century mathematician Pafnuty Chebyshev, who studied theoretical problems in kinematic mechanisms. One of the problems was the construction of a linkage that converts a rotary motion into an approximate straight-line motion (a straight line mechanism). This was also studied by James Watt in his improvements to the steam engine, which resulted in Watt's linkage. – Cross link straight-line mechanism Equations of motion The motion of the linkage can be constrained to an input angle that may be changed through velocities, forces, etc. The input angles can be either link ''L''2 with the horizontal or link ''L''4 with the hori ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exposition Universelle (1878)
The third Paris World's Fair, called an Exposition Universelle in French, was held from 1 May to 10 November 1878. It celebrated the recovery of France after the 1870–71 Franco-Prussian War. Construction The buildings and the fairgrounds were somewhat unfinished on opening day, as political complications had prevented the French government from paying much attention to the exhibition until six months before it was due to open. However, efforts made in April were prodigious, and by 1 June, a month after the formal opening, the exhibition was finally completed. This exposition was on a far larger scale than any previously held anywhere in the world. It covered over , the main building in the Champ de Mars and the hill of Chaillot, occupying . The Gare du Champ de Mars was rebuilt with four tracks to receive rail traffic occasioned by the exposition. The Pont d'Iéna linked the two exhibition sites along the central allée. The French exhibits filled one-half of the entir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acceleration
In mechanics, acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Accelerations are vector quantities (in that they have magnitude and direction). The orientation of an object's acceleration is given by the orientation of the ''net'' force acting on that object. The magnitude of an object's acceleration, as described by Newton's Second Law, is the combined effect of two causes: * the net balance of all external forces acting onto that object — magnitude is directly proportional to this net resulting force; * that object's mass, depending on the materials out of which it is made — magnitude is inversely proportional to the object's mass. The SI unit for acceleration is metre per second squared (, \mathrm). For example, when a vehicle starts from a standstill (zero velocity, in an inertial frame of reference) and travels in a straight line at increasing speeds, it is accelerating in the direction of travel. If the vehicle turns, an acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambda
Lambda (}, ''lám(b)da'') is the 11th letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiced alveolar lateral approximant . In the system of Greek numerals, lambda has a value of 30. Lambda is derived from the Phoenician Lamed . Lambda gave rise to the Latin L and the Cyrillic El (Л). The ancient grammarians and dramatists give evidence to the pronunciation as () in Classical Greek times. In Modern Greek, the name of the letter, Λάμδα, is pronounced . In early Greek alphabets, the shape and orientation of lambda varied. Most variants consisted of two straight strokes, one longer than the other, connected at their ends. The angle might be in the upper-left, lower-left ("Western" alphabets) or top ("Eastern" alphabets). Other variants had a vertical line with a horizontal or sloped stroke running to the right. With the general adoption of the Ionic alphabet, Greek settled on an angle at the top; the Romans put the angle at the lower-left. The HTML 4 character entity re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |