|
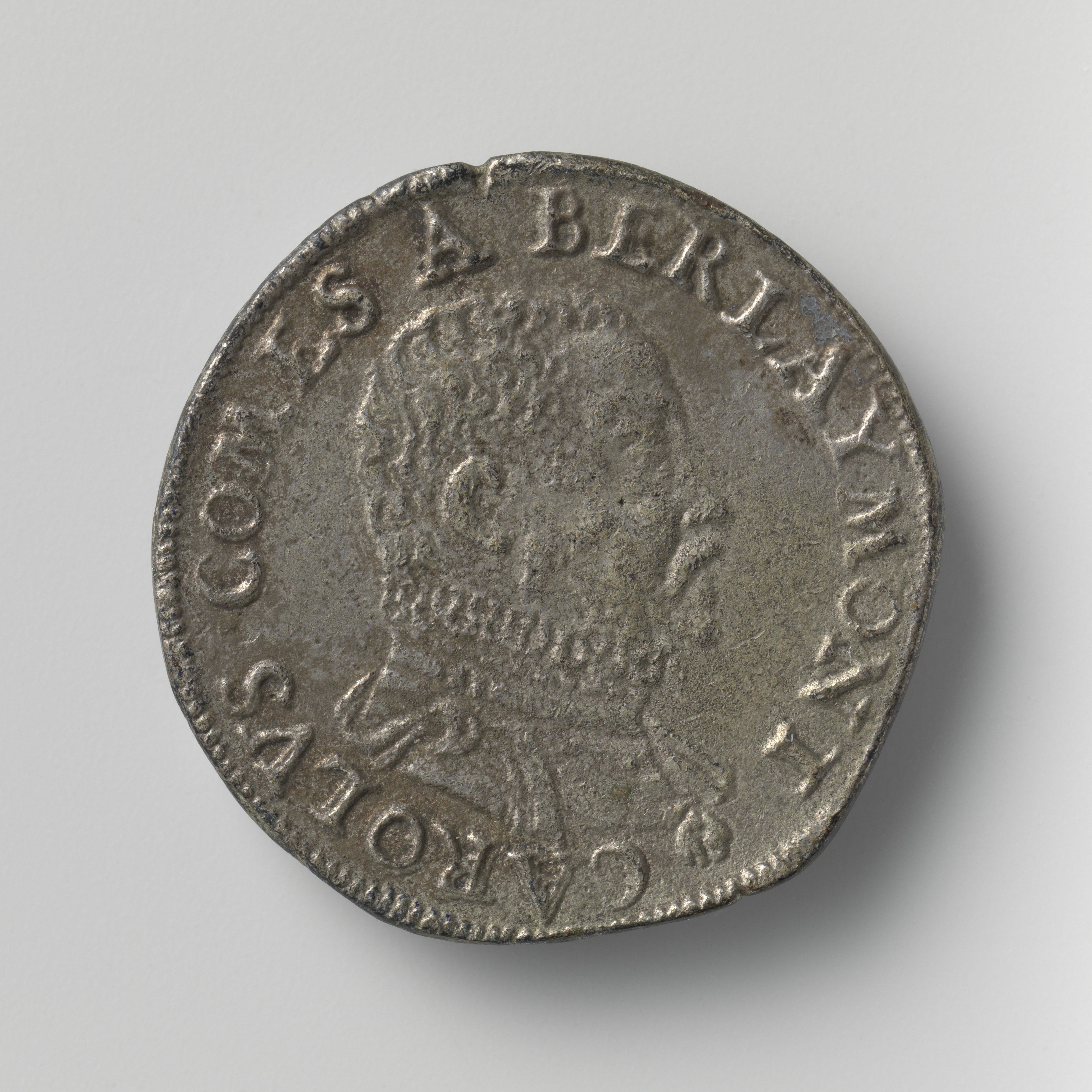
Charles De Berlaymont
Charles de Berlaymont (1510 in Berlaimont? – 1578 in Namur?) was a leading nobleman in the Low Countries in the 16th century. He was an important counselor of Margaret of Parma, Grand Huntsman of Brabant and generally sided with Spanish politics in the early years of the Eighty Years War. Biography He was the son of Michèl de Berlaymont and Maria de Berault. He was lord of Floyon and Haultpenne, and baron of Hierges. In 1553, he became stadtholder of Namur. Berlaymont was knight of the Order of the Golden Fleece, senior hunting master of Brabant, Flanders and Namur, member of the Council of State, hereditary chamberlain of finances and bailiff of the county of Namur. In 1567, he became a member of the much-dreaded Council of Troubles. In 1574, his home territory Berlaimont was elevated to the status of a county. In 1577, Berlaymont was one of the signees of the Union of Brussels, which he immediately repudiated. He is known for his famous comment on the Compromise of Nob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French denoting a jurisdiction under the sovereignty of a count (earl) or a viscount.The Oxford Dictionary of English Etymology, C. W. Onions (Ed.), 1966, Oxford University Press Literal equivalents in other languages, derived from the equivalent of "count", are now seldom used officially, including , , , , , , , and ''zhupa'' in Slavic languages; terms equivalent to commune/community are now often instead used. When the Normans conquered England, they brought the term with them. The Saxons had already established the districts that became the historic counties of England, calling them shires;Vision of Britai– Type details for ancient county. Retrieved 31 March 2012 many county names derive from the name of the county town (county seat) with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maastricht
Maastricht ( , , ; li, Mestreech ; french: Maestricht ; es, Mastrique ) is a city and a municipality in the southeastern Netherlands. It is the capital and largest city of the province of Limburg. Maastricht is located on both sides of the Meuse ( nl, Maas), at the point where the Jeker joins it. Mount Saint Peter (''Sint-Pietersberg'') is largely situated within the city's municipal borders. Maastricht is about 175 km south east of the capital Amsterdam and 65 km from Eindhoven; it is adjacent to the border with Belgium and is part of the Meuse-Rhine Euroregion, an international metropolis with a population of about 3.9 million, which includes the nearby German and Belgian cities of Aachen, Liège and Hasselt. Maastricht developed from a Roman settlement (''Trajectum ad Mosam'') to a medieval religious centre. In the 16th century it became a garrison town and in the 19th century an early industrial centre. Today, the city is a thriving cultural and regional hub. It beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Servatius
Saint Servatius ( nl, Sint Servaas; french: Saint Servais; li, Sintervaos; hy, Սուրբ Սերվատիոս ''Surb Servatios'') (born in Armenia, died in Maastricht, traditionally on 13 May 384) was bishop of Tongeren —Latin: ''Atuatuca Tungrorum'', the capital of the Tungri—. Servatius is patron saint of the city of Maastricht and the towns of Schijndel and Grimbergen. He is one of the Ice Saints. His feast day is May 13. History A widely travelled diplomat and a determined opponent of Arianism, the presence of Servatius is recorded at several synods and church councils. In 343, ''Sarbatios'' - Greek texts rendering ''v'' as ''b'' - was present at the Council of Sardica (modern Sofia). In the debates, Servatius represented the Trinitarian view, which clashed with the Arian view of most Eastern bishops. According to Sulpicius Severus, Servatius again eloquently denounced Arianism at the Council of Rimini in 359. When Athanasius, the leading opponent of Arianism, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provost (religion)
A provost is a senior official in a number of Christian Churches. Historical development The word ''praepositus'' (Latin: "set over", from ''praeponere'', "to place in front") was originally applied to any ecclesiastical ruler or dignitary. It was soon more specifically applied to the immediate subordinate to the abbot of a monastery, or to the superior of a single cell, and it was defined as such in the Rule of St Benedict. The dean (''decanus'') was a similarly ranked official. Chrodegang of Metz adopted this usage from the Benedictines when he introduced the monastic organization of canon-law colleges, especially cathedral capitular colleges. The provostship (''praepositura'') was normally held by the archdeacon, while the office of dean was held by the archpriest. In many colleges, the temporal duties of the archdeacons made it impossible for them to fulfil those of the provostship, and the headship of the chapter thus fell to the dean. The title became ''prevost'' in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrai
Cambrai (, ; pcd, Kimbré; nl, Kamerijk), formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a city in the Nord (French department), Nord Departments of France, department and in the Hauts-de-France Regions of France, region of France on the Scheldt river, which is known locally as the Escaut river. A Subprefectures in France, sub-prefecture of the department, Cambrai is a town which had 32,501 inhabitants in 2018. It is in the heart of the urban unit of Cambrai with 46,772 inhabitants. Its functional area (France), functional area, a more extensive range, included 94,576 inhabitants in 2018.Comparateur de territoire: Aire d'attraction des villes 2020 de Cambra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis De Berlaymont
Louis de Berlaymont (1542–1596) was an aristocratic clergyman in the Habsburg Netherlands who served as the second archbishop of Cambrai. Life Berlaymont was born in Brussels, the son of Charles de Berlaymont, one of the leading members of the nobility of the Low Countries. On 15 September 1570, aged only 28, he was elected archbishop of Cambrai.Wilfrid BrulezL'élection de Louis de Berlaimont comme archevêque de Cambrai en 1570 '' Revue belge de Philologie et d'Histoire'', 31:2-3 (1953), pp. 509-519. When Francis, Duke of Anjou, took Cambrai in 1580, Berlaymont withdrew to Mons, in the County of Hainaut, governing the archdiocese from there.Jules de Saint-Genois, "Berlaymont (Louis, comte de)", ''Biographie Nationale de Belgique''vol. 2(Brussels, 1868), 266-267. He was also provost of the Basilica of Saint Servatius in Maastricht from 1570 to 1596, as well as serving as apostolic administrator of the diocese of Tournai during the vacancy following the death of Jean Vendeville ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
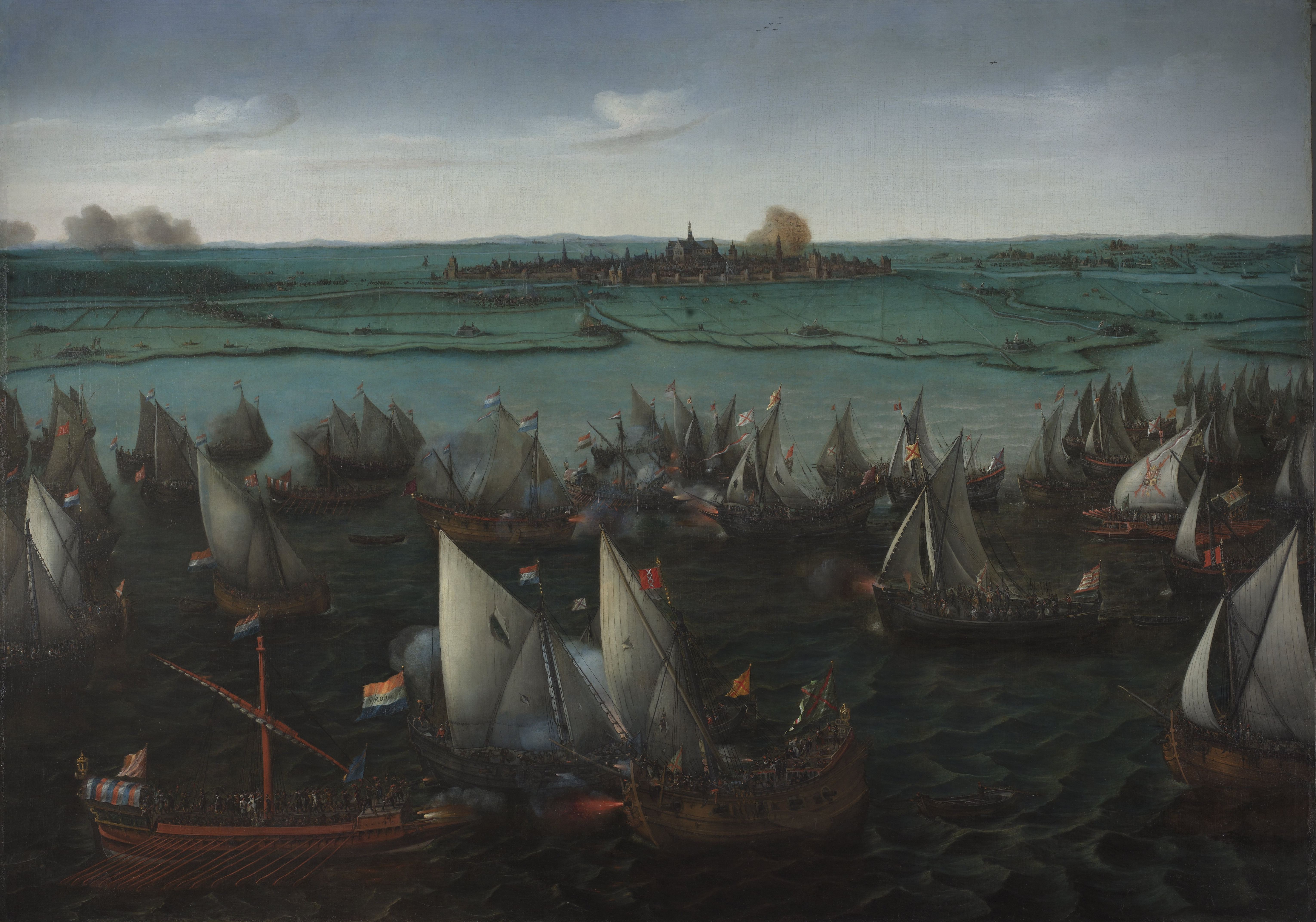
Siege Of Maastricht (1579)
The siege of Maastricht was a battle of the Eighty Years' War which lasted from March 12 – July 1, 1579. The Spanish were victorious. Prelude Political background The Siege of Maastricht was undertaken in a moment in which the Royal authority had almost collapsed in the Spanish Netherlands. A wave of Protestant, popular violence known as Beeldenstorm had erupted in 1566, leading Philip II to dispatch and army under the Duke of Alba to the region in 1567. Alba prosecuted the Protestants and those whose loyalty to the king was under suspicion, implenented a new episcopal reform and defeated an invasion by William of Orange from Germany. However, his fiscal policies, intended to finance the Spanish Army of Flanders, were highly unpopular and led to a new rebellion in the spring of 1572. This quickly spread across Zeeland, Holland and Gelderland, where the Geuzen and Orange's followers took control of many towns and cities. Alba failed to suppress the revolt and was replaced as gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
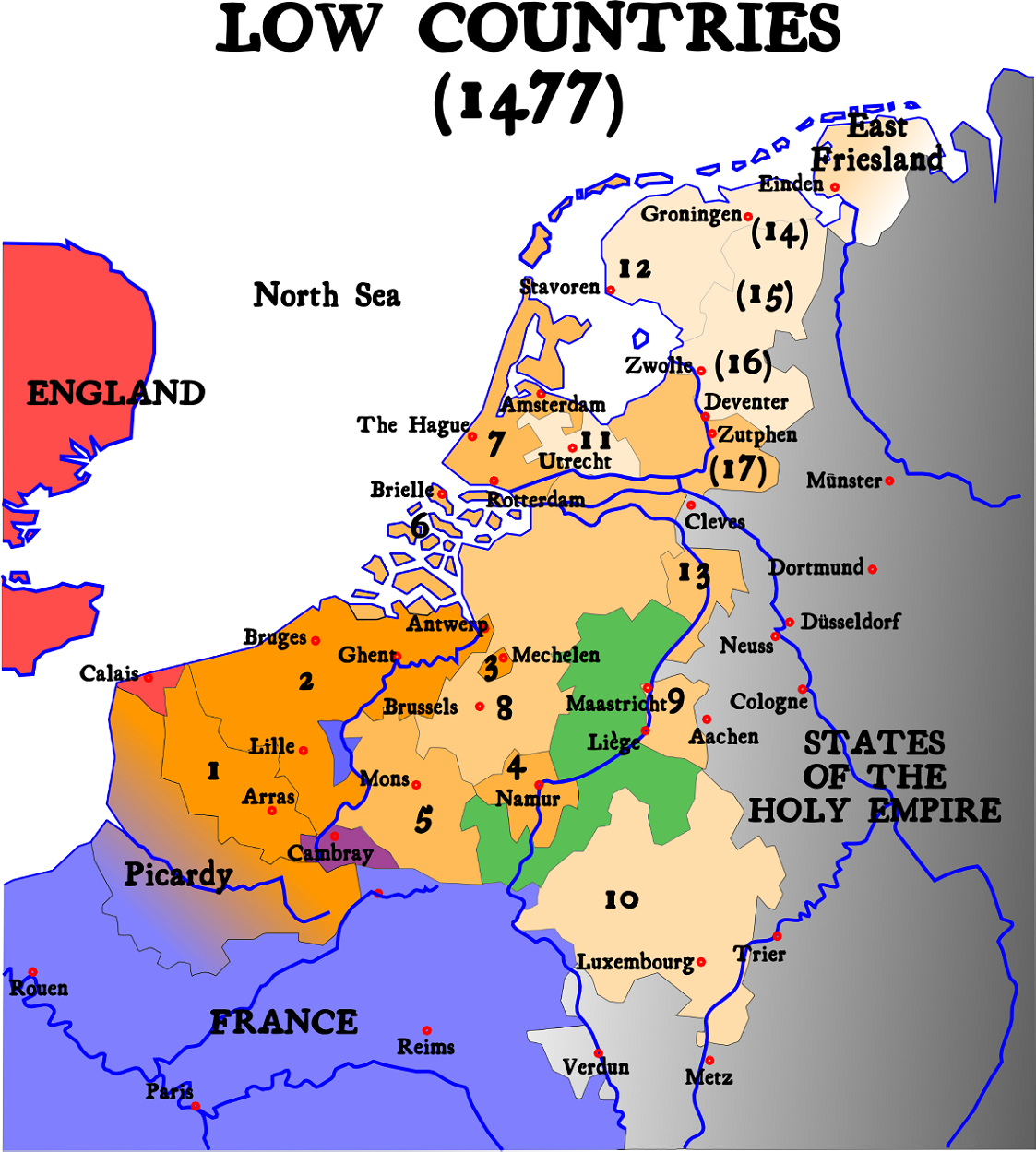
Seventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the French departments of Nord (French Flanders and French Hainaut) and Pas-de-Calais (Artois). Also within this area were semi-independent fiefdoms, mainly ecclesiastical ones, such as Liège, Cambrai and Stavelot-Malmedy. The Seventeen Provinces arose from the Burgundian Netherlands, a number of fiefs held by the House of Valois-Burgundy and inherited by the Habsburg dynasty in 1482, and held by Habsburg Spain from 1556. Starting in 1512, the Provinces formed the major part of the Burgundian Circle. In 1581, the Seven United Provinces seceded to form the Dutch Republic. Composition After the Habsburg emperor Charles V had re-acquired the Duchy of Guelders from Duke William of Jülich-Cleves-Berg by the 1543 Treaty of Venlo, the Seventeen Provinces comprised: #th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilles De Berlaymont
Gilles van Berlaymont (c. 1545 – 18 June 1579 in Maastricht) was stadtholder for the Spanish Crown of Drenthe, Friesland, Groningen and Overijssel (1572-1573), stadtholder of Guelders (1572–1577), substitute stadtholder of Holland, Zeeland and Utrecht (1574–1577), stadtholder of Namur and Artois (after 1578) and baron of Hierges. He was the son of Charles de Berlaymont and Adriana de Ligne Barbançon, and a brother of Claude de Berlaymont and Florent de Berlaymont. In 1572 he was made a Knight in the Order of the Golden Fleece, and on 2 September 1577 became a member of the Council of State. In 1567 Gilles took part in the Siege of Valenciennes (1567), the first siege of the Eighty Years' War. He captured and sacked Schoonhoven, and Oudewater in August 1575. He was killed during the Siege of Maastricht (1579) The siege of Maastricht was a battle of the Eighty Years' War which lasted from March 12 – July 1, 1579. The Spanish were victorious. Prelude Political b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geuzen
Geuzen (; ; french: Les Gueux) was a name assumed by the confederacy of Calvinist Dutch nobles, who from 1566 opposed Spanish rule in the Netherlands. The most successful group of them operated at sea, and so were called Watergeuzen (; ; french: links=no, Gueux de mer). In the Eighty Years' War, the Capture of Brielle by the Watergeuzen in 1572 provided the first foothold on land for the rebels, who would conquer the northern Netherlands and establish an independent Dutch Republic. They can be considered either as privateers or pirates, depending on the circumstances or motivations. Origin of the name The leaders of the nobles who signed a solemn league known as the Compromise of Nobles, by which they bound themselves to assist in defending the rights and liberties of the Netherlands against the civil and religious despotism of Philip II of Spain, were Louis of Nassau and Hendrick van Brederode. On 5 April 1566, permission was obtained for the confederates to present a petition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to be growing Criticism of the Catholic Church, errors, abuses, and discrepancies within it. Protestantism emphasizes the Christian believer's justification by God in faith alone (') rather than by a combination of faith with good works as in Catholicism; the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by Grace in Christianity, divine grace or "unmerited favor" only ('); the Universal priesthood, priesthood of all faithful believers in the Church; and the ''sola scriptura'' ("scripture alone") that posits the Bible as the sole infallible source of authority for Christian faith and practice. Most Protestants, with the exception of Anglo-Papalism, reject the Catholic doctrine of papal supremacy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |