|
Chapleau, Ontario
Chapleau is a township in Sudbury District, Ontario, Canada. It is home to one of the world's largest wildlife preserves. Chapleau has a population of 1,942 according to the 2016 Canadian census. The major industries within the town are the logging mill, Rayonier Advanced Materials (RYAM) (formerly, Tembec), and the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) rail yards. History The first European settlement in the area was established in 1777 by the Hudson's Bay Company. The settlement was a fur trading post about to Chapleau's north, on Big Missinabi Lake. In 1885 the Canadian Pacific Railway was built through the area. The CPR chose this as a divisional point, and the town was founded. It was named in honour of Sir Joseph-Adolphe Chapleau, a lawyer, journalist, businessman, politician, and most notably the 5th Premier of Quebec. Louis Hémon, author of the French novel ''Maria Chapdelaine'', was struck and killed by a train in Chapleau on 8 July 1913. After a fire in 1948, the governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
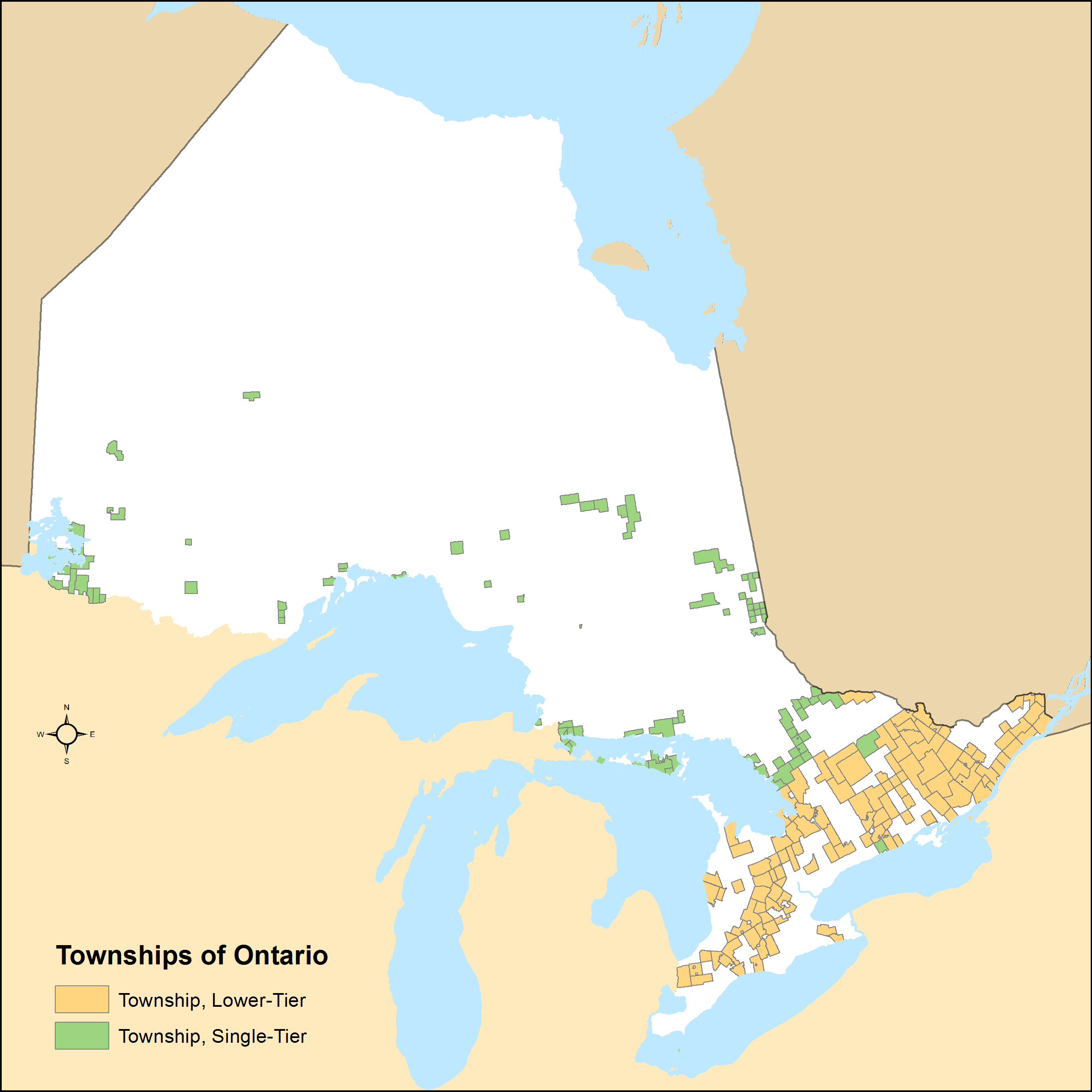
List Of Township Municipalities In Ontario
A township is a type of municipality in the Canadian province of Ontario. They can have either single-tier status or lower-tier status. Ontario has 200 townships that had a cumulative population of 990,396 and an average population of 4,952 in the 2011 Census. Ontario's largest and smallest townships are Centre Wellington and Cockburn Island with populations of 26,693 and 0 respectively. History Under the former ''Municipal Act, 1990'', a township was a type of local municipality. Under this former legislation, a locality with a population of 1,000 or more could have been incorporated as a township by Ontario's Municipal Board upon review of an application from 75 or more residents of the locality. It also provided that a township could include "a union of townships and a municipality composed of two or more townships". In the transition to the ''Municipal Act, 2001'', these requirements were abandoned and, as at December 31, 2002, every township ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2016 Canadian Census
The 2016 Canadian census was an enumeration of Canadian residents, which counted a population of 35,151,728, a change from its 2011 population of 33,476,688. The census, conducted by Statistics Canada, was Canada's seventh quinquennial census. The official census day was May 10, 2016. Census web access codes began arriving in the mail on May 2, 2016. The 2016 census marked the reinstatement of the mandatory long-form census, which had been dropped in favour of the voluntary National Household Survey for the 2011 census. With a response rate of 98.4%, this census is said to be the best one ever recorded since the 1666 census of New France. This census was succeeded by Canada's 2021 census. Planning Consultation with census data users, clients, stakeholders and other interested parties closed in November 2012. Qualitative content testing, which involved soliciting feedback regarding the questionnaire and tests responses to its questions, was scheduled for the fall of 2013, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontario Highway 101
King's Highway 101, commonly referred to as Highway 101, is a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. The highway connects Highway 17 west of Wawa with Highway 11 in Matheson before continuing east to the Ontario–Quebec border where it becomes Route 388. The highway forms one of the only connections between the two routes of the Trans-Canada Highway between Nipigon and Temagami, and crosses some of the most remote regions of Northern Ontario. Major junctions are located with Highway 129 near Chapleau and Highway 144 southwest of Timmins, though the distance between these junctions is significant. Highway 101 was first assumed in 1940, though it was not given a numerical designations until 1944. The route initially connected Timmins with Highway 11. In the 1950s and 1960s, it was extended east to the Quebec border and west to the newly opened Highway 17 over Lake Superior. The highway reached its m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontario Highway 129
King's Highway 129, commonly referred to as Highway 129, is a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. Located in the Algoma and Sudbury districts, the highway extends for from a junction with Highway 17 in Thessalon to the town of Chapleau, just north of Highway 101. The route is isolated and lightly travelled throughout its length; while providing access to several remote settlements, the only sizable communities along the route are the two termini. The highway was established in 1956 along the Chapleau Road. From the early 1960s to mid-1970s, Highway 129 was designated as the ''Chapleau Route'' of the Trans-Canada Highway. Route description Highway 129 is one of the most isolated in Ontario and among the least used of the King's Highways. Although the highway is an important access route for several isolated communities, including Little Rapids, Sultan, Kormak and Nemegos, as well as provincial parks such as Aubrey Falls, Five Mile Lake an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maria Chapdelaine
''Maria Chapdelaine'' is a romance novel written in 1913 by the Breton writer Louis Hémon, who was then residing in Quebec.Guy Laflèche. Polémiques'. Editions du Singulier; 1992. . p. 126 – 128. Aimed at young French and Quebecois people, the book had been included in school curricula, translated, and has been extensively analyzed and adapted. Plot After the man she loves dies suddenly, Maria must choose which of two suitors to marry. One offers a change to life in the big city, but Maria decides to stay in the countryside.David Stouck. Major Canadian Authors: A Critical Introduction to Canadian Literature in English'. U of Nebraska Press; 1 January 1988. . p. 143–. Publication Hémon, a journalist, came to rural Quebec to gather ideas for a novel. He supported himself by working on a farm. After hearing various stories from area residents, he wrote a romantic story, basing the character of the heroine on a young woman he had met. In 1913, he submitted the manuscript f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Hémon
Louis Hémon (12 October 1880 – 8 July 1913), was a French writer best known for his novel ''Maria Chapdelaine''. Biography He was born in Brest, France. In Paris, where he resided with his family, he was enrolled in the Montaigne and Louis-le-Grand secondary schools. A bilingual secretary in several maritime agencies, he collaborated, starting from 1904, in a Parisian sports journal. After his studies of law and oriental languages in the Sorbonne, he moved to London. In 1911, he moved to Canada, settling initially in Montreal. Hémon wrote ''Maria Chapdelaine'' during his time working at a farm in the Lac Saint-Jean region. Hémon died when he was struck by a train at Chapleau, Ontario. He never saw the widespread publication of his landmark novel. Since his death, ''Maria Chapdelaine'' has been translated into more than 20 languages in 23 countries, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premier Of Quebec
The premier of Quebec ( French: ''premier ministre du Québec'' (masculine) or ''première ministre du Québec'' (feminine)) is the head of government of the Canadian province of Quebec. The current premier of Quebec is François Legault of the Coalition Avenir Québec, sworn in on October 18, 2018, following that year's election. Selection and qualifications The premier of Quebec is appointed as president of the Executive Council by the Lieutenant Governor of Quebec, the viceregal representative of the Queen in Right of Quebec. The premier is most usually the head of the party winning the most seats in the National Assembly of Quebec and is normally a sitting member of the National Assembly. An exception to this rule occurs when the winning party's leader fails to win a riding. In that case, the premier would have to attain a seat by winning a by-election. This has happened, for example, to Robert Bourassa in 1985. The role of the premier of Quebec is to set the legislati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph-Adolphe Chapleau
Sir Joseph-Adolphe Chapleau (November 9, 1840 – June 13, 1898), born in Sainte-Thérèse, Quebec, was a French-Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 7th Lieutenant Governor of Quebec from 1892 to 1898. Life As a lawyer, he defended Ambroise-Dydime Lépine against the charge of murdering Thomas Scott during the Red River Rebellion of 1869–1870. He served as the fifth premier of Quebec, federal Cabinet minister, and the seventh lieutenant governor of Quebec. After the 1878 Quebec election, he was the Leader of the Opposition. He became premier in 1879 after the fall of the minority government of Henri-Gustave Joly de Lotbinière. He won the 1881 election, but resigned on July 29, 1882, to seek election to the federal House of Commons. He won a by-election held on August 16, 1882. Chapleau planned to quit politics in 1885 when Louis Riel was sentenced to be hanged but decided to stay, fearing it would only inflame the situation. After Riel was hanged, he wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divisional Point
In Canada, a divisional point (or division point) is a local operational headquarters for a railway. Divisional points are significant in railway maintenance of way operations. Especially historically, they could be the location of facilities and infrastructure such as a siding or junction, roundhouse and turntable, water tower, bunkhouse or hotel, coaling tower, passenger station, telegraph office, or freight shed. Stretches of railway line managed from a divisional point were known as divisions, and were further divided into segments known as subdivisions. The logistics of steam locomotives required numerous facilities for reversing, servicing, and supplying water and fuel for passing trains. This required an on-site workforce, which in some cases led to the growth of railway towns. Divisional points were historically significant in the westward colonization and development of Canada, supplanting the Hudson's Bay Company trading post in a number of cases as a focal point for e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fur Trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the most valued. Historically the trade stimulated the exploration and colonization of Siberia, northern North America, and the South Shetland and South Sandwich Islands. Today the importance of the fur trade has diminished; it is based on pelts produced at fur farms and regulated fur-bearer trapping, but has become controversial. Animal rights organizations oppose the fur trade, citing that animals are brutally killed and sometimes skinned alive. Fur has been replaced in some clothing by synthetic imitations, for example, as in ruffs on hoods of parkas. Continental fur trade Russian fur trade Before the European colonization of the Americas, Russia was a major supplier of fur pelts to Western Europe and parts of Asia. Its trade developed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business division is Hudson's Bay, commonly referred to as The Bay ( in French). After incorporation by English royal charter in 1670, the company functioned as the ''de facto'' government in parts of North America for nearly 200 years until the HBC sold the land it owned (the entire Hudson Bay drainage basin, known as Rupert's Land) to Canada in 1869 as part of the Deed of Surrender, authorized by the Rupert's Land Act 1868. At its peak, the company controlled the fur trade throughout much of the English- and later British-controlled North America. By the mid-19th century, the company evolved into a mercantile business selling a wide variety of products from furs to fine homeware in a small number of sales shops (as opposed to trading posts) acros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway (french: Chemin de fer Canadien Pacifique) , also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), is a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway is owned by Canadian Pacific Railway Limited, which began operations as legal owner in a corporate restructuring in 2001. Headquartered in Calgary, Alberta, the railway owns approximately of track in seven provinces of Canada and into the United States, stretching from Montreal to Vancouver, and as far north as Edmonton. Its rail network also serves Minneapolis–St. Paul, Milwaukee, Detroit, Chicago, and Albany, New York, in the United States. The railway was first built between eastern Canada and British Columbia between 1881 and 1885 (connecting with Ottawa Valley and Georgian Bay area lines built earlier), fulfilling a commitment extended to British Columbia when it entered Confederation in 1871; the CPR was Canada's first transcontinental railway. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |