|
Central Asian Southern Desert
The Central Asian southern desert ecoregion (WWF ID: PA1312) is an arid but ecologically active region between the east coast of the Caspian Sea and steppes at the base of the mountains of central Asia. Most of Turkmenistan and eastern Uzbekistan is in this ecoregion. The winters are milder than in the cold desert to the north (the Central Asian northern desert ecoregion), and a large number of endemic species have adapted to living in the particular climate and soil of the region. As with sandy deserts in general, the region is notable for high numbers of endemic species of reptiles and insects. Location and description The ecoregion covers the arid territory from the Caspian Sea on the west, almost to the Pamir-Alay Mountains to the east. Most of Turkmenistan and the eastern half of Uzbekistan is this region. Covered are the coastal plains of the Caspian, the Krasnovodsk and Ustyurt Plateaus of northwest Turkmenistan, the Karakum Desert ('Black Sand' desert) of central Tur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karakum Desert
The Karakum Desert, also spelled Kara-Kum and Gara-Gum ( tk, Garagum, ; rus, Караку́мы, Karakumy, kərɐˈkumɨ), is a desert in Central Asia. Its name in Turkic languages means "black sand": "" means sand; "" is a contraction of : "dark" or may pre-date that (be a derivation from a likely broader meaning which the word for black bore: ) in this language family. This refers to the shale-rich sand generally beneath the sand of much of the desert. It occupies about 70 percent, , of Turkmenistan. The population is sparse, with an average of one person per . Rainfall is also rare, ranging from per year. Geography The desert covers roughly seventy percent of Turkmenistan, a long east–west swath. It sits east of the Caspian Sea which has a steep east bank. It adjoins, to the north, the long delta feeding the South Aral Sea further north, another endorheic lake, about higher than the Caspian Sea. The delta is that of the Amu Darya river to the northeast, demarcating the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haloxylon Persicum
''Haloxylon persicum'', the white saxaul, is a small tree belonging to the family Amaranthaceae. Its range is Western Asia, including the Palestine (region)#Flora distribution, Palestine region, Egypt, Sinai Peninsula, Sinai, South Iraq, Saudi Arabia, Iran, Oman, UAE, Afghanistan, and Pakistan, to Central Asia (Kyrgyzstan, Turkmenistan, etc.), and China (Xinjiang etc.). Description The ''Haloxylon persicum'' has a stout rugged stem and light grey bark, growing up to 4.5–5 metres in height. It lacks large foliage-type leaves; in fact, its leaves have retrogressed as succulent branches. The plant is found in sandhills, deserts and sand ridges, where it often forms pure stands, with an average density up to 400-500 trees a hectare. The white saxaul is a hardy tree that can grow in nutritionally poor soil and can tolerate drought. The tree is in leaf all year, and flowers in May–June. Uses The plant's extensive root system is useful for stabilising sandy soils. The wood is durab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repetek Biosphere State Reserve
Repetek Biosphere State Reserve, often referred to as Repetek Nature or Desert Reserve, ( tk, Repetek goraghanasy, ''Репетек горагханасы'') is a desert nature reserve (''zapovednik'') of Turkmenistan, located in Lebap Province, East Karakum Desert, near Amu Darya. It is located approximately south from Türkmenabat and is known for its ''zemzen'' (desert monitor which is ''Varanus griseus''). Established in 1928 for the study and preservation of a sand-desert ecosystem, it covers an area of . Geography The landscape of the reserve is arid, with extensive ridged sand dunes some in height and in length in many areas, large areas of sand dune and valley-like depressions. Black saxaul (''Haloxylon aphyllum''), rare to most part of Central Asia covers more than , approximately 4.5% of the territory of the reserve. The soils have sandy subsoils, but some "21 trees, 104 grasses, 8 mushrooms, 1 moss, 68 soil algae and 197 fungi" grow within the reserve. History The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaplaňgyr Nature Reserve
Gaplaňgyr or Kaplankyr is a mountain plateau and nature reserve ('' zapovednik'') of northern Turkmenistan. It was established in 1979. It is a place for the protection and restoration of indigenous flora and fauna, it is located on the Gaplaňgyr Plateau at the southern spur of the Ustyurt Plateau at the border with Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan in the north-west of Daşoguz Province. It covers an area of 2822 km². Fauna and flora 26 species of mammals, 147 species of birds, and 918 species of higher plants have been recorded in Kaplankyr reserve. Protected rare species of animals found in the reserve include, Central Asian gazelle, the Ustyurt mountain sheep, ratel as well as substantial populations of saiga antelopes The saiga antelope (, ''Saiga tatarica''), or saiga, is a critically endangered antelope which during antiquity inhabited a vast area of the Eurasian steppe spanning the foothills of the Carpathian Mountains in the northwest and Caucasus in ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
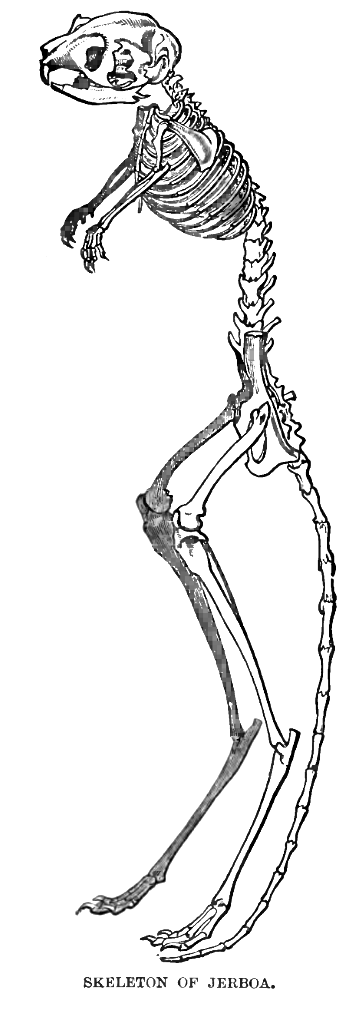
Jerboa
Jerboas (from ar, جربوع ') are hopping desert rodents found throughout North Africa and Asia, and are members of the family Dipodidae. They tend to live in hot deserts. When chased, jerboas can run at up to . Some species are preyed on by little owls (''Athene noctua'') in central Asia. Most species of jerboas have excellent hearing that they use to avoid becoming the prey of nocturnal predators. The typical lifespan of a jerboa is around 6 years. Taxonomy Jerboas, as previously defined, were thought to be paraphyletic, with the jumping mice (Zapodidae) and birch mice (Sminthidae) also classified in the family Dipodidae. However, phylogenetic analysis split all three as distinct families, leaving just the jerboas in Dipodidae and revealing them to be a monophyletic group. Anatomy and body features Jerboas look somewhat like miniature kangaroos, and have some external similarities. Both have long hind legs, short forelegs, and long tails. Jerboas move around in a similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerbillinae
Gerbillinae is one of the subfamilies of the rodent family Muridae and includes the gerbils, jirds, and sand rats. Once known as desert rats, the subfamily includes about 110 species of African, Indian, and Asian rodents, including sand rats and jirds, all of which are adapted to arid habitats. Most are primarily active during the day, making them diurnal (but some species, including the common household pet, exhibit crepuscular behavior), and almost all are omnivorous. The gerbil got its name as a diminutive form of "jerboa," an unrelated group of rodents occupying a similar ecological niche. Gerbils are typically between long, including the tail, which makes up about half of their total length. One species, the great gerbil (''Rhombomys opimus''), originally native to Turkmenistan, can grow to more than . The average adult gerbil weighs about . One species, the Mongolian gerbil ('' Meriones unguiculatus''), also known as the ''clawed jird'', is a gentle and hardy animal th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepus Tolai
The tolai hare (''Lepus tolai'') is a species of hare native to Central Asia, Mongolia, and Northern and Central China. It inhabits semi-desert, steppes, rocky habitats, and forest meadows. It is relatively common, even in areas with heavy human disturbance, due to its fast reproductive rate. It is mainly active at dusk and at night but is occasionally active during the day.Aulagnier S.; P. Haffner, A. J. Mitchell-Jones, F. Moutou & J. Zima (2009) ''Mammals of Europe, North Africa and the Middle East'', A&C Black, London. The taxon is formerly included with the cape hare. Description The tolai hare grows to a head-and-body length of between with a tail of . It is rather variable in colouration across its range. The upper parts are some shade of dull yellow, pale brown, or sandy grey with brownish or reddish stripes. The hip region is sometimes ochre or grey. The head has a pale, bare, greyish or ochraceous patch of skin surrounding the eye and extending forwards to near the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraechinus Hypomelas
Brandt's hedgehog (''Paraechinus hypomelas'') is a species of desert hedgehog native to parts of the Middle East and Central Asia. Its common name derives from its having first been described by Johann Friedrich von Brandt, a director of the Zoological Department at the St Petersburg Academy of Sciences. Description Brandt's hedgehog is approximately the size of the West European hedgehog (about 500–1,000 g in weight and 25 cm in length), but has distinctively large ears (similar to the long-eared hedgehog), and is a much faster runner, due to lighter needle protection. Unlike the long-eared hedgehog, however, it is predominantly nocturnal. The first and only study of the Brandt's hedgehog histological skin characteristics found three layers of skin the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis; while previous studies of other hedgehogs sited only two. Habitat Brandt's hedgehog prefers arid desert areas and mountains. It often uses natural shelter, although it is still capable of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemiechinus Auritus
The long-eared hedgehog (''Hemiechinus auritus'') is a species of hedgehog native to Central Asian countries and some countries of the Middle East. The long-eared hedgehog lives in burrows that it either makes or finds and is distinguished by its long ears. It is considered one of the smallest Middle Eastern hedgehogs.Qumsiyeh, M. B.. (1996Mammals of the Holy Land Texas Tech University Press, Lubbock Texas. pp. 64–66 . This hedgehog is insectivorous but may also feed on small vertebrates and plants. In captivity they can live for over 7 years. Since the long-eared hedgehog is naturally parasite prone and can carry diseases as bad as plague, it is highly recommended that, if kept as a pet, it should be purchased from a respected dealer. Wild hedgehogs have been found to carry ''Rhipicephalus sanguineus'', the brown dog tick, which can transmit Boutonneuse fever. Description The length of the head and body of the long-eared hedgehog is approximately 120–270 mm, and the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suaeda
__NOTOC__ ''Suaeda'' is a genus of plants also known as seepweeds and sea-blites. Most species are confined to saline or alkaline soil habitats, such as coastal salt-flats and tidal wetlands. Many species have thick, succulent leaves, a characteristic seen in various plant genera that thrive in salty habitats (halophile plants). There are about 110 species in the genus ''Suaeda''. The most common species in northwestern Europe is ''S. maritima''. It grows along the coasts, especially in saltmarsh areas, and is known in Britain as "common sea-blite", but as "herbaceous seepweed" in the USA. It is also common along the east coast of North America from Virginia northward. One of its varieties is common in tropical Asia on the land-side edge of mangrove tidal swamps. Another variety of this polymorphic species is common in tidal zones all around Australia (''Suaeda maritima var. australis'' is also classed as ''S. australis''). On the coasts of the Mediterranean Sea a common ''Sua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halocnemum Strobilaceum
''Halocnemum strobilaceum'' is a species of flowering plant in the subfamily Salicornioideae of the family Amaranthaceae. It is native to coastal areas of the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea and parts of the Middle East and central Asia, where it grows in coastal and inland salt marshes, alkali flats, and other habitats with saline soils. Description ''Halocnemum strobilaceum'' is a much-branched, semi-prostrate, sub-shrub with erect branches up to a metre or so high. The woody stems at the base are jointed and have sterile, rounded or conical shaped buds, arranged in whorls on the terminal part of each portion. The erect stems are cylindrical and succulent, with green joints that turn yellow as they age. The stubby, bluish-green, scale-like leaves clasp the stem at each node. The flowers are hermaphrodite and very small, and are arranged in whorls of three on the upper part of the branches. Distribution and habitat ''Halocnemum strobilaceum'' is found around the coasts borde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halostachys
''Halostachys'' is a genus of flowering plants in the plant family Amaranthaceae, containing a single species, ''Halostachys caspica''. The plants are small to medium halophytic shrubs with apparently jointed fleshy stems and scale-like leaves. They are native to Asia and southeastern Europe. Description ''Halostachys caspica'' grows as a shrub to 1–3 m height and width. The erect stems are much branched, older twigs are mostly leafless. The young twigs are blue-green, fleshy, apparently jointed (articulated), with glabrous fine papillose surface. The opposite leaves are fleshy, glabrous, connate basally and surrounding the stem (thus forming the joints), with very short scale-like triangular blades. The inflorescences consist of numerous opposite lateral cylindrical spikes, 15-30 × 2–5 mm, on jointed peduncles. Groups of three bisexual flowers are sitting in the axils of rhombic-quadrate bracts. The opposite bracts are not connate to each other. The obovoid to obpyrami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |