|
Chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. Chalk is common throughout Western Europe, where deposits underlie parts of France, and steep cliffs are often seen where they meet the sea in places such as the Dover cliffs on the Kent coast of the English Channel. Chalk is mined for use in industry, such as for quicklime, bricks and builder's putty, and in agriculture, for raising pH in soils with high acidity. It is also used for " blackboard chalk" for writing and drawing on various types of surfaces, although these can also be manufactured from other carbonate-based minerals, or gypsum. Description Chalk is a fine-textured, earthy type of limestone distinguished by its light color, softness, and high porosity. It is composed mostly of tiny fragments of the calcite shells or skeletons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackboard
A blackboard (also known as a chalkboard) is a reusable writing surface on which text or drawings are made with sticks of calcium sulphate or calcium carbonate, known, when used for this purpose, as chalk. Blackboards were originally made of smooth, thin sheets of black or dark grey slate stone. Design A blackboard can simply be a board painted with a dark matte paint (usually black, occasionally dark green). Matte black plastic sign material (known as closed-cell PVC foamboard) is also used to create custom chalkboard art. Blackboards on an A-frame are used by restaurants and bars to advertise daily specials. A more modern variation consists of a coiled sheet of plastic drawn across two parallel rollers, which can be scrolled to create additional writing space while saving what has been written. The highest grade blackboards are made of a rougher version porcelain enamelled steel (black, green, blue or sometimes other colours). Porcelain is very hard wearing, and blackboar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern England Chalk Formation
Downland, chalkland, chalk downs or just downs are areas of open chalk hills, such as the North Downs. This term is used to describe the characteristic landscape in southern England where chalk is exposed at the surface. The name "downs" is derived from the Old English word dun, meaning "hill". Distribution The largest area of downland in southern England is formed by Salisbury Plain, mainly in Wiltshire. To the southwest, downlands continue via Cranborne Chase into Dorset as the Dorset Downs and southwards through Hampshire as the Hampshire Downs onto the Isle of Wight. To the northeast, downlands continue along the Berkshire Downs and Chiltern Hills through parts of Berkshire, Oxfordshire, Buckinghamshire, Hertfordshire, Bedfordshire and into Cambridgeshire. To the east downlands are found north of the Weald in Surrey, Kent and part of Greater London, forming the North Downs. To the southeast the downlands continue into West Sussex and East Sussex as the South Downs. Similar cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dover Cliffs
The White Cliffs of Dover is the region of English coastline facing the Strait of Dover and France. The cliff face, which reaches a height of , owes its striking appearance to its composition of chalk accented by streaks of black flint, deposited during the Late Cretaceous. The cliffs, on both sides of the town of Dover in Kent, stretch for eight miles (13 km). The White Cliffs of Dover form part of the North Downs. A section of coastline encompassing the cliffs was purchased by the National Trust in 2016. The cliffs are part of the Dover to Kingsdown Cliffs Site of Special Scientific Interest and Special Area of Conservation. The point where Great Britain is closest to continental Europe, on a clear day the cliffs are visible from France (approximately away). A celebrated UK landmark, the cliffs have featured on commemorative postage stamps issued by the Royal Mail, including in their British coastline series in 2002 and UK A-Z series in 2012. Location The cliff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for limes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
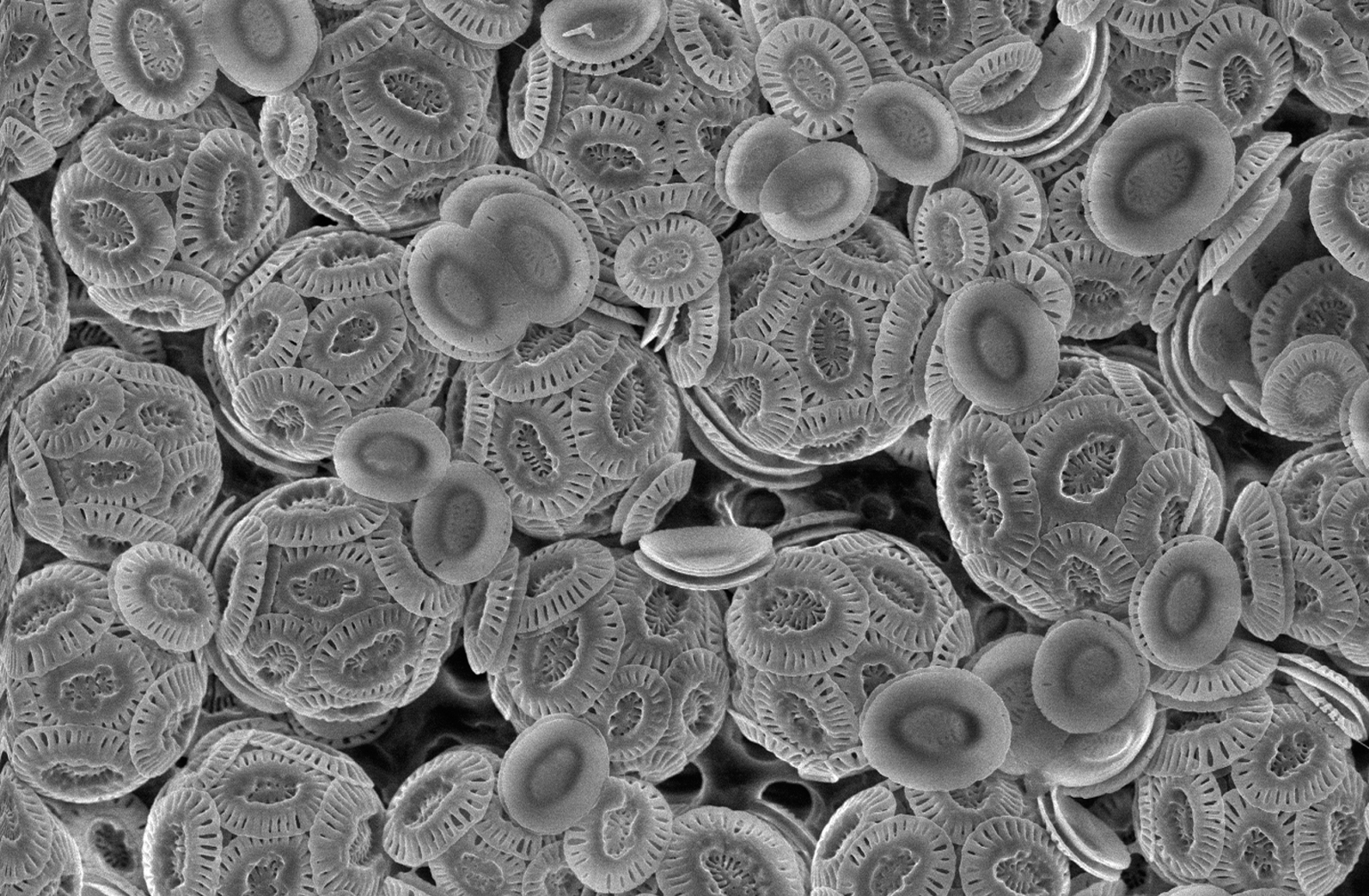
Coccolithophore
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the kingdom Protista, according to Robert Whittaker's Five kingdom classification, or clade Hacrobia, according to a newer biological classification system. Within the Hacrobia, the coccolithophores are in the phylum or division Haptophyta, class Prymnesiophyceae (or Coccolithophyceae). Coccolithophores are almost exclusively marine, are photosynthetic, and exist in large numbers throughout the sunlight zone of the ocean. Coccolithophores are the most productive calcifying organisms on the planet, covering themselves with a calcium carbonate shell called a ''coccosphere''. However, the reasons they calcify remains elusive. One key function may be that the coccosphere offers protection against microzooplankton predation, which is one of the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces the French department of Pas-de-Calais across the Strait of Dover. The county town is Maidstone. It is the fifth most populous county in England, the most populous non-Metropolitan county and the most populous of the home counties. Kent was one of the first British territories to be settled by Germanic tribes, most notably the Jutes, following the withdrawal of the Romans. Canterbury Cathedral in Kent, the oldest cathedral in England, has been the seat of the Archbishops of Canterbury since the conversion of England to Christianity that began in the 6th century with Saint Augustine. Rochester Cathedral in Medway is England's second-oldest cathedral. Located between London and the Strait of Dover, which separates England from mainla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seale Chalk Pit 02
Seale may refer to: *Seale, Alabama, an unincorporated community in the United States *Seale, Surrey, a village in England *Seale Hayne College, military hospital in Ivybridge, Devon, UK Seale is also a surname: * Seale Baronets (since 1838), noble family *Charles Seale-Hayne (1833–1903), British member of Parliament from 1885 to 1903 *Alvin Seale (1871–1958), American ichthyologist *Arthur Seale (born 1946), convicted murderer *Bobby Seale (born 1937), American civil rights activist *Clive Seale (born 1955), British medical sociologist *Douglas Seale (1913–1999), British actor *James Ford Seale (1936–2011), Ku Klux Klan member *John Seale (born 1942), Australian cinematographer * Patrick Seale (1930–2014), British journalist *Shonte Seale (born 1999), Barbadian netball player See also * Seal (other) * Seals (other) Seals may refer to: * Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly: ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywall. Alabaster, a fine-grained white or lightly tinted variety of gypsum, has been used for sculpture by many cultures including Ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, Ancient Rome, the Byzantine Empire, and the Nottingham alabasters of Medieval England. Gypsum also crystallizes as translucent crystals of selenite. It forms as an evaporite mineral and as a hydration product of anhydrite. The Mohs scale of mineral hardness defines gypsum as hardness value 2 based on scratch hardness comparison. Etymology and history The word ''gypsum'' is derived from the Greek word (), "plaster". Because the quarries of the Montmartre district of Paris have long furnished burnt gypsum (calcined gypsum) used for various purposes, this dehydrated gypsum became known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitzana Chalk Curves (2), Western Negev, Israel , a communal settlement also known as Kadesh Barne'a after the Exodus station of that name.
{{disambig, geo ...
Nitzana ( he, נִצָּנָה) may refer to: *Nitzana (Nabataean city), a city of the ancient Nabataeans located in the Negev desert in Israel *Nitzana, Israel, a communal settlement near the ruins of the Nabataean city *Nitzana Border Crossing, a border crossing between Israel and Egypt See also *Ashdod Nitzanim Sand Dune Park *Nitzan, a communal settlement in southern Israel located among the Nitzanim sand dunes north of Ashkelon *Nitzanei Sinai Nitzanei Sinai ( or ), also known as Kadesh Barnea (), is a community settlement in the western Negev desert in Israel. Located near Nitzana, it falls under the juridisction of Ramat HaNegev Regional Council. In it had a population of . Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
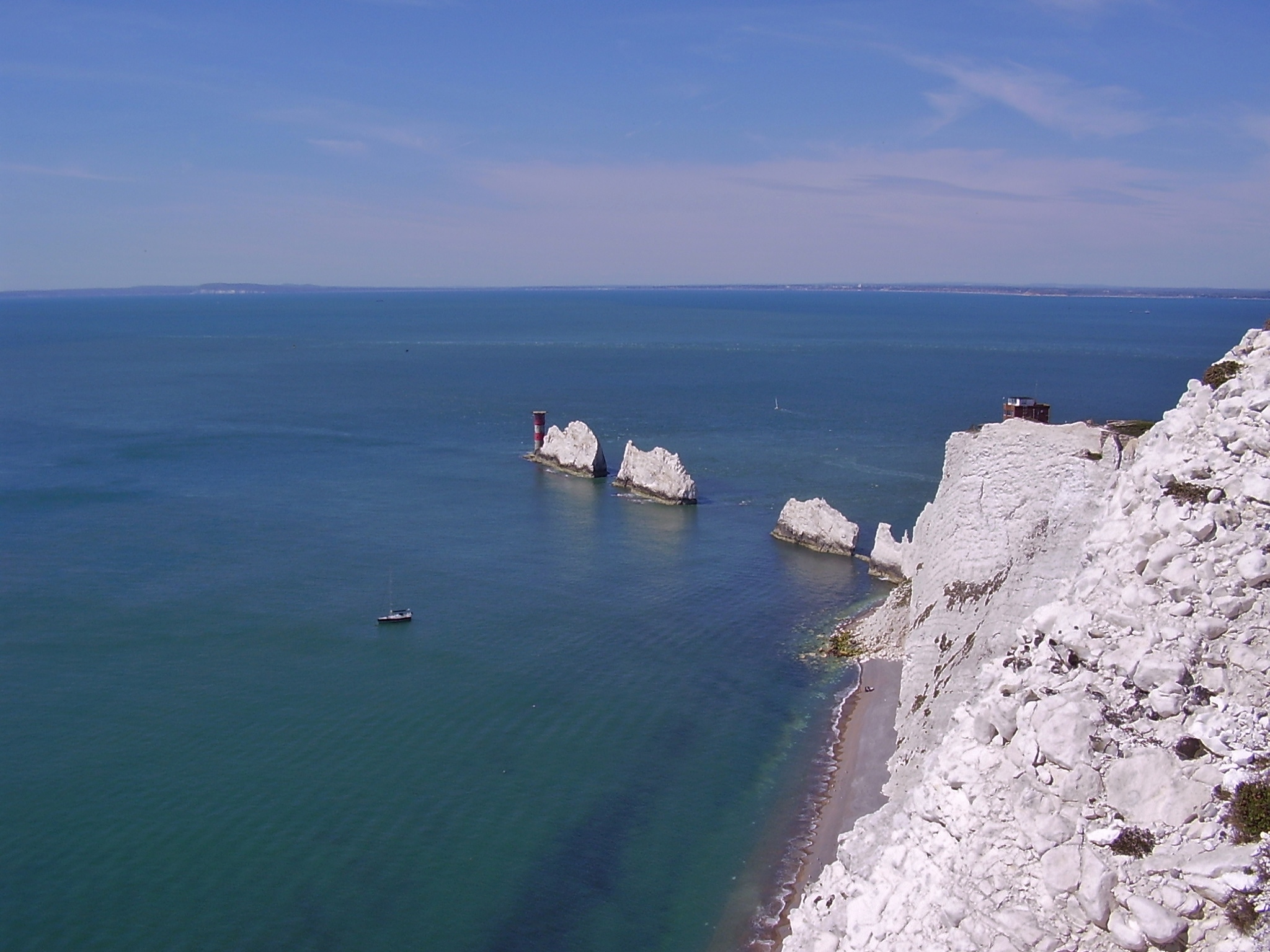
The Needles
The Needles is a row of three stacks of chalk that rise about out of the sea off the western extremity of the Isle of Wight in the English Channel, United Kingdom, close to Alum Bay and Scratchell's Bay, and part of Totland, the westernmost civil parish of the Isle of Wight. The Needles Lighthouse stands at the outer, western end of the formation. Built in 1859, it has been automated since 1994. The waters and adjoining seabed form part of the Needles Marine Conservation Zone and the Needles along with the shore and heath above are part of the Headon Warren and West High Down Site of Special Scientific Interest. The formation takes its name from a fourth needle-shaped pillar called Lot's Wife, which collapsed in a storm in 1764. The remaining rocks are not at all needle-like, but the name has stuck. The Needles were featured on the BBC Two TV programme ''Seven Natural Wonders'' (2005) as one of the wonders of Southern England. During Storm Eunice on 18 February 2022, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foraminifera
Foraminifera (; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class of amoeboid protists characterized by streaming granular Ectoplasm (cell biology), ectoplasm for catching food and other uses; and commonly an external shell (called a "Test (biology), test") of diverse forms and materials. Tests of chitin (found in some simple genera, and Textularia in particular) are believed to be the most primitive type. Most foraminifera are marine, the majority of which live on or within the seafloor sediment (i.e., are benthos, benthic), while a smaller number float in the water column at various depths (i.e., are planktonic), which belong to the suborder Globigerinina. Fewer are known from freshwater or brackish conditions, and some very few (nonaquatic) soil species have been identified through molecular analysis of small subunit ribosomal DNA. Foraminifera typically produce a test (biology), test, or shell, which can have eithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to live in cities. The history of agriculture began thousands of years ago. After gathering wild grains beginning at least 105,000 years ago, nascent farmers began to plant them around 11,500 years ago. Sheep, goats, pigs and cattle were domesticated over 10,000 years ago. Plants were independently cultivated in at least 11 regions of the world. Industrial agriculture based on large-scale monoculture in the twentieth century came to dominate agricultural output, though about 2 billion people still depended on subsistence agriculture. The major agricultural products can be broadly grouped into foods, fibers, fuels, and raw materials (such as rubber). Food classes include cereals (grains), vegetables, fruits, cooking oils, meat, milk, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
%2C_Western_Negev%2C_Israel.jpg)