|
Chachapoyas Province
Chachapoyas is a province of the Amazonas Region, Peru. The province of Chachapoyas was a part of the department of Trujillo (according to the supreme decree of February 12, 1821) being its capital the city of Chachapoyas. After the department of Amazonas was created, by law of November 21, 1832, it became a province of the Amazonas region, and the city of Chachapoyas remained a regional capital. Its principal quarters are: *To the north: Luya Urco and Santo Domingo *To the south: Yanco and La Laguna. A big part of the province is constituted by soils of puna, located between in the oriental districts of Chiliquín, Quinjalca and Granada. Two principal rivers cover its territory: the Utcubamba, which runs from south to north and which right margin is dedicated to the agriculture in diverse form; and the Sonche, which runs from east to west and it is born from the meeting of several creeks that go down the heights of Molino Pampa district. This river flows into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Peru
The provinces of Peru () are the second-level administrative subdivisions of the country. They are divided into Districts of Peru, districts ( es, distritos, links=no). There are 196 provinces in Peru, grouped into 25 Regions of Peru, regions, except for Lima Province which does not belong to any region. This makes an average of seven provinces per region. The region with the fewest provinces is Callao (one) and the region with the most is Ancash Region, Ancash (twenty). While provinces in the sparsely populated Amazon rain forest of eastern Peru tend to be larger, there is a large concentration of them in the north-central area of the country. The province with the fewest districts is Purús Province, with just one district. The province with the most districts is Lima Province, with 43 districts. The most common number of districts per province is eight; a total of 29 provinces share this number of districts. Provinces table The table below shows all provinces with their capit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stream
A stream is a continuous body of water, body of surface water Current (stream), flowing within the stream bed, bed and bank (geography), banks of a channel (geography), channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a stream may be referred to by a variety of local or regional names. Long large streams are usually called rivers, while smaller, less voluminous and more intermittent river, intermittent streams are known as streamlets, brooks or creeks. The flow of a stream is controlled by three inputs – surface runoff (from precipitation or meltwater), daylighting (streams), daylighted subterranean river, subterranean water, and surfaced groundwater (Spring (hydrology), spring water). The surface and subterranean water are highly variable between periods of rainfall. Groundwater, on the other hand, has a relatively constant input and is controlled more by long-term patterns of precipitation. The stream encompasses surface, subsurface and groundwater fluxes th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levanto District
Levanto is a district of the province of Chachapoyas. History It was one of the principal centers in the province of Chachapoyas. In 1538 Alonso de Alvarado founded the city of Chachapoyas, Peru Chachapoyas () is a city in northern Peru at an elevation of 2,335 meters (7,661 ft). The city has a population of 32,026 people (2017). Situated in the mountains far from the Peruvian coast, Chachapoyas remains fairly isolated from other regi .... There are an enormous quantity of archaeological sites, including nine archaeological sites of major importance. Demographics According to the census carried out in 1993 and his projection. The district of Levanto has a population of 1,170 inhabitants for 2000 of whom 51% are men and the difference of 49% are women; most of the population is located in the Urban area with 57%; and in Rural area 43%, being his valuation of population growth raised in the order of 2.6%. 58% of the population is under the age of 25. External linksLevanto d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conila (Peru)
Conila is a district of the Peruvian Luya Province of the Amazonas Region. Conila offers several attractive places for tourists such as the ruins of the culture Chachapoya. Many fruits grow in the zone. As of 2003, Conila was the last place where Chachapoyas Quechua is still spoken by all ages.Ethnologue.com: Chachapoyas Quechua. http://www.ethnologue.com/show_language.asp?code=quk The management holidays of the provincial capital Bribe are celebrated on June 24, and in Conila on June 16. Typical meals there are the Candy stick, the Stew and the Nickname. In the north the Conila borders the District of Jamalca, in the East, the Saint's District Catalina and the District of Luya Viejo. In the south it borders the District of Lonya Chico and the District of Ocalli and in the west, the District of Camporredondo. See also * Kuntur Puna Kuntur Puna (Quechua ''kuntur'' condor, '' puna'' an ecoregion near the Andes, "condor puna", Hispanicized spelling ''Condor Puna, Condorpuna, Cón ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peruvian Ancient Cultures
The Andean civilizations were complex societies of many cultures and peoples mainly developed in the river valleys of the coastal deserts of Peru. They stretched from the Andes of southern Colombia southward down the Andes to Chile and northwest Argentina. Archaeologists believe that Andean civilizations first developed on the narrow coastal plain of the Pacific Ocean. The Caral or Norte Chico civilization of Peru is the oldest known civilization in the Americas, dating back to 3200 BCE. Despite severe environmental challenges, the Andean civilizations domesticated a wide variety of crops, some of which became of worldwide importance. The Andean civilizations were also noteworthy for monumental architecture, textile weaving, and many unique characteristics of the societies they created. Less than a century prior to the arrival of the Spanish conquerors, the Incas, from their homeland centered on the city of Cusco, united most of the Andean cultures into one single empire that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alonso De Alvarado
Alonso de Alvarado Montaya González de Cevallos y Miranda (1500–1556) was a Spanish conquistador and knight of the Order of Santiago. He was born at Secadura de Trasmiera.Leon, P., 1998, The Discovery and Conquest of Peru, Chronicles of the New World Encounter, edited and translated by Cook and Cook, Durham: Duke University Press, After a period in Mexico under the orders of Hernán Cortés, he joined the campaign of Francisco Pizarro. He went to Peru with his uncle Pedro de Alvarado in search of gold in 1534. There he fought against the armies of Manco Inca Yupanqui that were besieging Lima in 1536, against Diego de Almagro in 1537 and at the Battle of Las Salinas in 1538. He later fought at Chupas and Jaquijahuana. While charged by some contemporaries with avarice and cruelty, it is undeniable that during the period of civil wars in Peru (about 1537 to 1555) Alvarado was an unflinching and determined adherent to the interests of the Spanish crown. He always side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Jalca (Peru)
La Jalca was the first Spanish foundation of the region in northern Peru. It was established as the first head office of the current city of Chachapoyas. There in 1538, he took the name of Saint John of the Border of the Chachapoyas, in honor to his holy boss. Also of this epoch they date the famous juanes, typical plate of the forest prepared and invented for the festivity and that, in contrast to the current juanes iquiteños were prepared with yucca ''Yucca'' is a genus of perennial shrubs and trees in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Agavoideae. Its 40–50 species are notable for their rosettes of evergreen, tough, sword-shaped leaves and large terminal panicles of white or whitish flo .... References Populated places in the Amazonas Region {{AmazonasPE-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
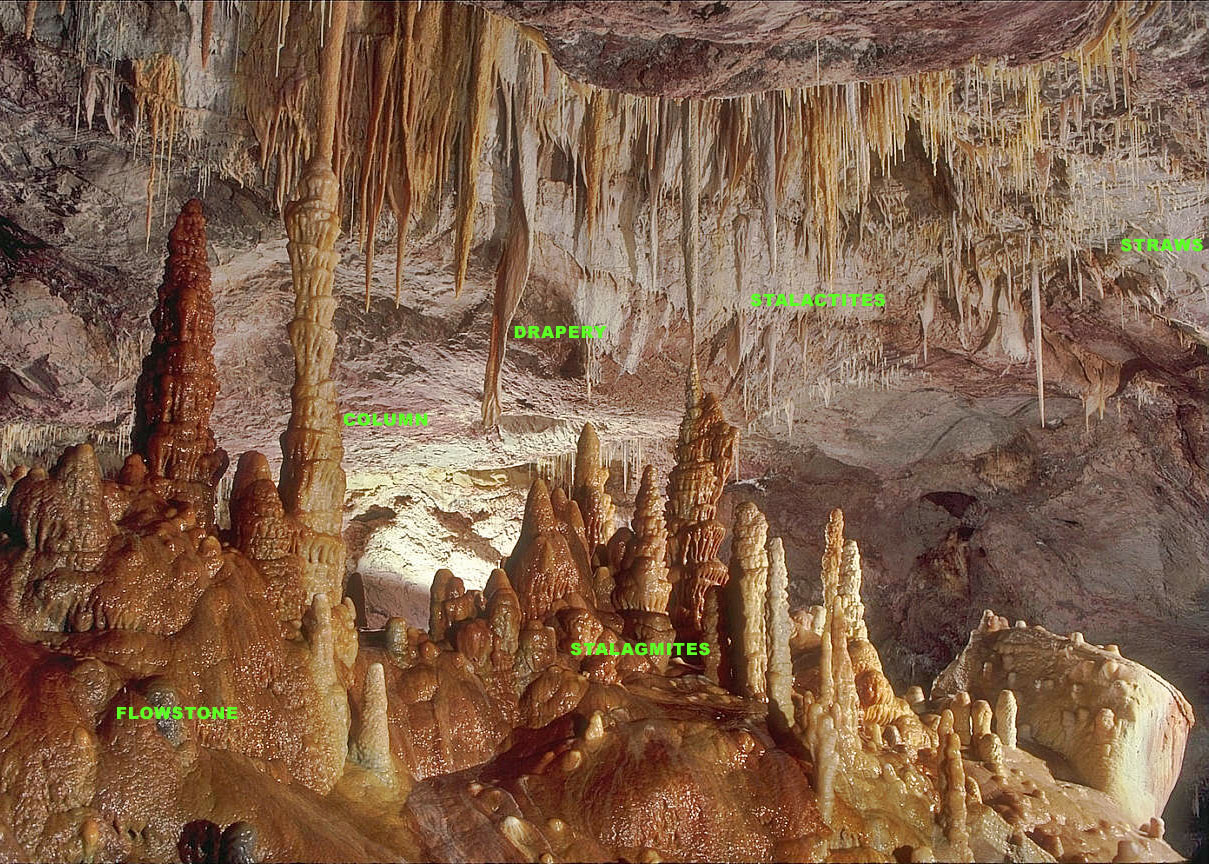
Stalagmite
A stalagmite (, ; from the Greek , from , "dropping, trickling") is a type of rock formation that rises from the floor of a cave due to the accumulation of material deposited on the floor from ceiling drippings. Stalagmites are typically composed of calcium carbonate, but may consist of lava, mud, peat, pitch, sand, sinter, and amberat (crystallized urine of pack rats). The corresponding formation hanging down from the ceiling of a cave is a stalactite. Mnemonics have been developed for which word refers to which type of formation; one is that ''stalactite'' has a C for "ceiling", and ''stalagmite'' has a G for "ground", another is that, as with ants in the pants, the mites go up and the tights (tites) come down. Formation and type Limestone stalagmites The most common stalagmites are speleothems, which usually form in limestone caves. Stalagmite formation occurs only under certain pH conditions within the cavern. They form through deposition of calcium carbonate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stalactites
A stalactite (, ; from the Greek 'stalaktos' ('dripping') via ''stalassein'' ('to drip') is a mineral formation that hangs from the ceiling of caves, hot springs, or man-made structures such as bridges and mines. Any material that is soluble and that can be deposited as a colloid, or is in suspension, or is capable of being melted, may form a stalactite. Stalactites may be composed of lava, minerals, mud, peat, pitch, sand, sinter, and amberat (crystallized urine of pack rats). A stalactite is not necessarily a speleothem, though speleothems are the most common form of stalactite because of the abundance of limestone caves. The corresponding formation on the floor of the cave is known as a stalagmite. Mnemonics have been developed for which word refers to which type of formation; one is that ''stalactite'' has a C for "ceiling", and ''stalagmite'' has a G for "ground". Another example is that ''stalactites'' "hang on ''T''ight" and ''stalagmites'' "''M''ight grow up" � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcareous
Calcareous () is an adjective meaning "mostly or partly composed of calcium carbonate", in other words, containing lime or being chalky. The term is used in a wide variety of scientific disciplines. In zoology ''Calcareous'' is used as an adjectival term applied to anatomical structures which are made primarily of calcium carbonate, in animals such as gastropods, i.e., snails, specifically about such structures as the operculum, the clausilium, and the love dart. The term also applies to the calcium carbonate tests of often more or less microscopic Foraminifera. Not all tests are calcareous; diatoms and radiolaria have siliceous tests. The molluscs are calcareous, as are calcareous sponges ( Porifera), that have spicules which are made of calcium carbonate. In botany ''Calcareous grassland'' is a form of grassland characteristic of soils containing much calcium carbonate from underlying chalk or limestone rock. In medicine The term is used in pathology, for example i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magdalena (Peru)
Magdalena is a district of the province of Chachapoyas in the Amazonas Region of Peru. Geography Magdalena is located in the south of the Chachapoyas Province, in the high part of the inter-Andean valley of the river Utcubamba. In the north the district borders with the District of San Isidro of Maino (Chachapoyas) and the District of Levanto (Chachapoyas), in the east with the Rodríguez de Mendoza Province, in the south with the District of The Jalca (Chachapoyas), in the southwest with the District of Saint John of Lopecancha and in the west with the District of Tingo. See also * Machu Pirqa Machu Pirqa (Quechua ''machu'' old, old person, ''pirqa'' wall,Teofilo Laime Ajacopa, Diccionario Bilingüe Iskay simipi yuyayk'ancha, La Paz, 2007 (Quechua-Spanish dictionary) "old wall", hispanicized spelling ''Machupirca'') is an archaeologica ... External linksMagdalena district official website Districts of the Chachapoyas Province Districts of the Amazonas Region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_nahe_dem_Weiherdamm_in_Wildbergerhütte.jpg)