|
Centripetal (other)
Centripetal usually refers to centripetal force, a force that keeps a body on a curved path. It may also refer to: *Centripetal acceleration *Centripetal Catmull–Rom spline (computer graphics) * Centripetal harmony * Centripetal obesity *Centripetal Spring Armchair *Centripetal structure (theoretical linguistics) – see Lucien Tesnière Lucien Tesnière (; May 13, 1893 – December 6, 1954) was a prominent and influential French linguist. He was born in Mont-Saint-Aignan on May 13, 1893. As a maître de conférences (senior lecturer) in University of Strasbourg (1924), and l ... See also * Centrifugal (other) * History of centrifugal and centripetal forces {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centripetal
A centripetal force (from Latin ''centrum'', "center" and ''petere'', "to seek") is a force that makes a body follow a curved trajectory, path. Its direction is always orthogonality, orthogonal to the motion of the body and towards the fixed point of the instantaneous osculating circle, center of curvature of the path. Isaac Newton described it as "a force by which bodies are drawn or impelled, or in any way tend, towards a point as to a centre". In Newtonian mechanics, gravity provides the centripetal force causing astronomical orbits. One common example involving centripetal force is the case in which a body moves with uniform speed along a circular path. The centripetal force is directed at right angles to the motion and also along the radius towards the centre of the circular path. The mathematical description was derived in 1659 by the Dutch physicist Christiaan Huygens. Formula The magnitude of the centripetal force on an object of mass ''m'' moving at Speed#Tangenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centripetal Acceleration
In mechanics, acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Accelerations are vector quantities (in that they have magnitude and direction). The orientation of an object's acceleration is given by the orientation of the ''net'' force acting on that object. The magnitude of an object's acceleration, as described by Newton's Second Law, is the combined effect of two causes: * the net balance of all external forces acting onto that object — magnitude is directly proportional to this net resulting force; * that object's mass, depending on the materials out of which it is made — magnitude is inversely proportional to the object's mass. The SI unit for acceleration is metre per second squared (, \mathrm). For example, when a vehicle starts from a standstill (zero velocity, in an inertial frame of reference) and travels in a straight line at increasing speeds, it is accelerating in the direction of travel. If the vehicle turns, an accel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
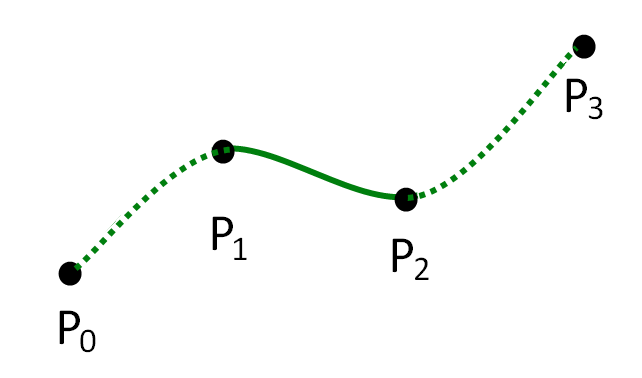
Centripetal Catmull–Rom Spline
In computer graphics, the centripetal Catmull–Rom spline is a variant form of the Catmull–Rom spline, originally formulated by Edwin Catmull and Raphael Rom, which can be evaluated using a recursive algorithm proposed by Barry and Goldman. It is a type of interpolating spline (a curve that goes through its control points) defined by four control points \mathbf_0, \mathbf_1, \mathbf_2, \mathbf_3, with the curve drawn only from \mathbf_1 to \mathbf_2. Definition Let \mathbf_i = _i \quad y_iT denote a point. For a curve segment \mathbf defined by points \mathbf_0, \mathbf_1, \mathbf_2, \mathbf_3 and knot sequence t_0, t_1, t_2, t_3, the centripetal Catmull–Rom spline can be produced by: : \mathbf = \frac\mathbf_1+\frac\mathbf_2 where : \mathbf_1 = \frac\mathbf_1+\frac\mathbf_2 : \mathbf_2 = \frac\mathbf_2+\frac\mathbf_3 : \mathbf_1 = \frac\mathbf_0+\frac\mathbf_1 : \mathbf_2 = \frac\mathbf_1+\frac\mathbf_2 : \mathbf_3 = \frac\mathbf_2+\frac\mathbf_3 and :t_ = \left sq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centripetal Harmony
In music, harmony is the process by which individual sounds are joined together or composed into whole units or compositions. Often, the term harmony refers to simultaneously occurring frequencies, pitches ( tones, notes), or chords. However, harmony is generally understood to involve both vertical harmony (chords) and horizontal harmony (melody). Harmony is a perceptual property of music, and, along with melody, one of the building blocks of Western music. Its perception is based on consonance, a concept whose definition has changed various times throughout Western music. In a physiological approach, consonance is a continuous variable. Consonant pitch relationships are described as sounding more pleasant, euphonious, and beautiful than dissonant relationships which sound unpleasant, discordant, or rough. The study of harmony involves chords and their construction and chord progressions and the principles of connection that govern them. Counterpoint, which refers to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centripetal Obesity
Abdominal obesity, also known as central obesity and truncal obesity, is a condition when excessive visceral fat around the stomach and abdomen has built up to the extent that it is likely to have a negative impact on health. Abdominal obesity has been strongly linked to cardiovascular disease, Alzheimer's disease, and other metabolic and vascular diseases. Visceral and central abdominal fat and waist circumference show a strong association with type 2 diabetes. Visceral fat, also known as organ fat or ''intra-abdominal fat'', is located inside the peritoneal cavity, packed in between internal organs and torso, as opposed to subcutaneous fat, which is found underneath the skin, and intramuscular fat, which is found interspersed in skeletal muscle. Visceral fat is composed of several adipose depots including mesenteric, epididymal white adipose tissue (EWAT), and perirenal fat. An excess of adipose visceral fat is known as central obesity, the "pot belly" or "beer belly" effect, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centripetal Spring Armchair
The Centripetal Spring Chair or Armchair was a 19th-century American office chair, and one of the first modern designs for office chairs. Designed in 1849 by the American inventor Thomas E. Warren (b. 1808), the chair was produced by the American Chair Company in Troy, New York. Made of cast iron and varnished steel with wood and velvet upholstery, it measured 107 × 61 × 71 centimeters with headrest and armrests, and had a seat height of 48 centimeters. The chair exhibited all features of today's office chairs except adjustable lumbar support: Referencing Olivares (2011). it allowed tilt movement in all directions and had a revolving seat, caster wheels for ease of movement, as well as a headrest and armrests in the armchair variant. Tilting was achieved through the flexion of the four large C-shaped steel springs on which the seat rested, using the sitter's feet as a fulcrum. The modernity of its design, which included an innovative use of cast iron for the frame, was visu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucien Tesnière
Lucien Tesnière (; May 13, 1893 – December 6, 1954) was a prominent and influential French linguist. He was born in Mont-Saint-Aignan on May 13, 1893. As a maître de conférences (senior lecturer) in University of Strasbourg (1924), and later professor in University of Montpellier (1937), he published many papers and books on Slavic languages. However, his importance in the history of linguistics is based mainly on his development of an approach to the syntax of natural languages that would become known as dependency grammar. He presented his theory in his book ''Éléments de syntaxe structurale'' (Elements of Structural Syntax), published posthumously in 1959. In the book he proposes a sophisticated formalization of syntactic structures, supported by many examples from a diversity of languages. Tesnière died in Montpellier on December 6, 1954. Many central concepts that the modern study of syntax takes for granted were developed and presented in ''Éléments''. For ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrifugal (other)
Centrifugal (a key concept in rotating systems) may refer to: *Centrifugal casting (industrial), Centrifugal casting (silversmithing), and Spin casting (centrifugal rubber mold casting), forms of centrifigual casting *Centrifugal clutch *Centrifugal compressor *Centrifugal evaporator *Centrifugal extractor *Centrifugal fan *Centrifugal force *Centrifugal force (rotating reference frame) *Centrifugal governor *Centrifugal gun * Centrifugal micro-fluidic biochip *Centrifugal pump * Centrifugal railway *Centrifugal switch *Centrifugal-type supercharger *Centrifugal water–oil separator *Centrifugation *Reactive centrifugal force See also *Centrifuge *Fictitious force *History of centrifugal and centripetal forces *''Centrifugal Funk'', a 1991 album by the Mark Varney Project *Centrifugal structure, a concept in theoretical linguistics – see Lucien Tesnière *Centripetal (other) * Centrifugal speciation - a variant model of allopatric speciation Allopatric speciation () ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |