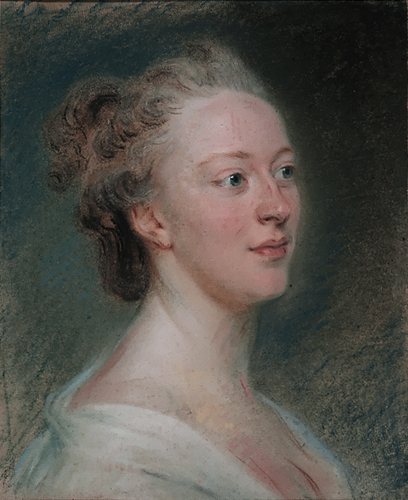|
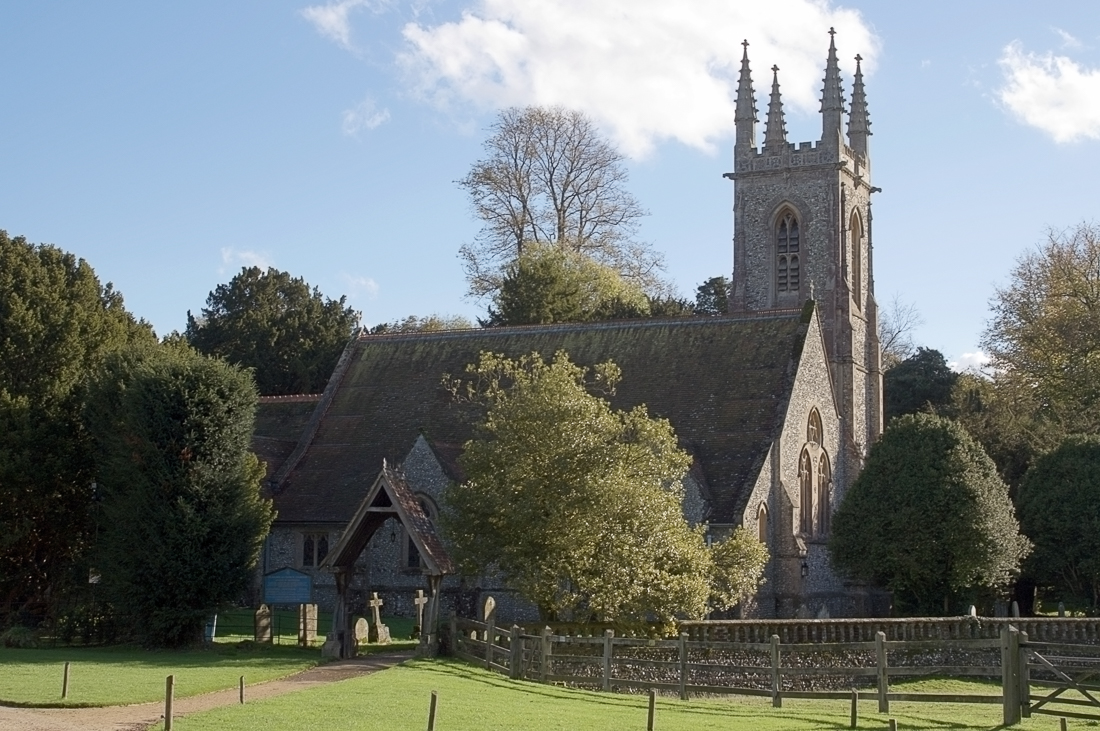
Chawton House Library
Chawton House is a Grade II* listed Elizabethan manor house in Hampshire. It is run as a historic property and also houses the research library of The Centre for the Study of Early Women's Writing, 1600–1830, using the building's connection with the English novelist Jane Austen. Chawton House, just outside the village of that name, used to be the home of the writer's brother, Edward Austen Knight. It remained a private family home into the late 20th century. At the turn of the millennium it was purchased by a charitable trust, extensively restored, and re-opened as a research centre. The centre, which runs study programmes in association with the nearby University of Southampton, incorporates a significant library, a collection of over 9000 books and related manuscripts. The house is now open to visitors, as well as library readers, for tours and during public events. The house It is set in of Hampshire countryside, and is used for conferences, filming and more rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chawton
Chawton is a village and civil parish in the East Hampshire district of Hampshire, England. The village lies within the South Downs National Park and is famous as the home of Jane Austen for the last eight years of her life. History Chawton's recorded history begins in the Domesday survey of 1086. The village held nineteen free residents, eight smallholders, six slaves (part of the sixty-seven slaves in the area from Alresford to the ridge parishes) and woodland with fifty pigs. In the 13th century, there was a royal manor house. The owner, John St John, served as deputy to Edward I in Scotland. Henry III visited the manor on over forty occasions. The descendants of John Knight, who built the present Chawton House at the time of the Armada (1588), added to it and modified the landscape in ways that reflect changes in politics, religion and taste. One of those descendants was Elizabeth Knight, whose progresses were marked by the ringing of church bells and whose two husbands both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cisco Systems
Cisco Systems, Inc., commonly known as Cisco, is an American-based multinational corporation, multinational digital communications technology conglomerate (company), conglomerate corporation headquartered in San Jose, California. Cisco develops, manufactures, and sells networking hardware, software, telecommunications equipment and other high-technology services and products. Cisco specializes in specific tech markets, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), internet domain, domain security, videoconferencing, and energy management with List of Cisco products, leading products including Webex, OpenDNS, XMPP, Jabber, Duo Security, and Cisco Jasper, Jasper. Cisco is one of the List of largest technology companies by revenue, largest technology companies in the world ranking 74 on the Fortune 100 with over $51 billion in revenue and nearly 80,000 employees. Cisco Systems was founded in December 1984 by Leonard Bosack and Sandy Lerner, two Stanford University computer scientists who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maria Edgeworth
Maria Edgeworth (1 January 1768 – 22 May 1849) was a prolific Anglo-Irish novelist of adults' and children's literature. She was one of the first realist writers in children's literature and was a significant figure in the evolution of the novel in Europe. She held views on estate management, politics and education, and corresponded with some of the leading literary and economic writers, including Sir Walter Scott and David Ricardo. Life Early life Maria Edgeworth was born at Black Bourton, Oxfordshire. She was the second child of Richard Lovell Edgeworth (who eventually fathered 19 children by four wives) and Anna Maria Edgeworth (''née'' Elers); Maria was thus an aunt of Francis Ysidro Edgeworth. She spent her early years with her mother's family in England, living at The Limes (now known as Edgeworth House) in Northchurch, by Berkhamsted in Hertfordshire. Her mother died when Maria was five, and when her father married his second wife Honora Sneyd in 1773, she went with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isabelle De Charrière
Isabelle de Charrière (20 October 174027 December 1805), known as Belle van Zuylen in the Netherlands, née Isabella Agneta Elisabeth van Tuyll van Serooskerken, and adameIsabelle de Charrière (married name) elsewhere, was a Dutch and Swiss writer of the Enlightenment who lived the latter half of her life in Colombier, Neuchâtel. She is now best known for her letters and novels, although she also wrote pamphlets, music and plays. She took a keen interest in the society and politics of her age, and her work around the time of the French Revolution is regarded as being of particular interest. Early life Isabelle van Tuyll van Serooskerken was born in Zuylen Castle in Zuilen near Utrecht in the Netherlands, to Diederik Jacob van Tuyll van Serooskerken (1707–1776), and Jacoba Helena de Vicq (1724–1768). She was the eldest of seven children. Her parents were described by the Scots author James Boswell, then a student in law in Utrecht and one of her suitors, as "one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margaret Cavendish, Duchess Of Newcastle-upon-Tyne
Margaret Lucas Cavendish, Duchess of Newcastle-upon-Tyne (1623 – 15 December 1673) was an English philosopher, poet, scientist, fiction writer and playwright. Her husband, William Cavendish, 1st Duke of Newcastle-upon-Tyne, was Royalist commander in Northern England during the First English Civil War and in 1644 went into self-imposed exile in France. Margaret accompanied him and remained abroad until the Stuart Restoration in 1660. She wrote in her own name in a period when most women writers remained anonymous. Background Born Margaret Lucas to Sir Thomas Lucas (1573–1625) and Elizabeth Leighton (died 1647), she was the youngest child of the family. She had four sisters and three brothers, the royalists Sir John Lucas, Sir Thomas Lucas and Sir Charles Lucas, who owned the manor of St John's Abbey, Colchester. She became an attendant on Queen Henrietta Maria and travelled with her into exile in France, living for a time at the court of the young King Louis XIV. She b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarah Burney
Sarah Harriet Burney (29 August 1772 – 8 February 1844) was an English novelist, the daughter of musicologist and composer Charles Burney, and half-sister of the novelist and diarist Frances Burney (Madame d'Arblay). She had some intermittent success with her novels. Life Sarah Burney was born at Lynn Regis, now King's Lynn, and baptised there on 29 September 1772. Her mother, Elizabeth Allen, was the second wife of Charles Burney, and relations within the family were often strained. Sarah was brought up in Norfolk by relations of her mother until 1775, when she joined the Burney household in London. This reunion features in a letter from Frances Burney to the dramatist Samuel Crisp: "Now for family.... Little Sally is come home, and is one of the most innocent, artless, ''queer'' little things you ever saw, and altogether she is very sweet, and a very engaging child." In 1781 she was sent with her brother Richard (1768–1808) to Corsier-sur-Vevey, Switzerland, to complete he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frances Burney
Frances Burney (13 June 1752 – 6 January 1840), also known as Fanny Burney and later Madame d'Arblay, was an English satirical novelist, diarist and playwright. In 1786–1790 she held the post as "Keeper of the Robes" to Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, George III's queen. In 1793, aged 41, she married a French exile, General Alexandre d'Arblay. After a long writing career and wartime travels that stranded her in France for over a decade, she settled in Bath, England, where she died on 6 January 1840. The first of her four novels, ''Evelina'' (1778), was the most successful and remains her most highly regarded. Most of her plays were not performed in her lifetime. She wrote a memoir of her father (1832) and many letters and journals that have been gradually published since 1889. Overview of career Frances Burney was a novelist, diarist and playwright. In all, she wrote four novels, eight plays, one biography and twenty-five volumes of journals and letters. She has gained c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Brunton
Mary Brunton (née Balfour) (1 November 1778 – 7 December 1818) was a Scottish novelist, whose work has been seen as redefining femininity. Fay Weldon praised it as "rich in invention, ripe with incident, shrewd in comment, and erotic in intention and fact." Life Mary Balfour (married name Brunton) was the daughter of Colonel Thomas Balfour of Elwick, a British Army officer, and Frances Ligonier, daughter of Colonel Francis Ligonier and sister of the second earl of Ligonier. She was born on 1 November 1778 on Burray in the Orkney Islands. Her early education was limited, but her mother taught her music, Italian and French.Isabelle Bour: Brunton , Mary... In: ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' (Oxford: OUP, 2004; online e. October 2005)Retrieved 18 November 2010. Subscription required./ref> About 1798, she met the Rev. Alexander Brunton, a Church of Scotland minister. Although her mother disapproved of the match, she eloped with Brunton on 4 December 1798, when he r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frances Brooke
Frances Brooke ( Moore; 12 January 1724 – 23 January 1789) was an English novelist, essayist, playwright and translator. Hers was the first English novel known to have been written in Canada. Biography Frances Moore was born in Claypole, Lincolnshire, England, the daughter of a clergyman. She was only three years old when her father died. Her mother's death followed soon after. By the late 1740s, she had moved to London, where she embarked on her career as a poet and playwright. She did not drew attention until she published her essay serial ''The Old Maid''. Under the pseudonym of Mary Singleton, Spinster, she edited 37 issues of this weekly periodical (1755–1756), which was patterned after ''The Spectator''. In 1756 she married Rev. Dr John Brooke, rector at Colney, Norfolk. The following year he left for Canada as a military chaplain while his wife remained in England. In 1763 she wrote her first novel, ''The History of Lady Julia Mandeville''. In the same year Brooke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphra Behn
Aphra Behn (; bapt. 14 December 1640 – 16 April 1689) was an English playwright, poet, prose writer and translator from the Restoration era. As one of the first English women to earn her living by her writing, she broke cultural barriers and served as a literary role model for later generations of women authors. Rising from obscurity, she came to the notice of Charles II, who employed her as a spy in Antwerp. Upon her return to London and a probable brief stay in debtors' prison, she began writing for the stage. She belonged to a coterie of poets and famous libertines such as John Wilmot, Lord Rochester. Behn wrote under the pastoral pseudonym Astrea. During the turbulent political times of the Exclusion Crisis, she wrote an epilogue and prologue that brought her into legal trouble; she thereafter devoted most of her writing to prose genres and translations. A staunch supporter of the Stuart line, she declined an invitation from Bishop Burnet to write a welcoming p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penelope Aubin
Penelope Aubin (c. 1679 – 1738?) was an English novelist, poet, and translator. She published seven novels between 1721 and 1728. Aubin published poetry in 1707 and turned to novels in 1721; she translated French works in the 1720s, spoke publicly on moral and political issues at her Lady's Oratory in 1729, and wrote a play in 1730. Aubin died in April 1738, survived by her husband until his death in April 1740. After the author's death, her works were gathered and published as ''A Collection of Entertaining Histories and Novels, Designed to Promote the Cause of Virtue and Honor''. Aubin's works have a long history after her death, being both plagiarised and published transatlantically. She is one of a number of eighteenth-century women writers whose works and biography is being more rigorously explored by modern scholars. Early life Penelope Aubin née Charleton's exact birth date remains unknown; she was the illegitimate daughter of Sir Richard Temple of Stowe and most likely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Astell
Mary Astell (12 November 1666 – 11 May 1731) was an English protofeminist writer, philosopher, and rhetorician. Her advocacy of equal educational opportunities for women has earned her the title "the first English feminist."Batchelor, Jennie,Mary Astell. ''The Literary Encyclopedia''. 21 March 2002. Accessed 6 July 2008. Early life Few records of Mary Astell's life have survived. As biographer Ruth Perry explains: "as a woman she had little or no business in the world of commerce, politics, or law. She was born, she died; she owned a small house for some years; she kept a bank account; she helped to open a charity school in Chelsea: these facts the public listings can supply." Only four of her letters were saved and these because they had been written to important men of the period. Researching the biography, Perry uncovered more letters and manuscript fragments, but she notes that if Astell had not written to wealthy aristocrats who could afford to pass down entire estate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |