|
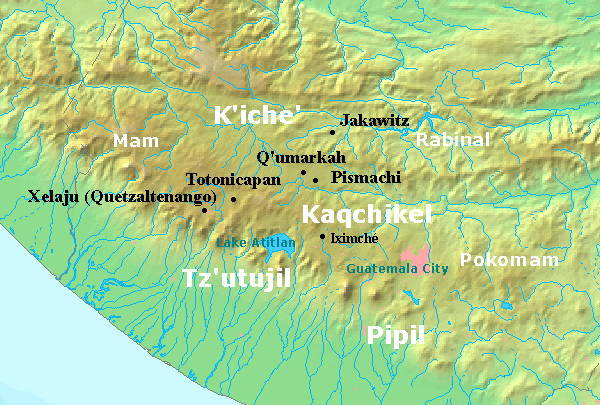
Chajoma
The Chajoma () were a Kaqchikel-speaking Maya people of the Late Postclassic period, with a large kingdom in the highlands of Guatemala. According to the indigenous chronicles of the K'iche' and the Kaqchikel, there were three principal Postclassic highland kingdoms; the K'iche', the Kaqchikel and the Chajoma.Hill 1998, p.233. In the Annals of the Cakchiquels the Chajoma of Jilotepeque were always referred to as the ''akajal vinak'', in the Popul Vuh these can probably be identified with the ''akul vinak''. Both ''akajal vinak'' and ''akul vinak'' mean "the bee people" or "the hive people". ''Chajoma'' means "people of ocote" (a type of pine).Carmack 2001, p.151. In colonial times this was rendered into Nahuatl as ''sacatepēc'' "Grass mountain" which led to its current Hispanicized name ''Sacatepéquez''. Early records, for example, record the placename San Juan Sacatepéquez as San Juan Chajoma. The Chajoma separated into six divisions, equivalent to the various colonial villa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixco Viejo
Mixco Viejo () ("Old Mixco"), occasionally spelt Mixcu Viejo, is an archaeological site in the north east of the Chimaltenango department of Guatemala, some to the north of Guatemala City and from the junction of the rivers Pixcaya and Motagua. It is a moderate sized ruined city of the Postclassic Maya civilization. The archaeological site and tourist attraction of Mixco Viejo was named after being erroneously associated with the Postclassic Poqomam capital referred to in colonial records by that name. The archaeological site has now been identified as Jilotepeque Viejo, the capital of the Chajoma Kaqchikel kingdom. To distinguish between the two, the ruins of the Chajoma capital are now referred to as Mixco Viejo (Jilotepeque Viejo) while the former Poqomam capital is referred to as Mixco Viejo (Chinautla Viejo). This confusion in the identification of the site has hindered study. The Chajoma capital has been investigated archaeologically, under the assumption that it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zacualpa
Zacualpa () is a town and municipality in the Guatemalan department of El Quiché. The family of Nobel Peace Prize winner is originally from this municipality. Etymology Many place names in Guatemala, including the name of the country, are Nahuatl names imposed by the conquering Spaniards, using words given to them by their Mexican allies. ''Sac'' in Maya means white, however, and the legend is that the white sediments in the banks and hills above the Polochic River are the origin of Sac Wal B'a. As of 1850, the British were calling Zacualpa, Sacualpa. Both spellings are still found informally. History Pre-colonial Zacualpa has its origins as a prominent Maya city in the Guatemalan highlands. Much of the research surrounding the site was undergone by American archaeologist Robert Wauchope who excavated the site from 1935-36 and again in 1947. Based on ceramic analysis, Zacualpa existed as early as the regional "Balan phase" (317 - 633) and was contemporaneous with the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iximche
Iximcheʼ () (or Iximché using Spanish orthography) is a Pre-Columbian Mesoamerican archaeological site in the western highlands of Guatemala. Iximche was the capital of the Late Postclassic Kaqchikel Maya kingdom from 1470 until its abandonment in 1524. The architecture of the site included a number of pyramid-temples, palaces and two Mesoamerican ballcourts. Excavators uncovered the poorly preserved remains of painted murals on some of the buildings and ample evidence of human sacrifice. The ruins of Iximche were declared a Guatemalan National Monument in the 1960s.Centro de Acción Legal - Ambiental y Social de Guatemala (CALAS). The site has a small museum displaying a number of pieces found there, including sculptures and ceramics. It is open daily. For many years the Kaqchikel served as loyal allies of the Kʼicheʼ Maya.Schele & Mathews 1999, p.295. The growing power of the Kaqchikel within the alliance eventually caused such friction that the Kaqchikel were forced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaqchikel People
The Kaqchikel (also called Kachiquel) are one of the indigenous Maya peoples of the midwestern highlands in Guatemala. They constitute Guatemala's third largest Maya group. The name was formerly spelled in various other ways, including Cakchiquel, Kakchiquel, Caqchikel, and Cachiquel. In Postclassic Maya times the capital of the main branch of the Kaqchikel was Iximché. Like the neighboring K'iche' (Quiché), they were governed by four lords: Tzotzil, Xahil, Tucuché and Acajal, who were responsible for the administrative, military and religious affairs. The Kakchikel recorded their history in the book ''Annals of the Cakchiquels'', also known as '' Memorial de Sololá''. The Chajoma were another Kaqchikel-speaking people; the ruins of Mixco Viejo have been identified as their capital. Iximché was conquered by the Spanish conquistador Pedro de Alvarado in 1524. At that time, the Kaqchikel were the enemies of the neighbouring K'iche' Kingdom, and helped the Spaniards to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Juan Sacatepéquez
San Juan Sacatepéquez () is a city, with a population of 155,965 (2018 census) Population of the major cities in Guatemala making it the eighth largest in Guatemala, and a in the of , northwest of . The city is known for flower-growing and wooden furn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by Honduras; to the southeast by El Salvador and to the south by the Pacific Ocean. With an estimated population of around million, Guatemala is the most populous country in Central America and the 11th most populous country in the Americas. It is a representative democracy with its capital and largest city being Nueva Guatemala de la Asunción, also known as Guatemala City, the most populous city in Central America. The territory of modern Guatemala hosted the core of the Maya civilization, which extended across Mesoamerica. In the 16th century, most of this area was conquered by the Spanish and claimed as part of the viceroyalty of New Spain. Guatemala attained independence in 1821 from Spain and Mexico. In 1823, it became part of the Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poqomam People
The Poqomam are a Maya people in Guatemala and El Salvador. Their indigenous language is also called Poqomam and is closely related to Poqomchi'. Notable Poqomam settlements are located in Chinautla (Guatemala (department)), Palín (Escuintla), and in San Luis Jilotepeque (Jalapa). Before the Spanish Conquest, the Poqomam had their capital at Chinautla Viejo.Hill 1996, p.82. Carmack 2001, p.158. The Poqomam that advanced further east, to the territories of present-day El Salvador, were largely displaced by the migration of the Pipil people in the 11th century. The few Poqomam that remained in El Salvador live near the Guatemala border, in the departments of Santa Ana and Ahuachapan. See also * Mixco Viejo Mixco Viejo () ("Old Mixco"), occasionally spelt Mixcu Viejo, is an archaeological site in the north east of the Chimaltenango department of Guatemala, some to the north of Guatemala City and from the junction of the rivers Pixcaya and Mo ... Notes References * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixco Viejo 2
Mixco () is a city and municipality in the Guatemala department of Guatemala. It is next to the main Guatemala City municipality and has become part of the Guatemala City Metropolitan Area. Most of Mixco is separated from the city by canyons, for which a multitude of bridges have been created. Ciudad San Cristóbal, one of Guatemala's largest cities, is located in this municipality. It is the second largest city in Guatemala Department, after Guatemala City, with a population of 465,773. Administrative division The municipality is divided into zones with residential neighborhoods, villages, settlements and the municipal capital. Due to its close proximity to Guatemala City, several villages were turned into residential neighborhoods. From the residential neighborhoods it is excluded "La Florida", which separated from Mixco to join Guatemala City in 1958. Mayors Universities * UruralG * UPANA * USAC * URL *UNI Sports Deportivo Mixco football club play in the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
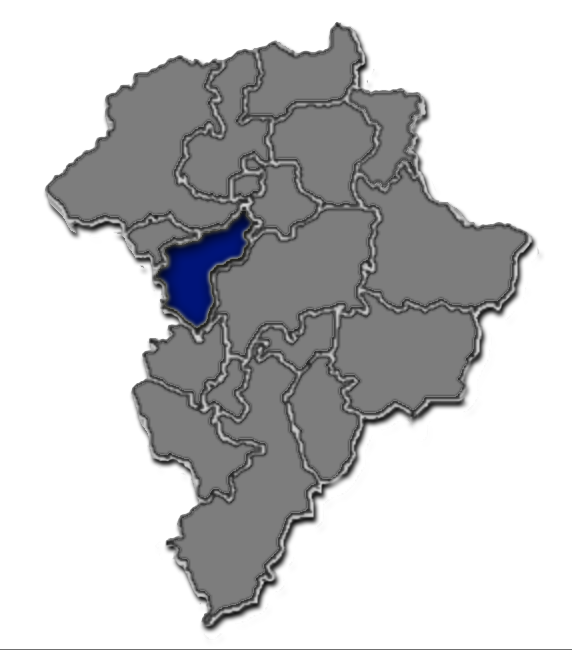
Guatemala Department
Guatemala Department is one of the 22 departments of Guatemala. The capital is Guatemala City, which also serves as the national capital. The department consists of Guatemala City and several of its suburbs. The department covers a surface area of , and had a population of 3,015,081 at the 2018 census. Municipalities # Amatitlán # Chinautla # Chuarrancho # Fraijanes # Guatemala City # Mixco # Palencia # San José del Golfo # San José Pinula # San Juan Sacatepéquez # San Miguel Petapa # San Pedro Ayampuc # San Pedro Sacatepéquez # San Raymundo # Santa Catarina Pinula # Villa Canales Villa Canales is a city and municipality in the Guatemala department of Guatemala, situated 22 km south of the capital Guatemala City. As of the 2018 census, the city had a population of 124,680, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphic Rock
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causing profound physical or chemical changes. During this process, the rock remains mostly in the solid state, but gradually recrystallizes to a new texture or mineral composition. The protolith may be an igneous, sedimentary, or existing metamorphic rock. Metamorphic rocks make up a large part of the Earth's crust and form 12% of the Earth's land surface. They are classified by their protolith, their chemical and mineral makeup, and their texture. They may be formed simply by being deeply buried beneath the Earth's surface, where they are subject to high temperatures and the great pressure of the rock layers above. They can also form from tectonic processes such as continental collisions, which cause horizontal pressure, friction, and distorti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tz'utujil People
Tz'utujil (), Tzutujil, Tzutuhil, Sutujil, and Zutuhil may refer to * Tz'utujil people, an ethnic subgroup of the Maya * Tz'utujil language Tz'utujil (), Tzutujil, Tzutuhil, Sutujil, and Zutuhil may refer to * Tz'utujil people Tz'utujil (), Tzutujil, Tzutuhil, Sutujil, and Zutuhil may refer to * Tz'utujil people, an ethnic subgroup of the Maya * Tz'utujil language, spoken by those p ..., spoken by those people {{disamb Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schistose
Schist ( ) is a medium-grained metamorphic rock showing pronounced schistosity. This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a low-power hand lens, oriented in such a way that the rock is easily split into thin flakes or plates. This texture reflects a high content of platy minerals, such as micas, talc, chlorite, or graphite. These are often interleaved with more granular minerals, such as feldspar or quartz. Schist typically forms during regional metamorphism accompanying the process of mountain building (orogeny) and usually reflects a medium grade of metamorphism. Schist can form from many different kinds of rocks, including sedimentary rocks such as mudstones and igneous rocks such as tuffs. Schist metamorphosed from mudstone is particularly common and is often very rich in mica (a ''mica schist''). Where the type of the original rock (the protolith) is discernible, the schist is usually given a name reflecting its protolith, such as ''schistose met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |