|
Channar (surname)
Channar or Channan was a surname used in Kerala until the early 20th century by families of the ezhava caste. The same surname is also being used by Jatt clans. Along with Panicker, Vaidyar and Thandar families, Channar families were high status ezhavas with caste privileges. Yenathinathar Yenathinathar, also known as Yenatinata, Yenathi Nayanar, Yenadhinatha, Yenadinath, Yenadinatha Nayanar and Yenadhinatha Nayanar, was a Nayanar saint hailing from Channar clan, venerated in the Hindu sect of Shaivism. He is generally counted ..., a saivite saint and chola military general had this surname. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Channar (surname) Indian surnames Ezhava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South Canara, and Thiruvithamkoor. Spread over , Kerala is the 21st largest Indian state by area. It is bordered by Karnataka to the north and northeast, Tamil Nadu to the east and south, and the Lakshadweep Sea to the west. With 33 million inhabitants as per the 2011 census, Kerala is the 13th-largest Indian state by population. It is divided into 14 districts with the capital being Thiruvananthapuram. Malayalam is the most widely spoken language and is also the official language of the state. The Chera dynasty was the first prominent kingdom based in Kerala. The Ay kingdom in the deep south and the Ezhimala kingdom in the north formed the other kingdoms in the early years of the Common Era (CE). The region had been a prominent spic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ezhava
The Ezhavas () are a community with origins in the region of India presently known as Kerala, where in the 2010s they constituted about 23% of the population and were reported to be the largest Hindu community. They are also known as ''Ilhava'', ''Irava'', ''Izhava'' and ''Erava'' in the south of the region; as ''Chovas'', ''Chokons'' and ''Chogons'' in Central Travancore; and as ''Thiyyar'', ''Tiyyas'' and ''Theeyas'' in the Malabar region. Some are also known as ''Thandan'', which has caused administrative difficulties due to the presence of a distinct caste of Thandan in the same region. The Malabar Ezhava Pullapilly (1976) pp. 31–32 group have claimed a higher ranking in the Hindu caste system than do the others, although from the perspective of the colonial and subsequent administrations they were treated as being of similar rank. Nossiter (1982) p. 30 Ezhava dynasties such as the Mannanar existed in Kerala. Pullapilly (1976) pp. 31–32 The Chekavar, a warrior section wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caste System In India
The caste system in India is the paradigmatic ethnographic example of classification of castes. It has its origins in Outline of ancient India, ancient India, and was transformed by various ruling elites in medieval, early-modern, and modern India, especially the Mughal Empire and the British Raj. It is today the basis of Reservation in India, affirmative action programmes in India as enforced through constitution of India, its constitution. The caste system consists of two different concepts, ''Varna (Hinduism), varna'' and ''Jāti, jati'', which may be regarded as different levels of analysis of this system. Based on DNA analysis, endogamous i.e. non-intermarrying Jatis originated during the Gupta Empire. Our modern understanding of caste as an institution in India has been influenced by the collapse of the Mughal era and the rise of the British Raj, British colonial government in India. The collapse of the Mughal era saw the rise of powerful men who associated themselves w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
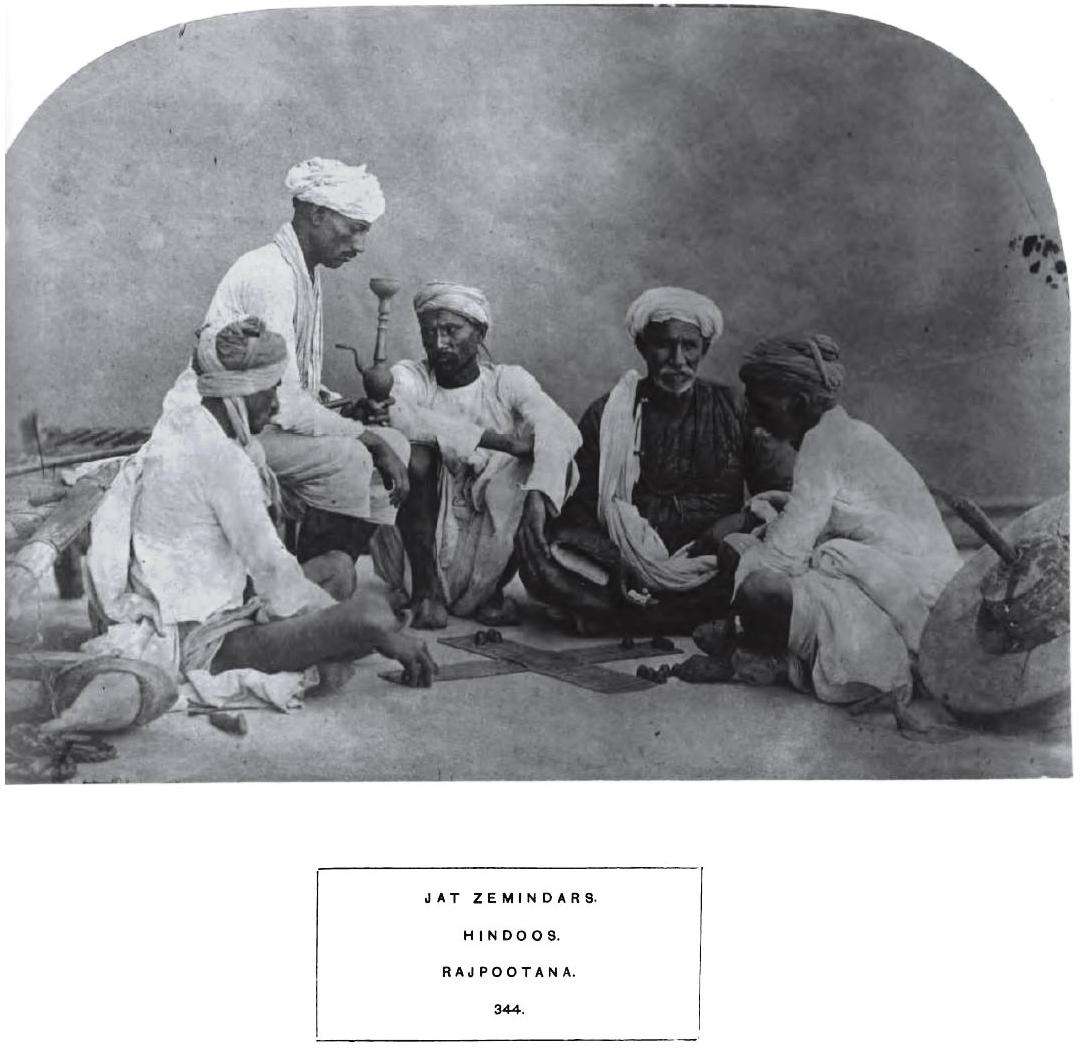
Jat People
The Jat people ((), ()) are a traditionally agricultural community in Northern India and Pakistan. Originally pastoralists in the lower Indus river-valley of Sindh, Jats migrated north into the Punjab region in late medieval times, and subsequently into the Delhi Territory, northeastern Rajputana, and the western Gangetic Plain in the 17th and 18th centuries. Quote: "Hiuen Tsang gave the following account of a numerous pastoral-nomadic population in seventh-century Sin-ti (Sind): 'By the side of the river.. f Sind along the flat marshy lowlands for some thousand li, there are several hundreds of thousands very great manyfamilies ..hichgive themselves exclusively to tending cattle and from this derive their livelihood. They have no masters, and whether men or women, have neither rich nor poor.' While they were left unnamed by the Chinese pilgrim, these same people of lower Sind were called Jats' or 'Jats of the wastes' by the Arab geographers. The Jats, as 'dromedary men.' we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panicker
Panicker was a title conferred by the king of Travancore to distinguished individuals. Kiriyathil/Illathu Nair panickers should not be confused with Kalari Panicker They were well known as the masters of Kalari tradition, having their ''Nalpatheeradi Kalari'' (name derived from its area of 42 x 21 feet). They are the people who propagated and practised Kalaripayattu, the martial art form of Kerala.Some of them were Kalari masters while the others trained and recruited men for the King or chief's army. Etymology The Portuguese traveller Duarte Barbosa said that "''They are the skillful men who teach this art Kalarippayattu, and they are called the Panickers: these are the captains in war."'' In Journal of the Epigraphical Society of India it, is given that "The teachers of martial arts in order to distinguish themselves from other Panikkars, named themselves as Vanma, Varma Panikkars, Other titles include a middle name of "Kalarikkal" (literally, '''of the kalari')'' generally f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thandar
Thandan or Thandayan is the honorary title given to the headman of the Thiyya community people in Palakkad, Thrissur district, who reside in the Indian State of Kerala. Thandan is the hereditary headman of a Thiyyar tara (village) and is a Thiyyar by caste. He is appointed by the senior Rani of the Zamorin's family or by a local Raja in territories outside the Zamorin's jurisdiction. Thandan becomes the of the or . They are designated as Other Backward Classes by the Government of Kerala as per anthropological studies conducted by the Kerala Institute of Research, and Development Studies. Status ''Thandan'' was the most commonly-used title to represent the highest privilege among the Thiyyar of the Malabar area. The most notable Thiyyar of the Malabars received the title as Thandan for their service to the state either in the administration of Malabar district Malabar District, also known as Malayalam District, was an administrative district on the southwestern Malaba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yenathinathar
Yenathinathar, also known as Yenatinata, Yenathi Nayanar, Yenadhinatha, Yenadinath, Yenadinatha Nayanar and Yenadhinatha Nayanar, was a Nayanar saint hailing from Channar clan, venerated in the Hindu sect of Shaivism. He is generally counted as the ninth in the list of 63 Nayanars. In 1901, P.Sv. Perumal Nadar formed at Aruppukottai Life The life of Yenathinathar is described in the Tamil ''Periya Puranam'' by Sekkizhar (12th century), which is a hagiography of the 63 Nayanars. His name "Enathinatha" means "Lord of the Generals". Yenathinathar was born Channar family in Eyinanur, in Chola kingdom. Eyinanur is located on the banks of river Arisil, south-east of Kumbakonam in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. A brilliant swordsman and a general in the Chola military himself, he was also the tutor to the Chola princes in swordsmanship. He was a Shaiva, a devotee of the god Shiva. He became rich owing to his prowess and spent his wealth on serving the devotees of Shiva. Atis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Surnames
Indian names are based on a variety of systems and naming conventions, which vary from region to region. Names are also influenced by religion and caste and may come from epics. India's population speaks a wide variety of languages and nearly every major religion in the world has a following in India. This variety makes for subtle, often confusing, differences in names and naming styles. Due to historical Indian cultural influences, several names across South and Southeast Asia are influenced by or adapted from Indian names or words. In some cases, Indian birth name is different from their official name; the birth name starts with a randomly selected name from the person's horoscope (based on the ''nakshatra'' or lunar mansion corresponding to the person's birth). Many children are given three names, sometimes as a part of religious teaching. Pronunciation When written in Latin script, Indian names may use the vowel characters to denote sounds different from conventional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |