|
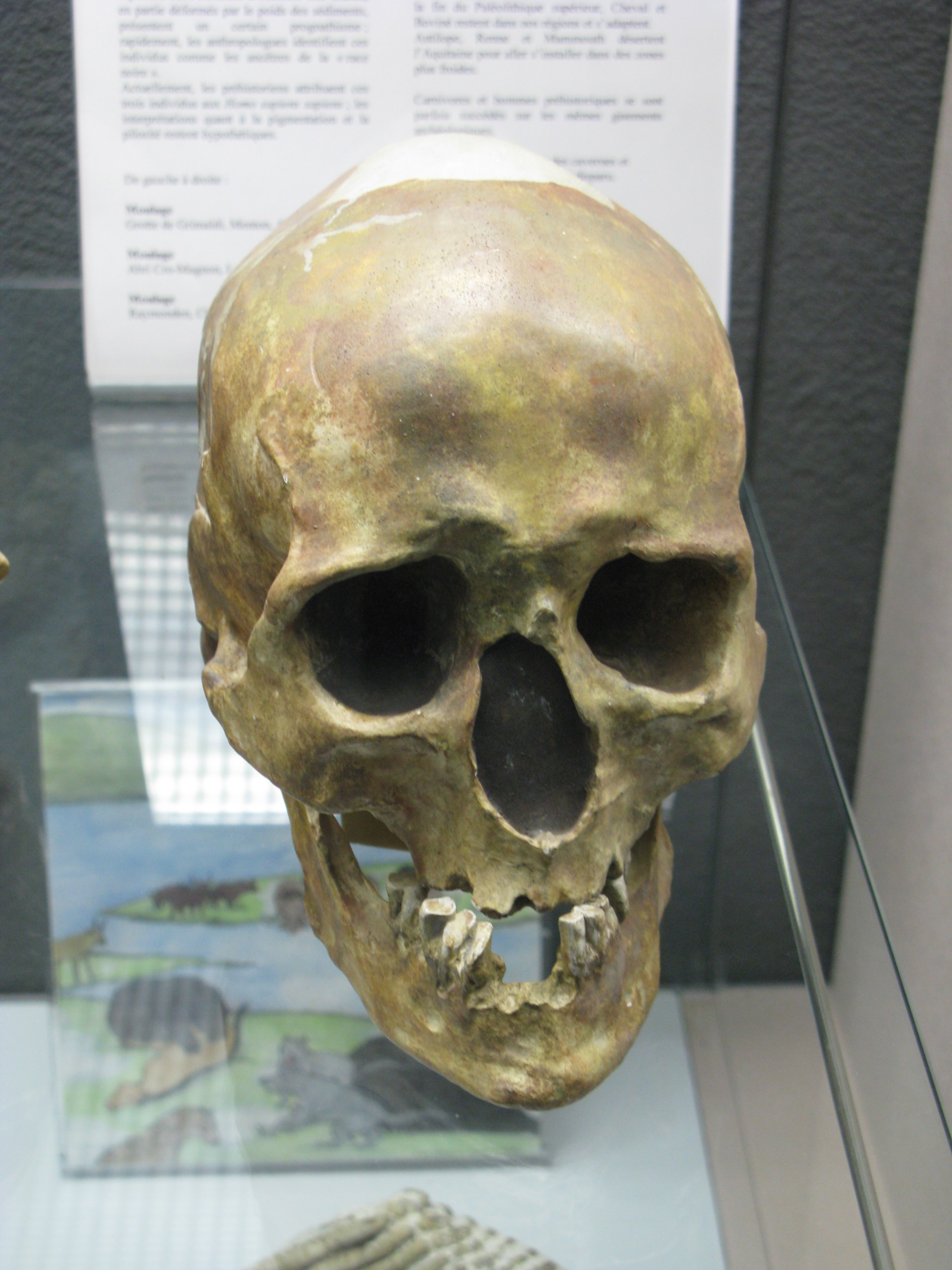
Chancelade Man
Chancelade man (the Chancelade cranium) is an ancient Anatomically modern humans, anatomically modern human fossil of a male found in Chancelade in France in 1888. The skeleton was that of a rather short man, who stood a mere tall. Due to morphological differences with the Cro-Magnon 1 cranium, early interpretations postulated that the individual belonged to a separate lineage, possibly ancestral to Eskimos. G. M. Morant in 1930 recognized the skeleton as within the morphological range of EEMH, Upper Paleolithic European populations, and this interpretation has remained accepted since. Discovery The Chancelade find was discovered in 1888 in the cave of Raymonden Chancelade in the Dordogne. Lying all the way down by the bedrock, below three layers containing Magdalenian tools, the find contained a single skeleton. The skeleton was that of an adult man, estimated to have been between 55 and 65 at death. The man had been intentionally buried and liberally coated with ochre. The sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moulage De Crâne, Raymonden, Chancelade, Dordogne
Moulage () is the art of applying mock injuries for the purpose of training emergency response teams and other medical and military personnel. Moulage may be as simple as applying pre-made rubber or latex "wounds" to a healthy "patient's" limbs, chest, head, etc., or as complex as using makeup and theatre techniques to provide elements of realism (such as blood, vomitus, open fractures, etc.) to the training simulation. The practice dates to at least the Renaissance, when wax figures were used for this purpose. In Germany some universities and hospitals use their historical moulage collections for the training of students. The often very lifelike models are especially useful to show the students today the characteristics of rare diseases, such as skin tuberculosis or leprosy. History Up until the 16th century, European scientists had little knowledge about human anatomy and anatomy of animals. Medical students of Bologna and Paris studied the books of Aristotle, Galen, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laugerie-Basse
Laugerie-Basse is an important Upper Paleolithic archaeological site within the territory of the French commune Les Eyzies-de-Tayac-Sireuil in Dordogne. It is known for several works of art from the Magdalenian. In 1979, Laugerie-Basse, along with other nearby paleolithic sites, was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List as ''Prehistoric Sites and Decorated Caves of the Vézère Valley''. Geography, geology and location The impressive Abri of Laugerie-Basse, named after the village, is located on the right side of the Vézère valley, about 2 kilometers upstream from Les Eyzies. It was formed at the bottom of a 45 meters high and 500 meters long scarp slope of flat-lying limestones from the Coniacian. The 15-meter-deep Abri is located 15 meters above river level. Taking advantage of the natural conditions, the houses of Laugerie-Basse were built directly into the rocks so that building a back wall and the back half of the roof was dispensable. The prehistoric site c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
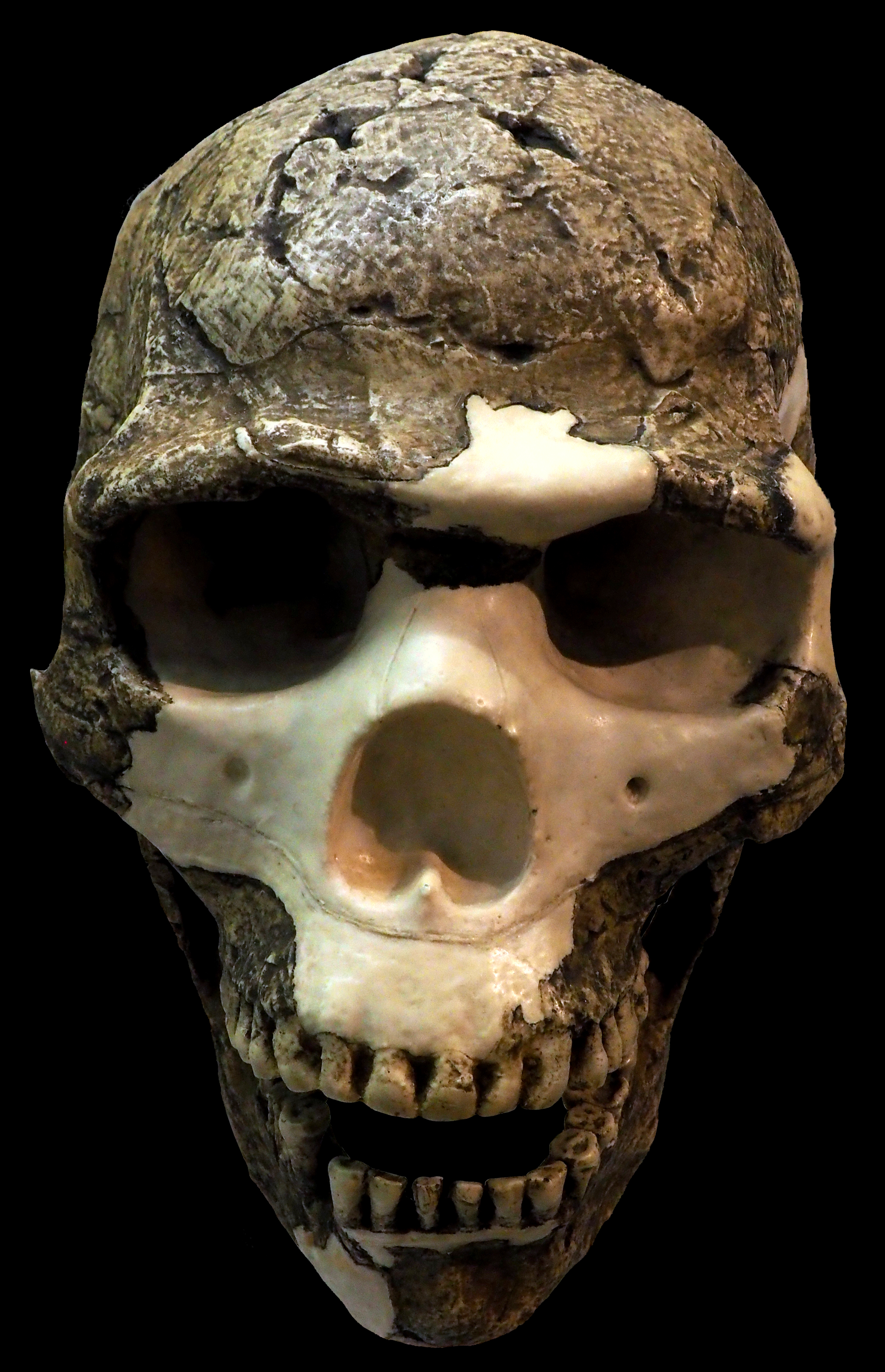
Anatomically Modern Humans
Early modern human (EMH) or anatomically modern human (AMH) are terms used to distinguish ''Homo sapiens'' (the only extant Hominina species) that are anatomically consistent with the range of phenotypes seen in contemporary humans from extinct archaic human species. This distinction is useful especially for times and regions where anatomically modern and archaic humans co-existed, for example, in Paleolithic Europe. Among the oldest known remains of ''Homo sapiens'' are those found at the Omo-Kibish I archaeological site in south-western Ethiopia, dating to about 233,000 to 196,000 years ago, the Florisbad site in South Africa, dating to about 259,000 years ago, and the Jebel Irhoud site in Morocco, dated about 315,000 years ago. Extinct species of the genus ''Homo'' include ''Homo erectus'' (extant from roughly 2 to 0.1 million years ago) and a number of other species (by some authors considered subspecies of either ''H. sapiens'' or ''H. erectus''). The divergence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minatogawa Man
The Minatogawa man or Minatogawa specimens are the prehistoric population of Okinawa, Japan, represented by four skeletons, two male and two female, and some isolated bones dated between 20,000 and 22,000 years BCE. They are among the oldest skeletons of hominins yet discovered in Japan. History of the finds The skeletons were found at the Minatogawa limestone quarry, located 10 km south of Naha, near the southern tip of the island. Okinawan businessman and amateur archaeologist Seiho Oyama noticed fossil bone fragments in some building stone blocks he had purchased from the quarry, and for two years he kept watch as the quarry was worked. In 1968, Oyama reported the finding of a human bone at the quarry to Hisashi Suzuki, a professor at Tokyo University. A team led by Suzuki excavated the site during three seasons (1968, 1970 and 1974). Their finds were described in 1982. The skeletons are now in the Anthropology Museum, Tokyo University. Description ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
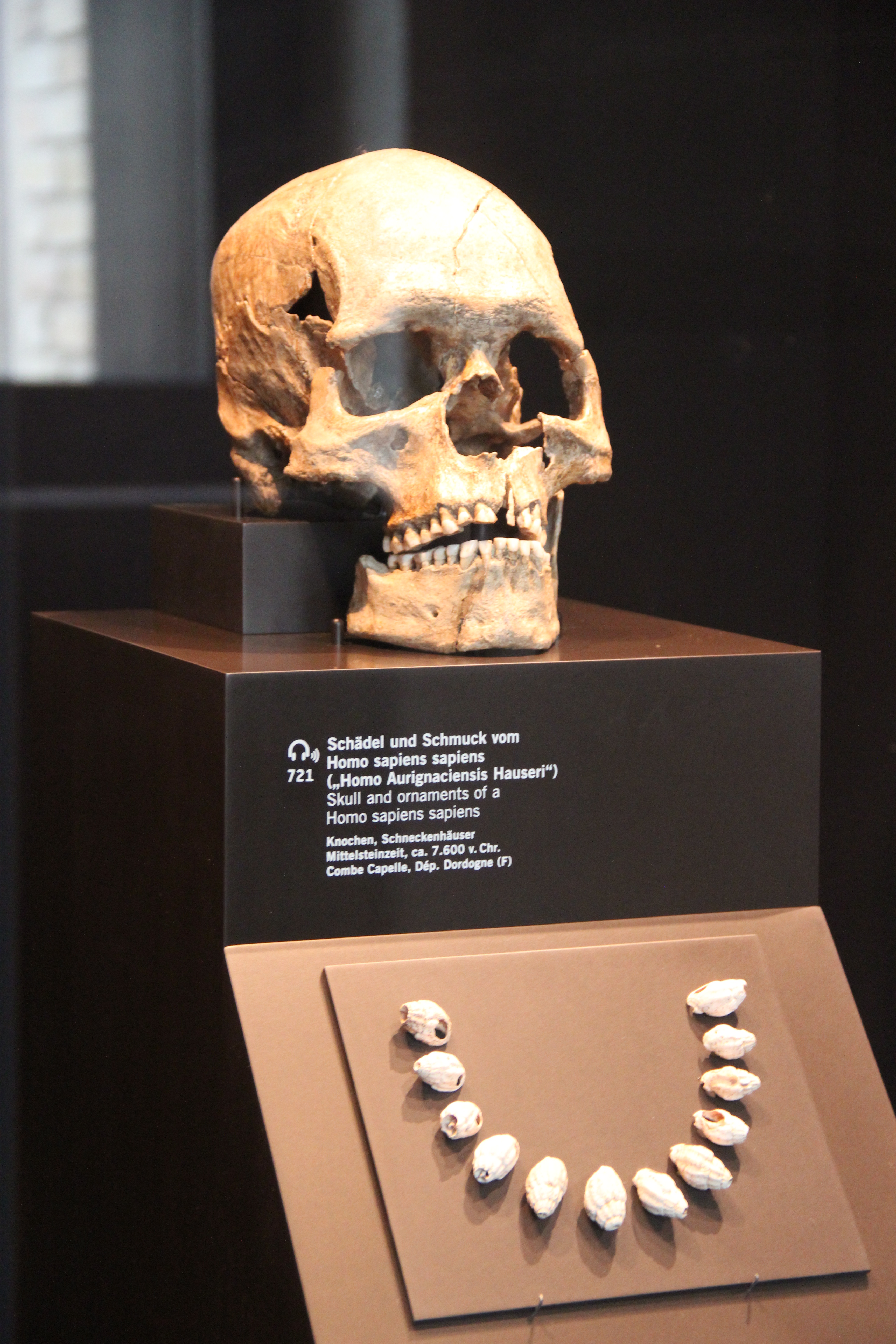
Combe-Capelle
Combe-Capelle is a Paleolithic and Epipaleolithic site situated in the Couze valley in the Périgord region of Southern France. Henri-Marc Ami carried out excavations in the area from the late 1920s until his death in 1931. The famous ''Homo sapiens'' fossil from Combe-Capelle, discovered in 1909 was sold to the Museum für Völkerkunde, Berlin, in 1910. It was for a long time considered to be 30,000 years old, an Upper Paleolithic Cro-Magnon man and one of the oldest finds of modern humans in Europe, formerly classified as '' Homo aurignaciensis hauseri''. This was revised in a 2011 study, which dated collagen from a tooth of the skull in Berlin with accelerator mass spectrometry. The fossil was found to date to the early Holocene (Mesolithic Europe The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea, and shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan to the east, and Egypt to the southwest. Israel also is bordered by the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip to the east and west, respectively. Tel Aviv is the economic and technological center of the country, while its seat of government is in its proclaimed capital of Jerusalem, although Israeli sovereignty over East Jerusalem is unrecognized internationally. The land held by present-day Israel witnessed some of the earliest human occupations outside Africa and was among the earliest known sites of agriculture. It was inhabited by the Canaanites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jebel Qafzeh Remains
The Skhul/Qafzeh hominins or Qafzeh–Skhul early modern humans are hominin fossils discovered in Es-Skhul and Qafzeh caves in Israel. They are today classified as ''Homo sapiens'', among the earliest of their species in Eurasia. Skhul Cave is on the slopes of Mount Carmel; Qafzeh Cave is a rockshelter near Nazareth in Lower Galilee. The remains found at Es Skhul, together with those found at the Nahal Me'arot Nature Reserve and Mugharet el-Zuttiyeh, were classified in 1939 by Arthur Keith and Theodore D. McCown as ''Palaeoanthropus palestinensis'', a descendant of ''Homo heidelbergensis''. History The remains exhibit a mix of traits found in archaic and anatomically modern humans. They have been tentatively dated at about 80,000-120,000 years old using electron paramagnetic resonance and thermoluminescence dating techniques. The brain case is similar to modern humans, but they possess brow ridges and a projecting facial profile like Neanderthals. They were initially rega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheikh Anta Diop
Cheikh Anta Diop (29 December 1923 – 7 February 1986) was a Senegalese historian, anthropologist, physicist, and politician who studied the human race's origins and pre-colonial African culture. Diop's work is considered foundational to the theory of Afrocentricity, though he himself never described himself as an Afrocentrist. The questions he posed about cultural bias in scientific research contributed greatly to the postcolonial turn in the study of African civilizations. Diop argued that there was a shared cultural continuity across African people that was more important than the varied development of different ethnic groups shown by differences among languages and cultures over time.Cheikh, Anta Diop, ''The Cultural Unity of Negro Africa'' (Paris: Présence Africaine, 1963), English translation: ''The Cultural Unity of Black Africa: The Domains of Patriarchy and of Matriarchy in Classical Antiquity'' (London: Karnak House: 1989), pp. 53–111. Some of his ideas have been c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afrocentrism
Afrocentrism is an approach to the study of world history that focuses on the history of people of recent African descent. It is in some respects a response to Eurocentric attitudes about African people and their historical contributions. It seeks to counter what it sees as mistakes and ideas perpetuated by the racist philosophical underpinnings of Western academic disciplines as they developed during and since Europe's Early Renaissance as justifying rationales for the enslavement of other peoples, in order to enable more accurate accounts of not only African but all people's contributions to world history. Afrocentricity deals primarily with self-determination and African agency and is a Pan-African point of view for the study of culture, philosophy, and history. Gates, Henry Louis, and Kwame Anthony Appiah (eds), '' Africana: The Encyclopedia of the African and African-American'' Volume 1, p. 111, Oxford University Press. 2005. Afrocentrism is a scholarly movement that see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negroid Race
Negroid (less commonly called Congoid) is an Historical race concepts, obsolete racial grouping of various people indigenous to Africa south of the area which stretched from the southern Sahara desert in the west to the African Great Lakes in the southeast, but also to isolated parts of South Asia, South and Southeast Asia (Negritos). The term is derived from now-discredited conceptions of race as a biological category. The concept of dividing humankind into three races called Caucasoid, Mongoloid, and Negroid (originally named "Ethiopian") was introduced in the 1780s by members of the Göttingen School of History and further developed by Western scholars in the context of "Racism, racist ideologies" during the age of colonialism. With the rise of modern genetics, the concept of distinct human races in a biological sense has become obsolete. In 2019, the American Association of Biological Anthropologists stated: "Race does not provide an accurate representation of human biologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |