|
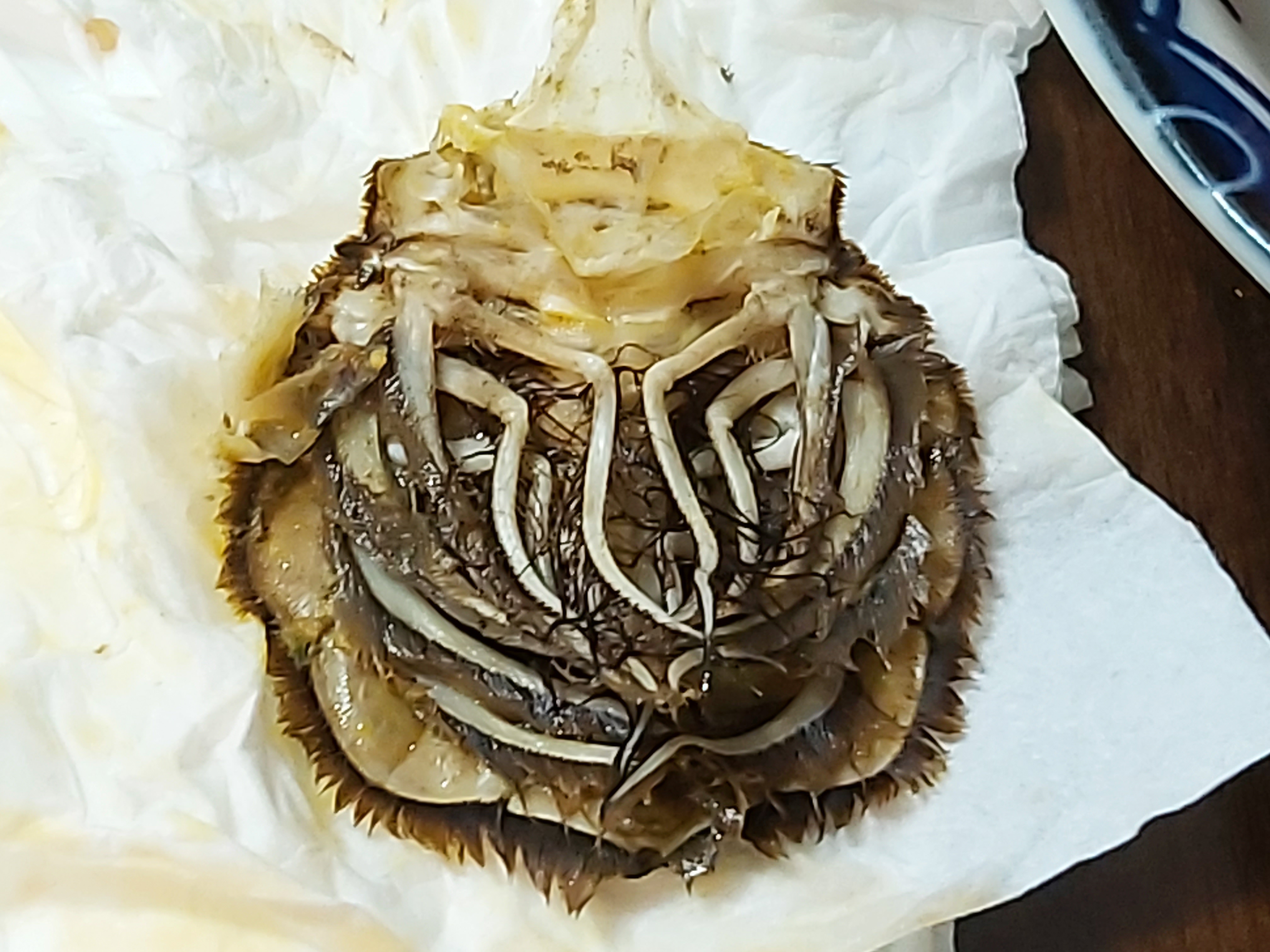
Ceratocumatidae
Ceratocumatidae is a family of crustaceans of the order Cumacea. Ceratocumatidae have a small free telson. The endopods (interior branches) of the uropods are present on only one segment. Males have 5, 4 or 3 pairs of pleopods. All maxillipeds and some of the pereiopods bear exopod The arthropod leg is a form of jointed appendage of arthropods, usually used for walking. Many of the terms used for arthropod leg segments (called podomeres) are of Latin origin, and may be confused with terms for bones: ''coxa'' (meaning hip, plur ...s (outer branches). The gill apparatus has no supporting gill plates. References Cumacea Crustacean families {{malacostraca-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Thomas Calman
William Thomas Calman (29 December 1871 – 29 September 1952) was a Scottish zoologist, specialising in the Crustacea. From 1927 to 1936 he was Keeper of Zoology at the British Museum (Natural History) (now the Natural History Museum). Life He was born in Dundee, the son of Thomas Calman, a music teacher, and Agnes Beatts Maclean. He studied at the High School of Dundee. In the scientific societies in Dundee, he met D'Arcy Thompson. He later became Thompson's lab boy, which allowed him to attend lectures at University College, Dundee for free. A. D. Peacock, one of Thompson's successors to the chair of Natural history at Dundee, believed this appointment came about following a letter sent by Calman in 1891 asking Thompson's advice as to applying for a post in Edinburgh. After his graduation with distinction in 1895, he took on a lecturership at the university, where he remained for eight years. When Thompson died, Calman, along with Douglas Young, wrote his obituary notice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumacea
Cumacea is an order of small marine crustaceans of the superorder Peracarida, occasionally called hooded shrimp or comma shrimp. Their unique appearance and uniform body plan makes them easy to distinguish from other crustaceans. They live in soft-bottoms such as mud and sand, mostly in the marine environment. There are more than 1,500 species of cumaceans formally described. The species diversity of Cumacea increases with depth. Anatomy Cumaceans have a strongly enlarged cephalothorax with a carapace, a slim abdomen, and a forked tail. The length of most species varies from . The carapace of a typical cumacean is composed of several fused dorsal head parts and the first three somites of the thorax. This carapace encloses the appendages that serve for respiration and feeding. In most species, there are two eyes at the front side of the head shield, often merged into a single dorsal eye lobe. The five posterior somites of the thorax form the pereon. The pleon (abdomen) consists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telson
The telson () is the posterior-most division of the body of an arthropod. Depending on the definition, the telson is either considered to be the final segment of the arthropod body, or an additional division that is not a true segment on account of not arising in the embryo from teloblast areas as other segments. It never carries any appendages, but a forked "tail" called the caudal furca may be present. The shape and composition of the telson differs between arthropod groups. Crustaceans In lobsters, shrimp and other decapods, the telson, along with the uropods, forms the tail fan. This is used as a paddle in the caridoid escape reaction ("lobstering"), whereby an alarmed animal rapidly flexes its tail, causing it to dart backwards. Krill can reach speeds of over 60 cm per second by this means. The trigger time to optical stimulus is, in spite of the low temperatures, only 55 milliseconds. In the Isopoda and Tanaidacea (superorder Peracarida), the last abdominal b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endopod
The arthropod leg is a form of jointed appendage of arthropods, usually used for walking. Many of the terms used for arthropod leg segments (called podomeres) are of Latin origin, and may be confused with terms for bones: ''coxa'' (meaning hip, plural ''coxae''), ''trochanter'', ''femur'' (plural ''femora''), ''tibia'' (plural ''tibiae''), ''tarsus'' (plural ''tarsi''), ''ischium'' (plural ''ischia''), ''metatarsus'', ''carpus'', ''dactylus'' (meaning finger), ''patella'' (plural ''patellae''). Homologies of leg segments between groups are difficult to prove and are the source of much argument. Some authors posit up to eleven segments per leg for the most recent common ancestor of extant arthropods but modern arthropods have eight or fewer. It has been argued that the ancestral leg need not have been so complex, and that other events, such as successive loss of function of a ''Hox''-gene, could result in parallel gains of leg segments. In arthropods, each of the leg segments artic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uropod
Uropods are posterior appendages found on a wide variety of crustaceans. They typically have functions in locomotion. Definition Uropods are often defined as the appendages of the last body segment of a crustacean. An alternative definition suggested by Frederick R. Schram restricts the term to those structures arising from the segment before the anal segment (the segment which carries the anus). Under this latter definition, the appendages of the anal segment are caudal ramus, caudal rami, which are analogy (biology), analogous to uropods. Form Uropods are typically biramous – comprising an endopod and an exopod. The exopod is typically the larger, and may be divided in two by a transverse suture known as the diaeresis. The uropods may work in concert with the telson to form a "tail fan". References {{Reflist, 32em Crustacean anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleopod
The decapod ( crustaceans such as a crab, lobster, shrimp or prawn) is made up of 20 body segments grouped into two main body parts: the cephalothorax and the pleon (abdomen). Each segment may possess one pair of appendages, although in various groups these may be reduced or missing. They are, from head to tail: Cephalothorax Head # antennules # antennae #mandibles # first maxillae # second maxillae The head also bears the (usually stalked) compound eyes. The distal portion of a mandible or maxilla which has a sensory function is known as a palp. Thorax / pereon #first maxillipeds #second maxillipeds #third maxillipeds #first pereiopods #second pereiopods #third pereiopods #fourth pereiopods #fifth pereiopods Maxillipeds are appendages modified to function as mouthparts. Particularly in the less advanced decapods, these can be very similar to the pereiopods. Pereiopods are primarily walking legs and are also used for gathering food. They are also the ten legs from which decapo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxilliped
An appendage (or outgrowth) is an external body part, or natural prolongation, that protrudes from an organism's body. In arthropods, an appendage refers to any of the homologous body parts that may extend from a body segment, including antennae, mouthparts (including mandibles, maxillae and maxillipeds), gills, locomotor legs ( pereiopods for walking, and pleopods for swimming), sexual organs (gonopods), and parts of the tail (uropods). Typically, each body segment carries one pair of appendages. An appendage which is modified to assist in feeding is known as a maxilliped or gnathopod. In vertebrates, an appendage can refer to a locomotor part such as a tail, fins on a fish, limbs (legs, flippers or wings) on a tetrapod; exposed sex organ; defensive parts such as horns and antlers; or sensory organs such as auricles, proboscis ( trunk and snout) and barbels. Appendages may become ''uniramous'', as in insects and centipedes, where each appendage comprises a single ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pereiopod
The decapod (crustaceans such as a crab, lobster, shrimp or prawn) is made up of 20 body segments grouped into two main body parts: the cephalothorax and the pleon (abdomen). Each segment may possess one pair of appendages, although in various groups these may be reduced or missing. They are, from head to tail: Cephalothorax Head # antennules # antennae #mandibles # first maxillae # second maxillae The head also bears the (usually stalked) compound eyes. The distal portion of a mandible or maxilla which has a sensory function is known as a palp. Thorax / pereon #first maxillipeds #second maxillipeds #third maxillipeds #first pereiopods #second pereiopods #third pereiopods #fourth pereiopods #fifth pereiopods Maxillipeds are appendages modified to function as mouthparts. Particularly in the less advanced decapods, these can be very similar to the pereiopods. Pereiopods are primarily walking legs and are also used for gathering food. They are also the ten legs from which decapods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |