|
Charybdis Feriata
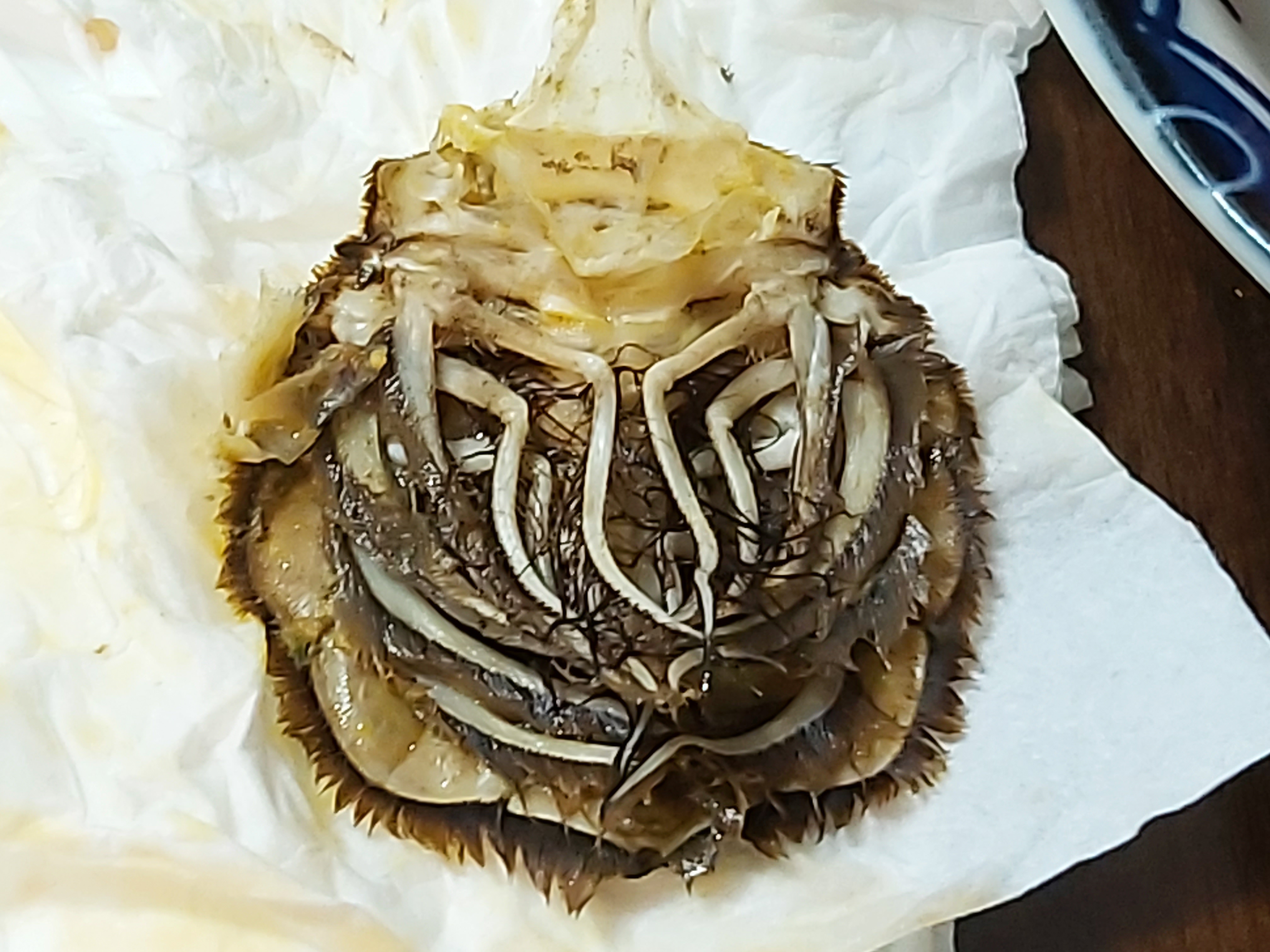
''Charybdis feriata'', the crucifix crab, is a species of swimming crab in the family Portunidae. It is found in the tropical and subtropical Indo-Pacific region. Description This crab grows to a width of about . The body is fan-shaped and the carapace is smooth, with some granular transverse lines. The front of the carapace bears six triangular teeth of similar size, and each side of the carapace bears six larger, truncated teeth which vary in size. The eyes are close together. There are three spines on the carpus of the cheliped (pincer leg), and smaller spines on the other joints. The hindmost pair of pleopods (walking legs) are paddle-shaped and are used in propulsion when swimming. The carapace is boldly patterned in cream and brown, and often bears a distinctive white cross on a dark background in the centre. The pincers are brown with white patches and the legs have brown and white bands. This crab gets its common name from the cross-shaped mark on the carapace. Traditi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was born in Råshult, the countryside of Småland, in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he continued to collect an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th Edition Of Systema Naturae
The 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' is a book written by Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus and published in two volumes in 1758 and 1759, which marks the starting point of zoological nomenclature. In it, Linnaeus introduced binomial nomenclature for animals, something he had already done for plants in his 1753 publication of '' Species Plantarum''. Starting point Before 1758, most biological catalogues had used polynomial names for the taxa included, including earlier editions of ''Systema Naturae''. The first work to consistently apply binomial nomenclature across the animal kingdom was the 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae''. The International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature therefore chose 1 January 1758 as the "starting point" for zoological nomenclature, and asserted that the 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' was to be treated as if published on that date. Names published before that date are unavailable, even if they would otherwise satisfy the rules. The only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portunidae
Portunidae is a family of crabs which contains the swimming crabs. Description Portunid crabs are characterised by the flattening of the fifth pair of legs into broad paddles, which are used for swimming. This ability, together with their strong, sharp claws, allows many species to be fast and aggressive predators. Examples Its members include many well-known shoreline crabs, such as the European shore crab (''Carcinus maenas''), blue crab (''Callinectes sapidus''), and velvet crab ('' Necora puber''). Two genera in the family are contrastingly named ''Scylla'' and ''Charybdis''; the former contains the economically important species black crab (''Scylla serrata'') and ''Scylla paramamosain''. Taxonomy The circumscription of the family varies, with some authors treating "Carcinidae", "Catoptridae" and "Macropipidae" as separate families, and others considering them subfamilies of a wider Portunidae. Swimming crabs reach their greatest species diversity in the Pacific and Indian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carapace
A carapace is a Dorsum (biology), dorsal (upper) section of the exoskeleton or shell in a number of animal groups, including arthropods, such as crustaceans and arachnids, as well as vertebrates, such as turtles and tortoises. In turtles and tortoises, the underside is called the plastron. Crustaceans In crustaceans, the carapace functions as a protective cover over the cephalothorax (i.e., the fused head and thorax, as distinct from the abdomen behind). Where it projects forward beyond the eyes, this projection is called a rostrum (anatomy), rostrum. The carapace is Calcification, calcified to varying degrees in different crustaceans. Zooplankton within the phylum Crustacea also have a carapace. These include Cladocera, ostracods, and Isopoda, isopods, but isopods only have a developed "cephalic shield" carapace covering the head. Arachnids In arachnids, the carapace is formed by the fusion of prosomal tergites into a single Plate (animal anatomy), plate which carries the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chela (organ)
A chela ()also called a claw, nipper, or pinceris a pincer (biology), pincer-like organ at the end of certain limbs of some arthropods. The name comes from Ancient Greek , through New Latin '. The plural form is chelae. Legs bearing a chela are called chelipeds. Another name is ''claw'' because most chelae are curved and have a sharp point like a claw. Chelae can be present at the tips of arthropod legs as well as their pedipalps. Chelae are distinct from spider chelicerae in that they do not contain venomous glands and cannot distribute venom. See also * Pincer (biology) * Pincer (tool) References Arthropod anatomy {{Arthropod-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decapod Anatomy
The decapod (crustaceans such as a crab, lobster, shrimp or prawn) is made up of 20 body segments grouped into two main body parts: the cephalothorax and the pleon (abdomen). Each segment may possess one pair of appendages, although in various groups these may be reduced or missing. They are, from head to tail: Cephalothorax Head # antennules # antennae #mandibles # first maxillae # second maxillae The head also bears the (usually stalked) compound eyes. The distal portion of a mandible or maxilla which has a sensory function is known as a palp. Thorax / pereon #first maxillipeds #second maxillipeds #third maxillipeds #first pereiopods #second pereiopods #third pereiopods #fourth pereiopods #fifth pereiopods Maxillipeds are appendages modified to function as mouthparts. Particularly in the less advanced decapods, these can be very similar to the pereiopods. Pereiopods are primarily walking legs and are also used for gathering food. They are also the ten legs from which decapods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Xavier
Francis Xavier (born Francisco de Jasso y Azpilicueta; Latin: ''Franciscus Xaverius''; Basque: ''Frantzisko Xabierkoa''; French: ''François Xavier''; Spanish: ''Francisco Javier''; Portuguese: ''Francisco Xavier''; 7 April 15063 December 1552), venerated as Saint Francis Xavier, was a Spanish Catholic missionary and saint who was a co-founder of the Society of Jesus. Born in Javier (Xavier in Old Spanish and in Navarro-Aragonese, or Xabier, a Basque word meaning "new house"), in the Kingdom of Navarre (in present-day Spain), he was a companion of Ignatius of Loyola and one of the first seven Jesuits who took vows of poverty and chastity at Montmartre, Paris in 1534. He led an extensive mission into Asia, mainly the Portuguese Empire in the East, and was influential in evangelisation work, most notably in early modern India. He was extensively involved in the missionary activity in Portuguese India. In 1546, Francis Xavier proposed the establishment of the Goan Inquisition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholics
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Australian Museum
The Western Australian Museum is a statutory authority within the Culture and the Arts Portfolio, established under the ''Museum Act 1969''. The museum has six main sites. The state museum, now known as WA Museum Boola Bardip, officially re-opened on 21 November 2020 in the Perth Cultural Centre. The other sites are: the WA Maritime Museum and WA Shipwrecks Museum in Fremantle, the Museum of the Great Southern in Albany, the Museum of Geraldton in Geraldton, and the Museum of the Goldfields in Kalgoorlie-Boulder. History Established in 1891 in the Old Perth Gaol, it was known as the Geological Museum and consisted of geological collections. In 1892, ethnological and biological exhibits were added, and in 1897, the museum officially became the Western Australian Museum and Art Gallery. The museum employed collectors to obtain series of specimens; Tunney ventured across the state from 1895 to 1909 obtaining animals and, later, the tools and artefacts of the indigenous inhabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portunoidea
__NOTOC__ Portunoidea is a superfamily of crabs that includes the family Portunidae, the swimming crabs. Which other crab families are also placed here is a matter of some contention, and may be revised following molecular phylogenetic analyses. Description Their rather flat and smooth carapace is usually wider than long and of hexagonal, subhexagonal, rectangular, or transversely ovate shape. It is usually widest between the hindmost spines of the forward rim; there may be up to 9 pairs of these spines, with a few smaller ones right above the head, but they are missing altogether in some species. In some, the first maxilliped's endopod is lobed, forming the characteristic portunid lobe. The chelipeds are usually robust, and in some the last pereiopod pair has ovate dactyls. The sutures of the sternum between segments 4 to 8 are usually incomplete, and in the Portunidae, the eighth sternite is usually visible if seen from below and has a penial groove. In males, the abdomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustaceans Described In 1758
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
