|
Chandler Formation
The Chandler Formation is a Mesozoic geologic formation in Canada. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, although none have yet been referred to a specific genus.Weishampel, et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution." Pp. 517-607. Vertebrate fauna Crinoidea Bony Fish Synapsids Dinosaurs See also *List of volcanoes in Canada *Volcanism of Canada *Volcanism of Northern Canada *Geography of Nunavut * List of dinosaur-bearing rock formations ** List of stratigraphic units with indeterminate dinosaur fossils This list of stratigraphic units with indeterminate dinosaur fossils includes stratigraphic units of formation rank or higher that have produced dinosaur body fossils, although none of these remains have been referred to a specific genus in the sci ... Footnotes References * Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. 861 pp. . He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Formation
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics ( lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by Abraham Gottlob Wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracopterus Magnificus
''Thoracopterus'' is an extinct genus of overwater gliding ray-finned fish. It was common to the late Middle Triassic and Late Triassic epochs in what is now Europe and China. ''Thoracopterus'' had elongate pectoral fins, similar to modern Exocoetidae, which are used to glide overwater in order to escape aquatic predators. ''Thoracopterus'' represents the earliest known example for overwater gliding in actinopterygians. References * Fishes of the World ''Fishes of the World'' by the American ichthyologist Joseph S. Nelson (1937–2011) is a standard reference for fish systematics. Now in its fifth edition (2016), the work is a comprehensive overview of the diversity and classification of the ... by Joseph S. Nelson (page 95) * Wildlife of Gondwana: Dinosaurs and Other Vertebrates from the Ancient Supercontinent (Life of the Past) by Pat Vickers Rich, Thomas Hewitt Rich, Francesco Coffa, and Steven Morton * The Rise of Fishes: 500 Million Years of Evolution by John A. Lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanism Of Nunavut
Volcanism, vulcanism or volcanicity is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the surface of the Earth or a solid-surface planet or moon, where lava, pyroclastics, and volcanic gases erupt through a break in the surface called a vent. It includes all phenomena resulting from and causing magma within the crust or mantle of the body, to rise through the crust and form volcanic rocks on the surface. Magmas, that reach the surface and solidify, form extrusive landforms. Volcanic processes Magma from the mantle or lower crust rises through the crust towards the surface. If magma reaches the surface, its behavior depends on the viscosity of the molten constituent rock. Viscous (thick) magma produces volcanoes characterised by explosive eruptions, while non-viscous (runny) magma produce volcanoes characterised by effusive eruptions pouring large amounts of lava onto the surface. In some cases, rising magma can cool and solidify without reaching the surface. Instead, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
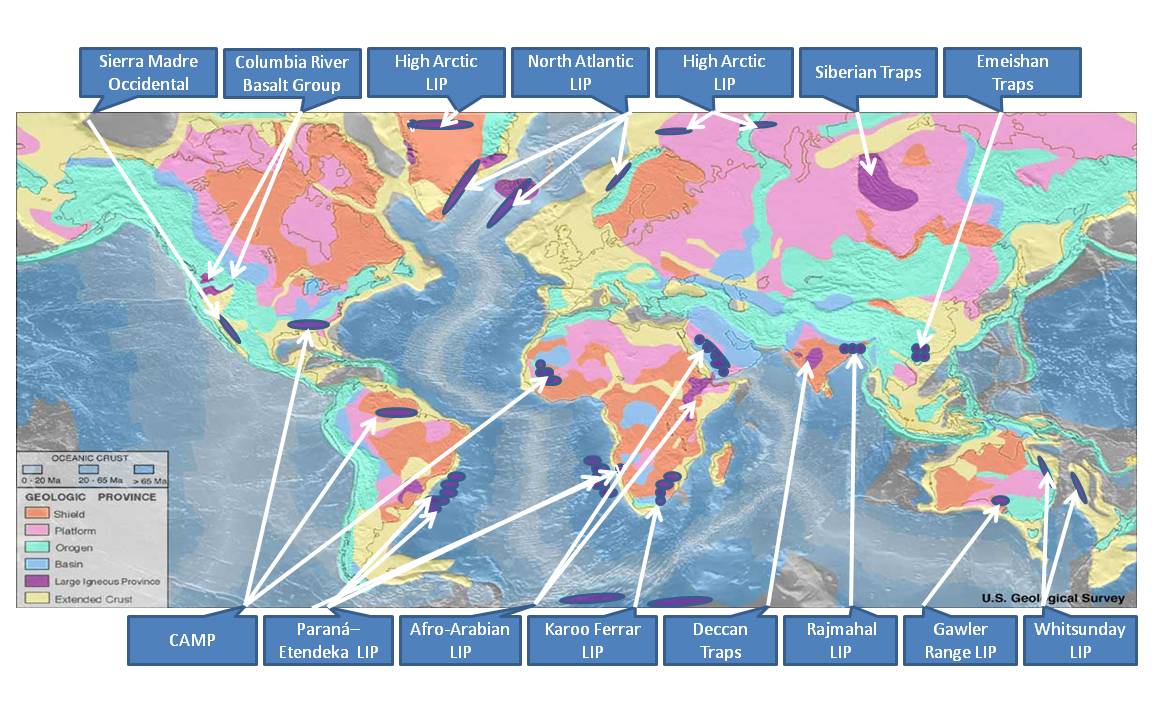
Large Igneous Provinces
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive (sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation of LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with divergent plate tectonics. The formation of some of the LIPs in the past 500 million years coincide in time with mass extinctions and rapid climatic changes, which has led to numerous hypotheses about causal relationships. LIPs are fundamentally different from any other currently active volcanoes or volcanic systems. Definition In 1992 researchers first used the term ''large igneous province'' to describe very large accumulations—areas greater than 100,000 square kilometers (approximately the area of Iceland)—of mafic igneous rocks that were erupted or emplaced at depth within an extremely short geological time interval: a few million years or less. Maf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hettangian Stage
The Hettangian is the earliest age and lowest stage of the Jurassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between 201.3 ± 0.2 Ma and 199.3 ± 0.3 Ma (million years ago). The Hettangian follows the Rhaetian (part of the Triassic Period) and is followed by the Sinemurian. In European stratigraphy the Hettangian is a part of the time span in which the Lias was deposited. An example is the British Blue Lias, which has an upper Rhaetian to Sinemurian age. Another example is the lower Lias from the Northern Limestone Alps where well-preserved but very rare ammonites, including Alsatites, have been found. Stratigraphic definitions The Hettangian was introduced in the literature by Swiss palaeontologist, Eugène Renevier, in 1864. The stage takes its name from Hettange-Grande, a town in north-eastern France, just south of the border with Luxembourg on the main road from Luxembourg City to Metz. The base of the Hettangian Stage (which is also the base of the Lower Jurass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Stratigraphic Units With Indeterminate Dinosaur Fossils
This list of stratigraphic units with indeterminate dinosaur fossils includes stratigraphic units of formation rank or higher that have produced dinosaur body fossils, although none of these remains have been referred to a specific genus in the scientific literature. Europe Africa and Middle East Australasia and Antarctica East Asia Western Hemisphere See also List of dinosaur-bearing rock formations This list of dinosaur-bearing rock formations is a list of geologic formations in which dinosaur fossils have been documented. Containing body fossils * List of stratigraphic units with dinosaur body fossils ** List of stratigraphic units with few ... Footnotes References * Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. 861 pp. . {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Stratigraphic Units With Indeterminate Dinosaur Fossils Indeterminiate dinosaur fossils ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Dinosaur-bearing Rock Formations
This list of dinosaur-bearing rock formations is a list of geologic formations in which dinosaur fossils have been documented. Containing body fossils * List of stratigraphic units with dinosaur body fossils ** List of stratigraphic units with few dinosaur genera ** List of stratigraphic units with indeterminate dinosaur fossils Containing trace fossils * List of stratigraphic units with dinosaur trace fossils ** List of stratigraphic units with dinosaur tracks *** List of stratigraphic units with ornithischian tracks *** List of stratigraphic units with sauropodomorph tracks *** List of stratigraphic units with theropod tracks See also * Lists of fossiliferous stratigraphic units * List of fossil sites * Mesozoic The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceo ... {{DEFAULTSOR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Nunavut
The Canadian territory of Nunavut covers about 1.9 million square kilometres (733,594 sq. miles) of land and water including part of the mainland, most of the Arctic islands, and all of the islands in Hudson Bay, James Bay, and Ungava Bay (including the Belcher Islands) which belonged to the Northwest Territories. This makes it the fifth largest country subdivision in the world. If Nunavut were a country, it would rank 13th in area, after the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Nunavut has land borders with Manitoba, the Northwest Territories on several islands as well as the mainland, and a tiny land border with Newfoundland and Labrador on Killiniq Island. Physical geography The mountains on the easternmost coasts of Nunavut are part of the Arctic Cordillera which stretches from northernmost Ellesmere Island to the northernmost tip of Labrador. The highest point is Barbeau Peak which offers some of the world's most spectacular scenery. Geologically, Nunavut lies on the Canadia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
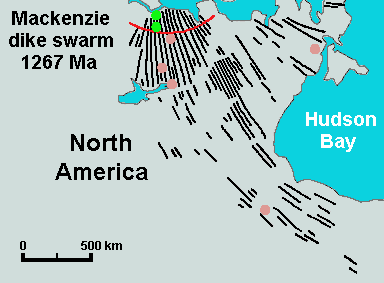
Volcanism Of Northern Canada
Volcanism of Northern Canada has produced hundreds of volcanic areas and extensive lava formations across Northern Canada. The region's different volcano and lava types originate from different tectonic settings and types of volcanic eruptions, ranging from passive lava eruptions to violent explosive eruptions. Northern Canada has a record of very large volumes of magmatic rock called large igneous provinces. They are represented by deep-level plumbing systems consisting of giant dike swarms, sill provinces and layered intrusions. Plume and rift complexes Vast volumes of basaltic lava covered Northern Canada in the form of a flood basalt event 1,267 million years ago that engulfed the landscape near the Coppermine River southwest of Coronation Gulf in the Canadian Arctic. This volcanic activity built an extensive lava plateau and large igneous province with an area of representing a volume of lavas of at least . With an area of and a volume of , it is larger than the Col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanism Of Canada
Volcanic activity is a major part of the geology of Canada and is characterized by many types of volcanic landform, including lava flows, volcanic plateaus, lava domes, cinder cones, stratovolcanoes, shield volcanoes, submarine volcanoes, calderas, diatremes, and maars, along with less common volcanic forms such as tuyas and subglacial mounds. Though Canada's volcanic history dates back to the Precambrian eon, at least 3.11 billion years ago, when its part of the North American continent began to form, volcanism continues to occur in Western and Northern Canada in modern times, where it forms part of an encircling chain of volcanoes and frequent earthquakes around the Pacific Ocean called the Pacific Ring of Fire. Because volcanoes in Western and Northern Canada are in relatively remote and sparsely populated areas and their activity is less frequent than with other volcanoes around the Pacific Ocean, Canada is commonly thought to occupy a gap in the Ring of Fire between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Volcanoes In Canada
List of volcanoes in Canada is an incomplete list of volcanoes found in Mainland Canada, in the Canadian islands and in Canadian waters. All but one province, Prince Edward Island, have at least one volcano. Alberta British Columbia New Brunswick Newfoundland and Labrador Northwest Territories Nova Scotia Nunavut Ontario Quebec Saskatchewan Yukon See also * Outline of Canada * Bibliography of Canada * Index of Canada-related articles * Volcanism of Canada ** Volcanism of Northern Canada ** Volcanism of Western Canada ** Volcanism of Eastern Canada ** List of Northern Cordilleran volcanoes * List of mountains in Canada * List of Cascade volcanoes External links Catalogue of Canadian Volcanoes {{Canadian volcanism Canada Volcanoes Volcanoes Volcanoes A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megalosauridae
Megalosauridae is a monophyletic family of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs within the group Megalosauroidea. Appearing in the Middle Jurassic, megalosaurids were among the first major radiation of large theropod dinosaurs. They were a relatively primitive group of basal tetanurans containing two main subfamilies, Megalosaurinae and Afrovenatorinae, along with the basal genus ''Eustreptospondylus'', an unresolved taxon which differs from both subfamilies. The defining megalosaurid, ''Megalosaurus bucklandii'', was first named and described in 1824 by William Buckland after multiple finds in Stonesfield, Oxfordshire, UK. ''Megalosaurus'' was the first formally described dinosaur and was the basis for the establishment of the clade Dinosauria. It is also one of the largest known Middle Jurassic carnivorous dinosaurs, with the best-preserved femur at 805 mm and a proposed body mass of around 943 kg. Megalosauridae has mainly been recognized as a European group of dinosaurs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |