|
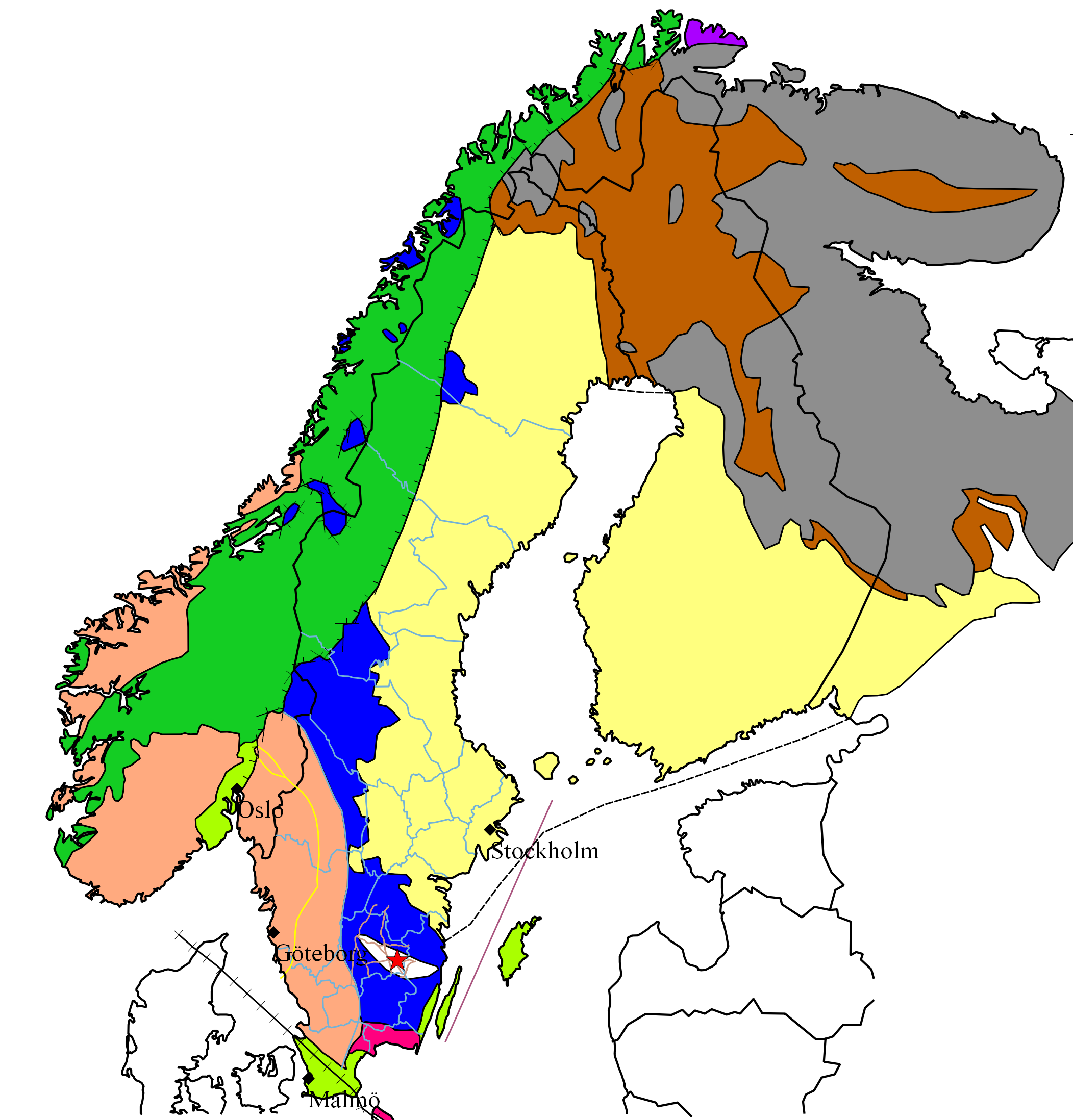
Central Swedish Ice-edge Zone
The central Swedish ice-edge zone was formed when the melting of inland ice slowed during a cold period approximately 12,000 years ago and the ice edge stood relatively still for around 800 years. This occurred during the Younger Dryas period. The two main terminal moraines of this zone are the Skövde and Billigen ones. These two terminal moraines form parallel and semicontinuous ridges spanning from the Västgöta plains though the Östgöta plains to the Stockholm archipelago. See also *Central Swedish lowland The Central Swedish lowland ( sv, Mellansvenska sänkan, Mellansvenska låglandet) is a large region of low relief and altitude in Sweden spanning from the Swedish West Coast at Bohuslän to Stockholm archipelago and Roslagen at the Baltic Sea. T ... References {{reflist Geology of Sweden Geography of Sweden Glacial deposits of Sweden Moraines of Europe Pleistocene Europe Pleistocene geology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are in Antarctica and Greenland; during the Last Glacial Period at Last Glacial Maximum, the Laurentide Ice Sheet covered much of North America, the Weichselian ice sheet covered Northern Europe and the Patagonian Ice Sheet covered southern South America. Ice sheets are bigger than ice shelves or alpine glaciers. Masses of ice covering less than 50,000 km2 are termed an ice cap. An ice cap will typically feed a series of glaciers around its periphery. Although the surface is cold, the base of an ice sheet is generally warmer due to geothermal heat. In places, melting occurs and the melt-water lubricates the ice sheet so that it flows more rapidly. This process produces fast-flowing channels in the ice sheet — these are ice streams. The present-day polar ice sheets are relatively young in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Younger Dryas
The Younger Dryas (c. 12,900 to 11,700 years BP) was a return to glacial conditions which temporarily reversed the gradual climatic warming after the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM, c. 27,000 to 20,000 years BP). The Younger Dryas was the last stage of the Pleistocene epoch (c. 2,580,000 to 11,700 years BP) and it preceded the current, warmer Holocene epoch. The Younger Dryas was the most severe and long lasting of several interruptions to the warming of the Earth's climate, and it was preceded by the Late Glacial Interstadial (c. 14,670 to 12,900 BP). The change was relatively sudden, taking place in decades, and it resulted in a decline of temperatures in Greenland by 4~10 °C (7.2~18 °F), and advances of glaciers and drier conditions over much of the temperate Northern Hemisphere. A number of theories have been put forward about the cause, and the most widely supported by scientists is that the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation, which transports warm water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary Science Reviews
''Quaternary Science Reviews'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering quaternary science. It was established in 1982 by Pergamon Press and is currently published by Elsevier. The editor-in-chief is C.V. Murray Wallace (University of Wollongong). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2013 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 4.571. References External links * Elsevier academic journals Biweekly journals English-language journals Publications established in 1982 Quaternary science journals Archaeology journals {{archaeology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terminal Moraine
A terminal moraine, also called end moraine, is a type of moraine that forms at the terminal (edge) of a glacier, marking its maximum advance. At this point, debris that has accumulated by plucking and abrasion, has been pushed by the front edge of the ice, is driven no further and instead is deposited in an unsorted pile of sediment. Because the glacier acts very much like a conveyor belt, the longer it stays in one place, the greater the amount of material that will be deposited. The moraine is left as the marking point of the terminal extent of the ice. Formation As a glacier moves along its path, the surrounding area is continuously eroding. Loose rock and pieces of bedrock are constantly being picked up and transported with the glacier. Fine sediment and particles are also incorporated into the glacial ice. The accumulation of these rocks and sediment together form what is called glacial till when deposited. Push moraines are formed when a glacier retreats from a previo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Västergötland
Västergötland (), also known as West Gothland or the Latinized version Westrogothia in older literature, is one of the 25 traditional non-administrative provinces of Sweden (''landskap'' in Swedish), situated in the southwest of Sweden. Västergötland is home to Gothenburg, the second largest city in Sweden, which is situated along a short stretch of the Kattegat strait. The province is bordered by Bohuslän, Dalsland, Värmland, Närke, Östergötland, Småland and Halland, as well as the two largest Swedish lakes Vänern and Vättern. Victoria, Crown Princess of Sweden is Duchess of Västergötland. Administration The provinces of Sweden serve no administrative function. Instead, that function is served by counties of Sweden. From the 17th century up until 31 December 1997, Västergötland was divided into Skaraborg County, Älvsborg County and a minor part of Gothenburg and Bohus County. From 1 January 1998 nearly all of the province is in the newly created ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Östergötland
Östergötland (; English exonym: East Gothland) is one of the traditional provinces of Sweden (''landskap'' in Swedish) in the south of Sweden. It borders Småland, Västergötland, Närke, Södermanland and the Baltic Sea. In older English literature, the Latinized version ''Ostrogothia'' is also used. The corresponding administrative county, Östergötland County, covers the entire province and parts of neighbouring provinces. Heraldry From 1560, Östergötland was represented with two separate coats-of-arms seals until 1884, when the current one was granted. The coat of arms is represented with a ducal coronet. Blazon: " gules a griffin with dragon wings, tail and tongue rampant or armed, beaked, langued and membered azure between four roses argent." Geography From west to east, in the middle parts, extends the Östgöta Plain (''Östgötaslätten''). It is largely agricultural. In the southern part of the province, the terrain becomes marked by the south Swedish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Swedish Lowland
The Central Swedish lowland ( sv, Mellansvenska sänkan, Mellansvenska låglandet) is a large region of low relief and altitude in Sweden spanning from the Swedish West Coast at Bohuslän to Stockholm archipelago and Roslagen at the Baltic Sea. The Central Swedish lowland forms a broad east-west trending belt north of the South Swedish highlands and south of the Norrland terrain. Traditionally the heartland of Sweden due to its large population and agricultural resources the region benefits additionally from the proximity of hydropower, forest and mineral resources. The lowland is also at a good position for trade with the Baltic region. These advantages are reflected in the location of Sweden's capital, Stockholm, at the eastern end of the lowlands. Most of Sweden's manufacturing industries lies in this region. Relief, soil and vegetation The reason on how the lowlands reached its sunken position relative to other parts of Sweden is not clear. Possibly its boundaries are flexu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Sweden
The geology of Sweden is the regional study of rocks, minerals, tectonics, natural resources and groundwater in the country. The oldest rocks in Sweden date to more than 2.5 billion years ago in the Precambrian. Complex orogeny mountain building events and other tectonic occurrences built up extensive metamorphic crystalline basement rock that often contains valuable metal deposits throughout much of the country. Metamorphism continued into the Paleozoic after the Snowball Earth glaciation as the continent Baltica collided with an island arc and then the continent Laurentia. Sedimentary rocks are most common in southern Sweden with thick sequences from the last 250 million years underlying Malmö and older marine sedimentary rocks forming the surface of Gotland. Stratigraphy, Tectonics & Geologic History The oldest rocks in Sweden date to the Archean, more than 2.5 billion years ago. Archean crystalline basement rocks are restricted to a few areas in the far north and are mainl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Sweden
Sweden is a country in Northern Europe on the Scandinavian Peninsula. It borders Norway to the west; Finland to the northeast; and the Baltic Sea and Gulf of Bothnia to the south and east. At , Sweden is the largest country in Northern Europe, the fifth largest in Europe, and the 55th largest country in the world. Sweden has a long coastline on its east, and the Scandinavian mountain chain (Scanderna) on its western border, separating it from Norway. It has maritime borders with Denmark, Germany, Poland, Russia, Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia, and it is also linked to Denmark (southwest) by the Öresund bridge. It has an Exclusive Economic Zone of . Terrain Much of Sweden is heavily forested, with 69% of the country being forest and woodland, while farmland constitutes only 8% of land use. Sweden consists of 39,960 km2 of water area, constituting around 95,700 lakes. The lakes are sometimes used for water power plants, especially the large northern rivers and lakes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacial Deposits Of Sweden
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate between glacial periods. The Last Glacial Period ended about 15,000 years ago. The Holocene is the current interglacial. A time with no glaciers on Earth is considered a greenhouse climate state. Quaternary Period Within the Quaternary, which started about 2.6 million years before present, there have been a number of glacials and interglacials. At least eight glacial cycles have occurred in the last 740,000 years alone. Penultimate Glacial Period The Penultimate Glacial Period (PGP) is the glacial period that occurred before the Last Glacial Period. It began about 194,000 years ago and ended 135,000 years ago, with the beginning of the Eemian interglacial. Last Glacial Period The last glacial period was the most recent glacial period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
.png)
