|
Charro (Mexican Politics)
{{Unreferenced, date=June 2009 In Mexican politics and labor, a ''charro'' or ''líder charro'' ("charro leader") is a government-appointed union boss. Dynamics Mexico has a long tradition of government control and cooptation of unions and their leaders. Following the Mexican Revolution, the coalition of generals leading the nation under the auspices of the ''jefe máximo'' Plutarco Elías Calles that eventually became the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI) sought to keep the often fractious labor movement under control, and did so by repressing leaders and movements outside the dominant party. Following the "social revolution" of the Cárdenas years, the government sought to centralize power in the federal government, replacing local union bosses, who had earned the nickname ''pistoleros'' ("gunmen") through their strongarm policies, with college-educated professionals. Under Cárdenas, the Confederation of Mexican Workers (CTM), an umbrella of PRI-affiliated unions, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Politics Of Mexico
The politics of Mexico take place in a framework of a federal presidential representative democratic republic whose government is based on a congressional system, whereby the President of Mexico is both head of state and head of government, and of a multi-party system. The federal government represents the United Mexican States and is divided into three branches: executive, legislative and judicial, as established by the Political Constitution of the United Mexican States, published in 1917. The constituent states of the federation must also have a republican form of government based on a congressional system as established by their respective constitutions. The executive power is exercised by the executive branch, which is headed by the President, advised by a cabinet of secretaries that are independent of the legislature. Legislative power is vested upon the Congress of the Union, a two-chamber legislature comprising the Senate of the Republic and the Chamber of Deputies. Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of Mexico
The president of Mexico ( es, link=no, Presidente de México), officially the president of the United Mexican States ( es, link=no, Presidente de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos), is the head of state and head of government of Mexico. Under the Constitution of Mexico, the president heads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the Mexican Armed Forces. The current president is Andrés Manuel López Obrador, who took office on 1 December 2018. The office of the president is considered to be revolutionary, in the sense that the powers of office are derived from the Revolutionary Constitution of 1917. Another legacy of the Mexican Revolution is the Constitution's ban on re-election. Mexican presidents are limited to a single six-year term, called a '' sexenio''. No one who has held the post, even on a caretaker basis, is allowed to run or serve again. The constitution and the office of the president closely follow the presidential system of go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Unions In The Soviet Union
Trade unions in the Soviet Union, headed by the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions (VTsSPS or ACCTU in English), had a complex relationship with industrial management, the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, and the Soviet government, given that the Soviet Union was ideologically supposed to be a state in which the members of the working class ruled the country and managed themselves. During the Russian Revolution and the Russian Civil War that immediately followed, there were all sorts of ideas about how to organize and manage industries, and many people thought that the trade unions would be the vehicle of workers' control of industries. By the Stalinist era of the 1930s, it was clear that the party and government made the rules and that the trade unions were not permitted to challenge them in any substantial way. In the decades after Stalin, the worst of the powerlessness of the unions was past, but Soviet trade unions remained something closer to company unions, ans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexican Labor Law
Mexican labor law governs the process by which workers in Mexico may organize labor unions, engage in collective bargaining, and strike. Current labor law reflects the historic interrelation between the state and the Confederation of Mexican Workers, the labor confederation officially aligned with the Institutional Revolutionary Party (the Institutional Revolutionary Party, or PRI), which ruled Mexico under various names for more than seventy years. While the law, at face value, promises workers the right to strike and to organize, in practice it makes it difficult or impossible for independent unions to organize while condoning the corrupt practices of many existing unions and the employers with which they deal. History of Mexican labor law The current system originated in the Mexican Revolution of 1910–1920, which produced the Constitution of 1917. Article 123 of that Constitution gave workers the right to organize labor unions and to strike. It also provided protection for wome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corruption In Mexico
Corruption in Mexico has permeated several segments of society – political, economic, and social – and has greatly affected the country's legitimacy, transparency, accountability, and effectiveness. Many of these dimensions have evolved as a product of Mexico's legacy of elite, oligarchic consolidation of power and authoritarian rule. Transparency International's 2021 Corruption Perceptions Index ranks the country 124th place out of 180 countries. PRI rule Although the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI) came to power through cooptation and peace, it maintained power for 71 years straight (1929 to 2000) by establishing patronage networks and relying on personalistic measures. That is why, Mexico functioned as a one-party state and was characterized by a system in which politicians provided bribes to their constituents in exchange for support and votes for reelection. This type of clientelism constructed a platform through which political corruption had the opportunity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rank And File
Rank and file may refer to: *A military term relating to the horizontal "ranks" (rows) and vertical "files" (columns) of individual foot-soldiers, exclusive of the officers *A term derived from the above used to refer to enlisted troops, as opposed to the officers * Rank and file (chess), the rows and columns on a chessboard *The individual members of a political organization or labour union, exclusive of its leadership *Rank and file movement, a blanket term for informal, Trotskyist militant groups among British trade unionists, generally strenuously opposed to the union hierarchies and often facing expulsion by them * Rank and File Movement, a militant movement which grew within the Amalgamated Association of Iron and Steel Workers in the United States in 1934 *Rank and File (band), an American cowpunk band * "The Rank and File" (''Playhouse 90''), a 1959 American television play * "The Rank and File" (''Play for Today''), a 1971 BBC television play written by Jim Allen and direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luis Gómez Z
Luis is a given name. It is the Spanish form of the originally Germanic name or . Other Iberian Romance languages have comparable forms: (with an accent mark on the i) in Portuguese and Galician, in Aragonese and Catalan, while is archaic in Portugal, but common in Brazil. Origins The Germanic name (and its variants) is usually said to be composed of the words for "fame" () and "warrior" () and hence may be translated to ''famous warrior'' or "famous in battle". According to Dutch onomatologists however, it is more likely that the first stem was , meaning fame, which would give the meaning 'warrior for the gods' (or: 'warrior who captured stability') for the full name.J. van der Schaar, ''Woordenboek van voornamen'' (Prisma Voornamenboek), 4e druk 1990; see also thLodewijs in the Dutch given names database Modern forms of the name are the German name Ludwig and the Dutch form Lodewijk. and the other Iberian forms more closely resemble the French name Louis, a derivat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesús Díaz De León
Jesus ( AD 30 or 33) was a Jewish preacher and religious leader who most Christians believe to be the incarnation of God and Muslims believe was a prophet. Jesus may also refer to: People Religious figures * Elymas Bar-Jesus, a Jew in the ''Acts of the Apostles'', chapter 13, who opposed the missionary Paul on Cyprus * Jesus Barabbas (Matthew 27:16–17 margin), pardoned criminal * Jesus Justus (Colossians 4:11), Christian in Rome mentioned by Paul Other people with the name * Jesus (name), as given name and surname, derived from the Latin name ''Iesus'' and the Greek ('). * Jesus ben Ananias (died ), Jewish nationalist mentioned by Josephus * Jesus Ben Sira (), religious writer, author of the Book of Sirach * Jesus Christ Allin or GG Allin (1956–1993), American punk rock musician * Jesús González Díaz (born 1994), simply known as Jesús, Spanish footballer * Jesús Malverde, legendary Mexican bandit-saint * Jesús Rodríguez (other) * Gabriel Jesus (born 1997) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
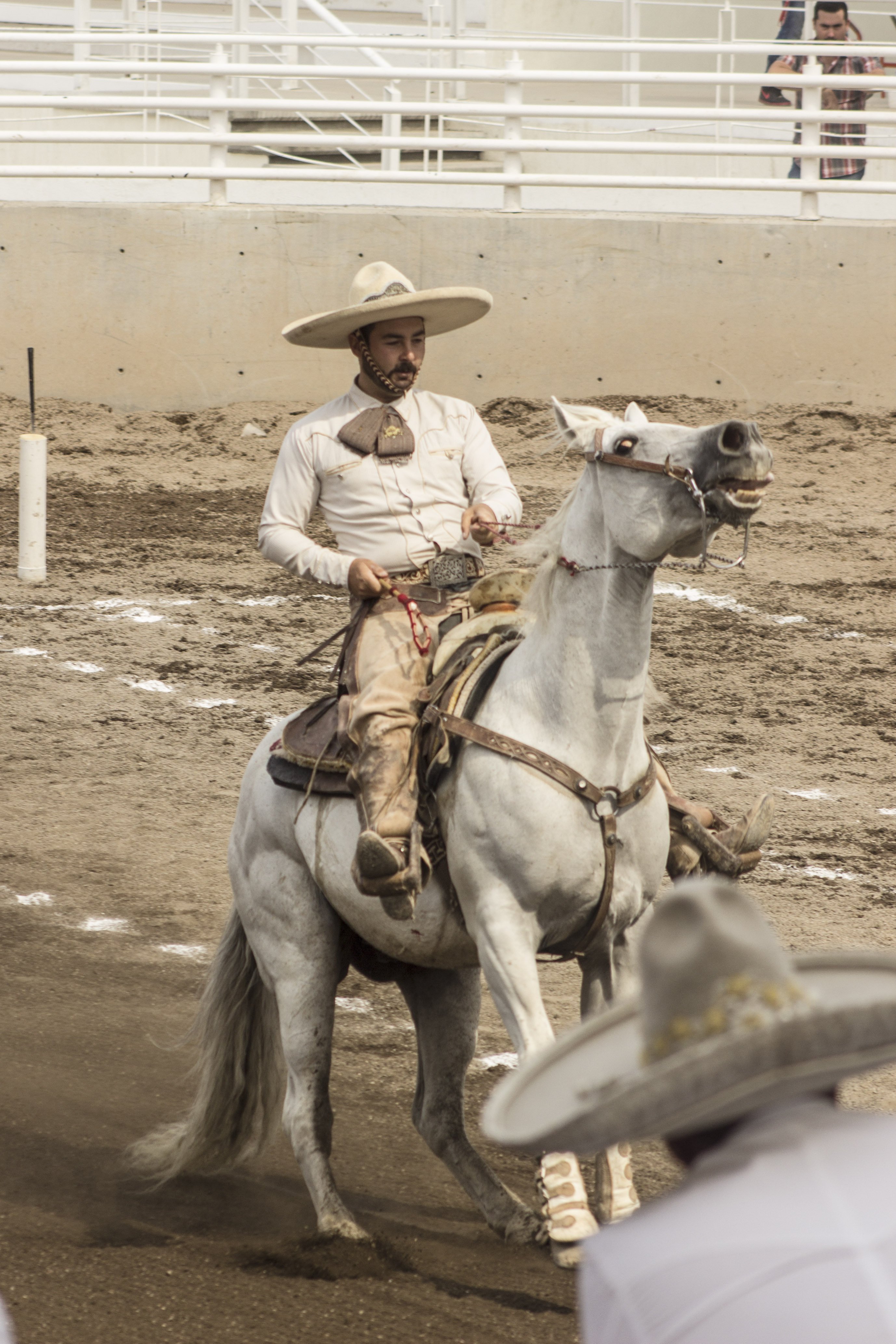
Charro
Charro has several meanings, but it generally refers to Mexican horse riders, who maintain traditional dress, such as some form of sombrero, which in Mexican Spanish are called ''sombrero de charro'' (a charro's hat). The charros could also be thought of as old Mexican cowboys who dress like such, although more modern dress is now seen on those who still work the ranches (''rancheros''). See also, '' vaquero''. Also old Mexican outlaws, bandits, revolutionaries, bounty hunters, and gunmen who wore similar dress are also called ''charro''. The traditional ''charro'' competition '' charreada'' (similar to a rodeo) has become the official sport of Mexico and maintains traditional rules and regulations in effect from colonial times up to the Mexican Revolution. Etymology The word ''charro'' (syn. ''charrar, charra'') is first documented in Spain in the book “Vocabulario de refranes y frases proverbiales” published in 1627 by Gonzalo Correas as a synonym of dumb or stupid p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miguel Alemán Valdés
Miguel Alemán Valdés (; 29 September 1900 – 14 May 1983) was a Mexican politician who served a full term as the President of Mexico from 1946 to 1952, the first civilian president after a string of revolutionary generals. His administration was characterized by Mexico's rapid industrialization, often called the Mexican Miracle, but also for a high level of personal enrichment for himself and his associates. His presidency was the first of a new generation of Mexican leaders, who had not directly participated in the Mexican Revolution, and many in his cabinet were also young, university-educated civilians, close friends from his days at university. Early life and career Alemán was born in Sayula in the state of Veracruz,''Current Biography 1946 Yearbook'', p. 9. the son of revolutionary Gen. Miguel Alemán González and Tomasa Valdés Ledezma. Both had been married before, with Alemán González having a son by his first wife. They had two sons together, Carlos a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confederation Of Mexican Workers
The Confederation of Mexican Workers (''Confederación de Trabajadores de México'' (CTM)) is the largest confederation of labor unions in Mexico. For many years, it was one of the essential pillars of the Partido Revolucionario Institucional (the Institutional Revolutionary Party, or PRI), which ruled Mexico for more than seventy years. However, the CTM began to lose influence within the PRI structure in the late 1980s, as technocrats increasingly held power within the party. Eventually, the union found itself forced to deal with a new party in power after the PRI lost the 2000 general election, an event that drastically reduced the CTM's influence in Mexican politics. Founding the CTM 250px, CTM's 14th National Congress The CTM was founded on February 21, 1936, during the term of President Lázaro Cárdenas del Río. Cárdenas's predecessors had relied heavily on the Confederación Regional Obrera Mexicana, or CROM, in order to garner support from the working class. Howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |