|
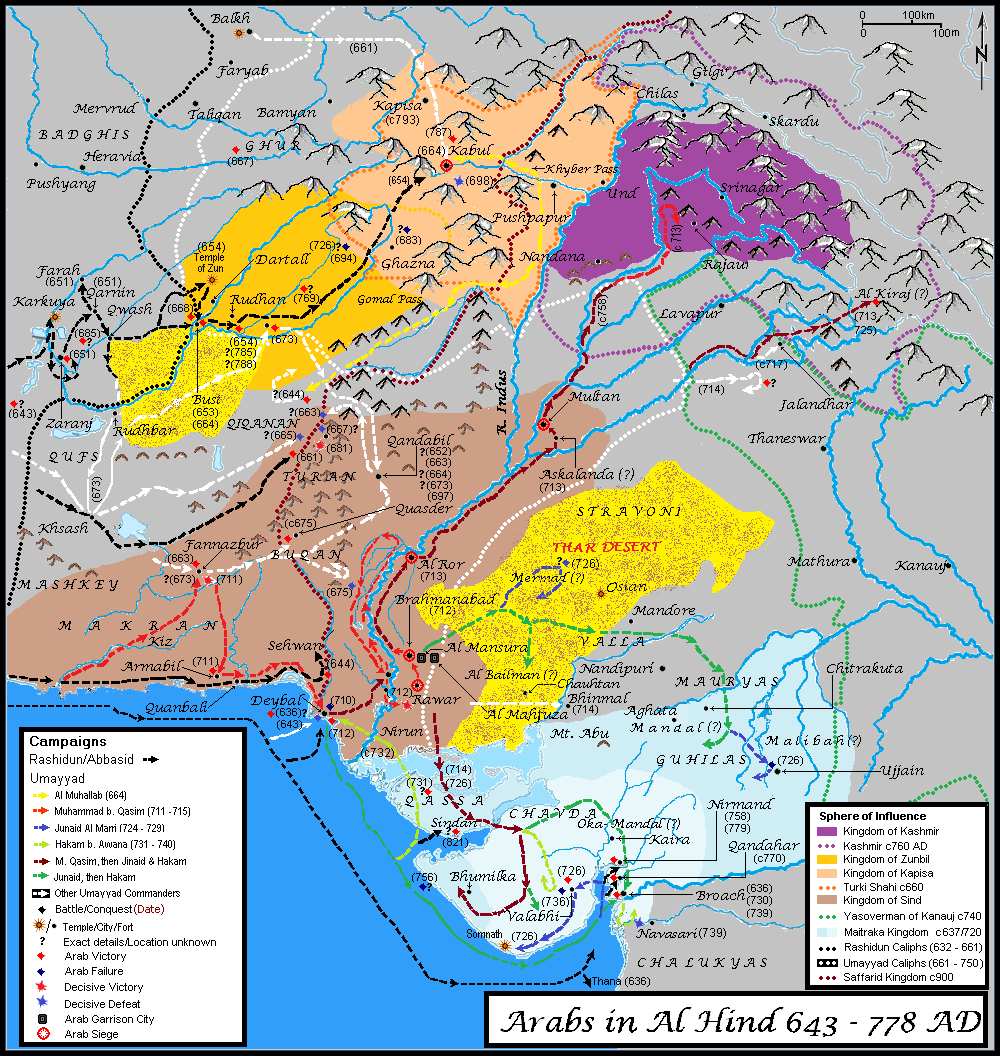
Chach Of Aror
Chach (c. 631-671 AD) ( sd, چچ)Wink, André. (1991)''Al- Hind, the Making of the Indo-Islamic World: The slave kings and the Islamic conquest''. 2, p. 153 Leiden: Brill. was a Hindu Brahmin king of Sindh region of the Indian subcontinent in the mid-7th century AD. Chach expanded the kingdom of Sindh, and his successful efforts to subjugate surrounding monarchies and ethnic groups into an empire covering the entire Indus valley and beyond were recorded in the ''Chach Nama''. Biography Chach was a Brahmin who rose to a position of influence under Rai Sahiras II, king of Sindh and a member of the Rai dynasty. Chach was the chamberlain to the King. According to the Chachnama, the last Rai emperor, Rai Sahasi II, died through illness without issue. By that time, Chach was in complete control of the affairs of the kingdom and had developed illicit sexual relations with Sahasi's wife (queen Rani Suhanadi). When Rai Sahasi II was near death, Suhanadi explained to Chach that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maharaja
Mahārāja (; also spelled Maharajah, Maharaj) is a Sanskrit title for a "great ruler", "great king" or " high king". A few ruled states informally called empires, including ruler raja Sri Gupta, founder of the ancient Indian Gupta Empire, and Chandragupta Maurya. 'Title inflation' soon led to most being rather mediocre or even petty in real power, which led to compound titles (among other efforts) being used in an attempt to distinguish some among their ranks. The female equivalent, Maharani (or Maharanee, Mahārājñī, Maharajin), denotes either the wife of a Maharaja (or Maharana etc.) or also, in states where it was customary, a woman ruling without a husband. The widow of a Maharaja is known as a Rajmata, "queen mother". Maharajakumar generally denotes a son of a Maharaja, but more specific titulatures are often used at each court, including Yuvaraja for the heir (the crown prince). The form "Maharaj" (without "-a") indicates a separation of noble and religious o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashmir
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompasses a larger area that includes the Indian-administered territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh, the Pakistani-administered territories of Azad Kashmir and Gilgit-Baltistan, and the Chinese-administered territories of Aksai Chin and the Trans-Karakoram Tract. Quote: "Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcontinent. It is bounded by the Uygur Autonomous Region of Xinjiang to the northeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region to the east (both parts of China), by the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south, by Pakistan to the west, and by Afghanistan to the northwest. The northern and western portions are administered by Pakistan and comprise three areas: Azad Kashmir, Gilgit, and Baltistan, ... The southern and sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uthman
Uthman ibn Affan ( ar, عثمان بن عفان, ʿUthmān ibn ʿAffān; – 17 June 656), also spelled by Colloquial Arabic, Turkish and Persian rendering Osman, was a second cousin, son-in-law and notable companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, as well as the third of the '' Rāshidun'', or "Rightly Guided Caliphs". Born into a prominent Meccan clan, Banu Umayya of the Quraysh tribe, he played a major role in early Islamic history, and is known for having ordered the compilation of the standard version of the Quran. When Caliph Umar ibn al-Khattab died in office aged 60/61 years, Uthman, aged 68–71 years, succeeded him and was the oldest to rule as Caliph. Under Uthman's leadership, the Islamic empire expanded into Fars (present-day Iran) in 650, and some areas of Khorāsān (present-day Afghanistan) in 651. The conquest of Armenia had begun by the 640s. His reign also saw widespread protests and unrest that eventually led to armed revolt and his assassinati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caliph
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of the entire Muslim world (ummah). Historically, the caliphates were polities based on Islam which developed into multi-ethnic trans-national empires. During the medieval period, three major caliphates succeeded each other: the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661), the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750), and the Abbasid Caliphate (750–1258). In the fourth major caliphate, the Ottoman Caliphate, the rulers of the Ottoman Empire claimed caliphal authority from 1517. Throughout the history of Islam, a few other Muslim states, almost all hereditary monarchies such as the Mamluk Sultanate (Cairo) and Ayyubid Caliphate, have claimed to be caliphates. The first caliphate, the Rashidun Caliphate, was establishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandar Of Sindh
Chandra or Chandar was a Brahmin ascetic who succeeded his brother, Chach of Alor, as king of Sindh region of the Indian subcontinent. An account of Chandar's reign is presented in the ''Chach Nama'', a recording of this period of Sindhi history and the broader history of the Indian subcontinent. Life and activity prior to reign According to the ''Chach Nama'', the Brahmin Chach of Alor was chamberlain and secretary to Rai Sahasi II, king of Sindh region of the Indian subcontinent. Chach ascended to the throne by marrying the king's widow, and appointed Chandar as his deputy. Chandar assisted in the administration of the kingdom during Chach's successful campaigns of expansion, and succeeded Chach upon his death. Conflict with Kannuaj After Chach's death, Matta, the ruler of Sehwan Sharif, began to conspire against Chandar. Matta had formerly been the autonomous chief of Siwistan; however, he had been subjugated during one of Chach's campaigns, and intended to regain indepen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bela, Pakistan
Bela ( bal, ) is an important city of Lasbela District in the Balochistan province of Pakistan. It is an ancient city in a historic track surrounded by hills above the Arabian Sea, nearly northwest of Karachi and south of Quetta. During the autumn of 325 BC, the settlement was part of the Asian campaign of Alexander the Great under the name Rhambacia ( el, Ῥαμβακία). After Alexander conquered the town, he commended the place and thought that if he built a city there it would become great and prosperous and he left Hephaestion behind to built it. In 711 AD, it was part of Muhammad bin Qasim's campaign under the name Armabil. Name Alexander's historians mention the river name as Arabius, and local people as Oreitans. The Arab sources call it Armabil or Armanil. The ''Chachnama'', in addition, uses the names Armael, Armana-Bil, Armapilla. It is described as the second port city of Sind, after Debal. Demographics Bela's population consists of Baloch and Sindhis. The p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uthal
Uthal ( ur, ) is a city of Lasbela District in the Balochistan province of Pakistan. Uthal is headquarters of Uthal Tehsil an administrative subdivision of the district. Demography The Bela population consists principally of Baloch, followed by Sindhis and Pashtuns. The population is predominantly Muslim. Education The Lasbela University of Agriculture, Water and Marine Science Lasbela University of Agriculture, Water & Marine Sciences (LUAWMS) is a public sector university located in Uthal, in the historic and magnificent district of Lasbela, in Balochistan, province of Pakistan Pakistan ( ur, ), officially ... is located in Uthal. References Union councils of Lasbela District Populated places in Lasbela District {{Balochistan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sassanid
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named after the Sasanian dynasty, House of Sasan, it endured for over four centuries, from 224 to 651 AD, making it the longest-lived List of monarchs of Persia, Persian imperial dynasty. The Sasanian Empire succeeded the Parthian Empire, and re-established the Persians as a major power in late antiquity alongside its neighbouring arch-rival, the Roman Empire (after 395 the Byzantine Empire).Norman A. Stillman ''The Jews of Arab Lands'' pp 22 Jewish Publication Society, 1979 International Congress of Byzantine Studies ''Proceedings of the 21st International Congress of Byzantine Studies, London, 21–26 August 2006, Volumes 1–3'' pp 29. Ashgate Pub Co, 2006 The empire was founded by Ardashir I, an Iranian ruler who rose to po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmanabad
Mansura ( ar, المنصورة, al-manṣūra, the triumphant ity}), referred to as Brahmanabad ( ur, برہمن آباد ; sd, برهمڻ آباد, barhamaṇabād) in later centuries, was the historic capital of the Muslim Caliphate in Sindh, during the eighth century under the Umayyad Caliphate and then Abbasid Caliphate from the year 750 AD to 1006 AD. The city was founded as a central garrison by the Umayyad Forces in Sindh, the city transformed into a very vibrant metropolis during the Abbasid Era surpassing the wealth of Multan in the north and Debal in the south. Mansura was the first capital established by the Muslims in the Indian subcontinent after Muhammad bin Qasim seized the Brahmanabad territory. Mansura was built on the shores of the Indus River, it was surrounded by fertile farmland, Ibn Hauqal mentioned the wealthy local merchants who wore ''Baghdad Costume'' and were of Sindhi-Arab origins, houses were made of clay, baked bricks and plaster. Mansura expo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agham Lohana
Agham Lohana was the powerful king of Brahmanabad, (in Sindh, modern Pakistan) contemporary and opponent to Chach of Alor. Agham was a Buddhist and belong to Lohana clan. Biography Agham Lohana is described in the Chachnama as a ruler of Brahmanabad; he is also noted to have controlled other adjacent territories known as ''Lakha'', ''Sama'' and '' Sahata'' He is estimated to have ruled around 632 AD. Agham Lohana professed Buddhism Decline and fall of Buddhism: a tragedy in ancient India by K. Jamanadas Chach of Alor, Chach after consolidating his hold on [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mansura (Brahmanabad)
Mansura ( ar, المنصورة, al-manṣūra, the triumphant ity}), referred to as Brahmanabad ( ur, برہمن آباد ; sd, برهمڻ آباد, barhamaṇabād) in later centuries, was the historic capital of the Muslim Caliphate in Sindh, during the eighth century under the Umayyad Caliphate and then Abbasid Caliphate from the year 750 AD to 1006 AD. The city was founded as a central garrison by the Umayyad Forces in Sindh, the city transformed into a very vibrant metropolis during the Abbasid Era surpassing the wealth of Multan in the north and Debal in the south. Mansura was the first capital established by the Muslims in the Indian subcontinent after Muhammad bin Qasim seized the Brahmanabad territory. Mansura was built on the shores of the Indus River, it was surrounded by fertile farmland, Ibn Hauqal mentioned the wealthy local merchants who wore ''Baghdad Costume'' and were of Sindhi-Arab origins, houses were made of clay, baked bricks and plaster. Mansura exporte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, Quote: "Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcontinent. It is bounded by the Uygur Autonomous Region of Xinjiang to the northeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region to the east (both parts of China), by the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south, by Pakistan to the west, and by Afghanistan to the northwest. The northern and western portions are administered by Pakistan and comprise three areas: Azad Kashmir, Gilgit, and Baltistan, ... The southern and southeastern portions constitute the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir. The Indian- and Pakistani-administered portions are divided by a "line of control" agreed to in 1972, although neither country recognizes it as an international boundary. In addition, China beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |