|
Charles L. Whitfield
Charles L. Whitfield was an American medical doctor in private practice specializing in assisting survivors of childhood trauma with their recovery, and with addictions including alcoholism and related disorders. He was certified by the American Society of Addiction Medicine, a founding member of the National Association for the Children of Alcoholics, and a member of the American Professional Society on the Abuse of Children. Whitfield taught at Rutgers University and was a best-selling author known for his books on the topics of general childhood trauma, childhood sexual abuse, and addiction recovery, including ''Healing the Child Within'' and ''Memory and Abuse: Remembering and Healing the Effects of Trauma''. Whitfield was recognized for his sixty published articles and fifteen published books. Some of his works were: ''Healing the Child Within'' (1987), ''Memory and Abuse'' (1995), and ''The Truth About Mental Illness'' (2004). Work on childhood trauma Whitfield was a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Society Of Addiction Medicine
The American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM), founded in 1954, is a professional medical society representing over 6,000 physicians, clinicians and associated professionals in the field of addiction medicine. ASAM is dedicated to increasing access and improving the quality of addiction treatment, educating physicians and the public, supporting research and prevention, and promoting the appropriate role of physicians in the care of patients with addiction. References {{authority control Medical associations based in the United States Addiction organizations in the United States Organizations established in 1954 1954 establishments in New York (state) Non-profit organizations based in Maryland Organizations based in the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area Chevy Chase, Maryland Medical and health organizations based in Maryland 501(c)(3) organizations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Association For The Children Of Alcoholics
National may refer to: Common uses * Nation or country ** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen Places in the United States * National, Maryland, census-designated place * National, Nevada, ghost town * National, Utah, ghost town * National, West Virginia, unincorporated community Commerce * National (brand), a brand name of electronic goods from Panasonic * National Benzole (or simply known as National), former petrol station chain in the UK, merged with BP * National Car Rental, an American rental car company * National Energy Systems, a former name of Eco Marine Power * National Entertainment Commission, a former name of the Media Rating Council * National Motor Vehicle Company, Indianapolis, Indiana, USA 1900-1924 * National Supermarkets, a defunct American grocery store chain * National String Instrument Corporation, a guitar company formed to manufacture the first resonator gui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutgers University
Rutgers University (; RU), officially Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, is a Public university, public land-grant research university consisting of four campuses in New Jersey. Chartered in 1766, Rutgers was originally called Queen's College, and was affiliated with the Reformed Church in America, Dutch Reformed Church. It is the eighth-oldest college in the United States, the second-oldest in New Jersey (after Princeton University), and one of the nine U.S. colonial colleges that were chartered before the American Revolution.Stoeckel, Althea"Presidents, professors, and politics: the colonial colleges and the American revolution", ''Conspectus of History'' (1976) 1(3):45–56. In 1825, Queen's College was renamed Rutgers College in honor of Colonel Henry Rutgers, whose substantial gift to the school had stabilized its finances during a period of uncertainty. For most of its existence, Rutgers was a Private university, private liberal arts college but it has evolved int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Child Sexual Abuse
Child sexual abuse (CSA), also called child molestation, is a form of child abuse in which an adult or older adolescent uses a child for sexual stimulation. Forms of child sexual abuse include engaging in sexual activities with a child (whether by asking or pressuring, or by other means), indecent exposure (of the genitals, female nipples, etc.), child grooming, and child sexual exploitation, such as using a child to produce child pornography. Child sexual abuse can occur in a variety of settings, including home, school, or work (in places where child labor is common). Child marriage is one of the main forms of child sexual abuse; UNICEF has stated that child marriage "represents perhaps the most prevalent form of sexual abuse and exploitation of girls". The effects of child sexual abuse can include depression, post-traumatic stress disorder, anxiety, complex post-traumatic stress disorder, propensity to further victimization in adulthood, and physical injury to the child ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substance Dependence
Substance dependence, also known as drug dependence, is a biopsychological situation whereby an individual's functionality is dependent on the necessitated re-consumption of a psychoactive substance because of an adaptive state that has developed within the individual from psychoactive substance consumption that results in the experience of withdrawal and that necessitates the re-consumption of the drug. A ''drug addiction'', a distinct concept from substance dependence, is defined as compulsive, out-of-control drug use, despite negative consequences. An ''addictive drug'' is a drug which is both rewarding and reinforcing. ΔFosB, a gene transcription factor, is now known to be a critical component and common factor in the development of virtually all forms of behavioral and drug addictions, but not dependence. The International Classification of Diseases classifies substance dependence as a mental and behavioural disorder. Within the framework of the 4th edition of the ''Diagn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cure
A cure is a substance or procedure that ends a medical condition, such as a medication, a surgical operation, a change in lifestyle or even a philosophical mindset that helps end a person's sufferings; or the state of being healed, or cured. The medical condition could be a disease, mental illness, genetic disorder, or simply a condition a person considers socially undesirable, such as baldness or lack of breast tissue. An incurable disease may or may not be a terminal illness; conversely, a curable illness can still result in the patient's death. The proportion of people with a disease that are cured by a given treatment, called the cure fraction or cure rate, is determined by comparing disease-free survival of treated people against a matched control group that never had the disease. Another way of determining the cure fraction and/or "cure time" is by measuring when the hazard rate in a diseased group of individuals returns to the hazard rate measured in the general populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
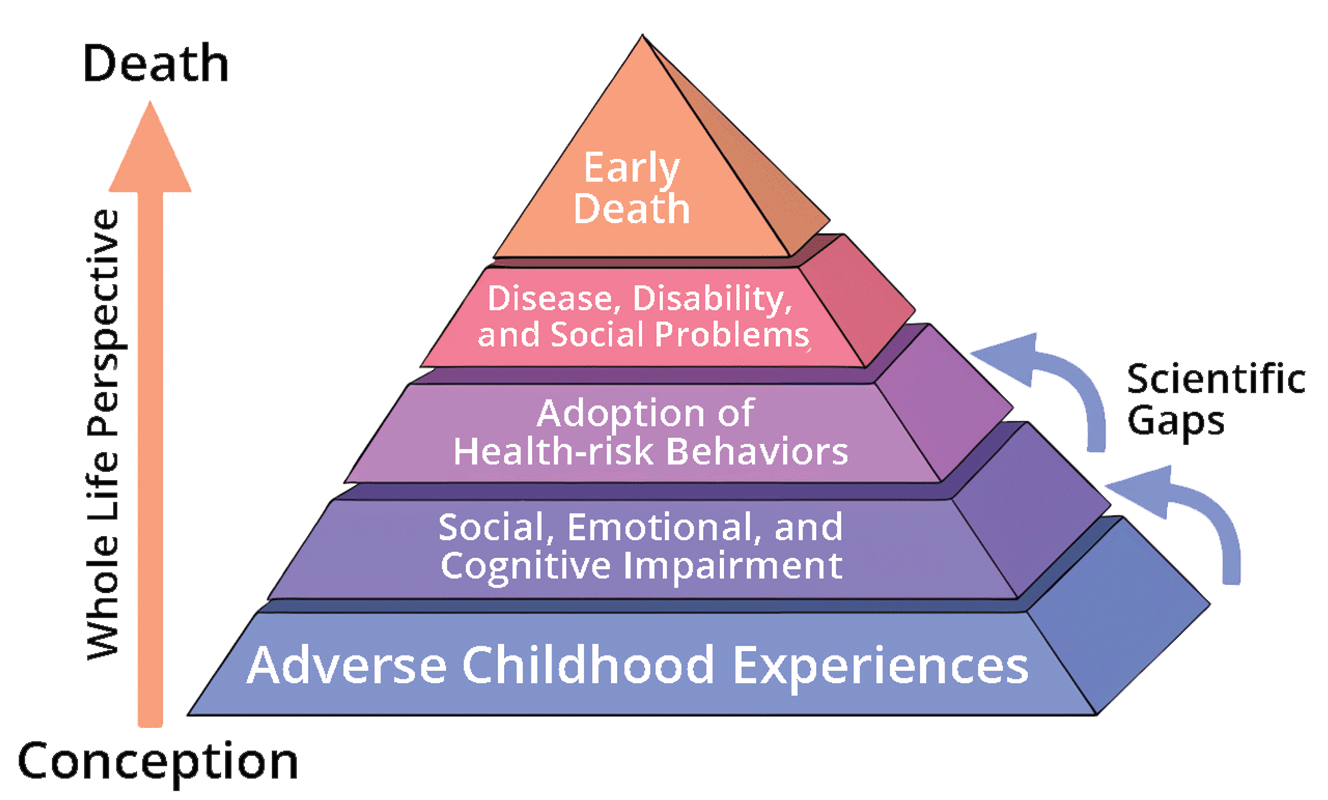
Adverse Childhood Experiences
Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) encompass various forms of physical and emotional abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction experienced in childhood. The harms of ACEs can be long-lasting, affecting people even in their adulthood. ACEs have been linked to premature death as well as to various health conditions, including those of mental disorders. Toxic stress linked to child abuse is related to a number of neurological changes in the structure of the brain and its function. Definition and types The concept of adverse childhood experiences refers to various traumatic events or circumstances affecting children before the age of 18 and causing mental or physical harm. There are 10 types of ACEs: * physical abuse * sexual abuse * psychological abuse * physical neglect * psychological neglect * witnessing domestic abuse * having a close family member who misused drugs or alcohol * having a close family member with mental health problems * having a close family member wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Boundaries
Personal boundaries or the act of'' setting boundaries'' is a life skill that has been popularized by self help authors and support groups since the mid 1980s. It is the practice of openly communicating and asserting personal values as way to preserve and protect against having them compromised or violated. The term "boundary" is a metaphor – with ''in-bounds'' meaning acceptable and ''out-of-bounds'' meaning unacceptable. Without values and boundaries our identities become diffused and often controlled by the definitions offered by others. The concept of ''boundaries'' has been widely adopted by the counseling profession.G. B. and J. S. Lundberg, ''I Don't Have to Make Everything All Better'' (2000) p. 13. ISBN 978-0-670-88485-8 Usage and application This life skill is particularly applicable in environments with controlling people or people not taking responsibility for their own life. Co-Dependents Anonymous recommends setting limits on what members will do to and for peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repressed Memory
Repressed memory is an inability to recall autobiographical information, usually of a traumatic or stressful nature. The concept originated in psychoanalytic theory where repression is defined as a protective mechanism that excludes memory of painful experiences from consciousness. Repressed memory is a controversial concept, particularly in legal contexts where it has been used to impugn individuals unfairly and inaccurately, leading to substantial harm. At the same time, an American Psychological Association working group indicated that while "most people who were sexually abused as children remember all or part of what happened to them, it is possible for memories of abuse that have been forgotten for a long time to be remembered". Although Sigmund Freud later revised his theory, he initially held that memories of childhood sexual trauma were often repressed (could not be recalled later in life) yet the traumas unconsciously influenced behavior and emotional responding. Des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
False Memory Syndrome
In psychology, false memory syndrome (FMS) is a condition in which a person's identity and relationships are affected by false memories of psychological trauma, recollections that are factually incorrect yet strongly believed. Peter J. Freyd originated the term partly to explain what he said was a false accusation of sexual abuse made against him by his daughter Jennifer Freyd and his False Memory Syndrome Foundation (FMSF) subsequently popularized the concept. The principle that individuals can hold false memories and the role that outside influence can play in their formation is widely accepted by scientists. However FMS is not recognized as a psychiatric illness in any medical manuals including the ICD-10 or the DSM-5. False memory syndrome may be the result of recovered memory therapy, a term also defined by the FMSF in the early 1990s, which describes a range of therapy methods that are prone to creating confabulations. The most influential figure in the genesis of the the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Missing (living People)
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |