|
Center Of Balance (horse)
In horsemanship, the center of balance of a horse is a position on the horse's back which correlates closely to the center of gravity of the horse itself. The term may also refer to the horse's center of gravity. For the best performance by the horse, as well as for better balance of the rider, the rider must be positioned over the center of balance of the horse. The location of the horse's center of balance depends on a combination of speed and degree of collection. For a standing or quietly walking horse, it is slightly behind the heart girth and below the withers. If a horse is moving at a trot or canter, the center of balance shifts slightly forward, and it moves even more forward when the horse is galloping or jumping. If a horse is highly collected, the center of balance will be farther back, regardless of gait, than if the horse is in an extended frame. For movements such as a rein back or the levade, the center of balance of horse and rider may be further back th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trakehner Reithengst, Auktion Neumünster 2004
Trakehner is a light warmblood breed of horse, originally developed at the East Prussian state stud farm in the town of Trakehnen from which the breed takes its name. The state stud ( :de:Hauptgestüt Trakehnen) was established in 1731 and operated until 1944, when the fighting of World War II led to the annexing of East Prussia by Russia, and the town containing the stud renamed as Yasnaya Polyana. The Trakehner typically stands between . They can be any color, with bay, gray, chestnut and black being the most common, though the breed also includes few roan and tobiano pinto horses. It is considered to be the lightest and most refined of the warmbloods, due to its closed stud book which allows entry of only Trakehner, as well as few selected Thoroughbred, Anglo-Arabian, Shagya and Arabian bloodlines. Characteristics Owing to its Thoroughbred ancestry, the Trakehner is of rectangular build, with a long sloping shoulder, good hindquarters, short cannons, and a medium-lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse Gait
Horses can use various gaits (patterns of leg movement) during locomotion across solid ground, either naturally or as a result of specialized training by humans.Ensminger, M. E. ''Horses and Horsemanship'' 6th edition USA: Interstate Publishers 1990 pp. 65–66 Classification Gaits are typically categorized into two groups: the "natural" gaits that most horses will use without special training, and the " ambling" gaits that are various smooth-riding four-beat footfall patterns that may appear naturally in some individuals. Special training is often required before a horse will perform an ambling gait in response to a rider's command. Another system of classification that applies to quadrupeds uses three categories: walking and ambling gaits, running or trotting gaits, and leaping gaits.Tristan David Martin Roberts (1995) ''Understanding Balance: The Mechanics of Posture and Locomotion'', Nelson Thornes, The British Horse Society Dressage Rules require competitors to per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dressage
Dressage ( or ; a French term, most commonly translated to mean "training") is a form of horse riding performed in exhibition and competition, as well as an art sometimes pursued solely for the sake of mastery. As an equestrian sport defined by the International Equestrian Federation, dressage is described as "the highest expression of horse training" where "horse and rider are expected to perform from memory a series of predetermined movements." Competitions are held at all levels from amateur to the Olympic Games and World Equestrian Games. Its fundamental purpose is to develop, through standardized progressive training methods, a horse's natural athletic ability and willingness to perform, thereby maximizing its potential as a riding horse. At the peak of a dressage horse's gymnastic development, the horse responds smoothly to a skilled rider's minimal aids. The rider is relaxed and appears effort-free while the horse willingly performs the requested movement. The discipli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
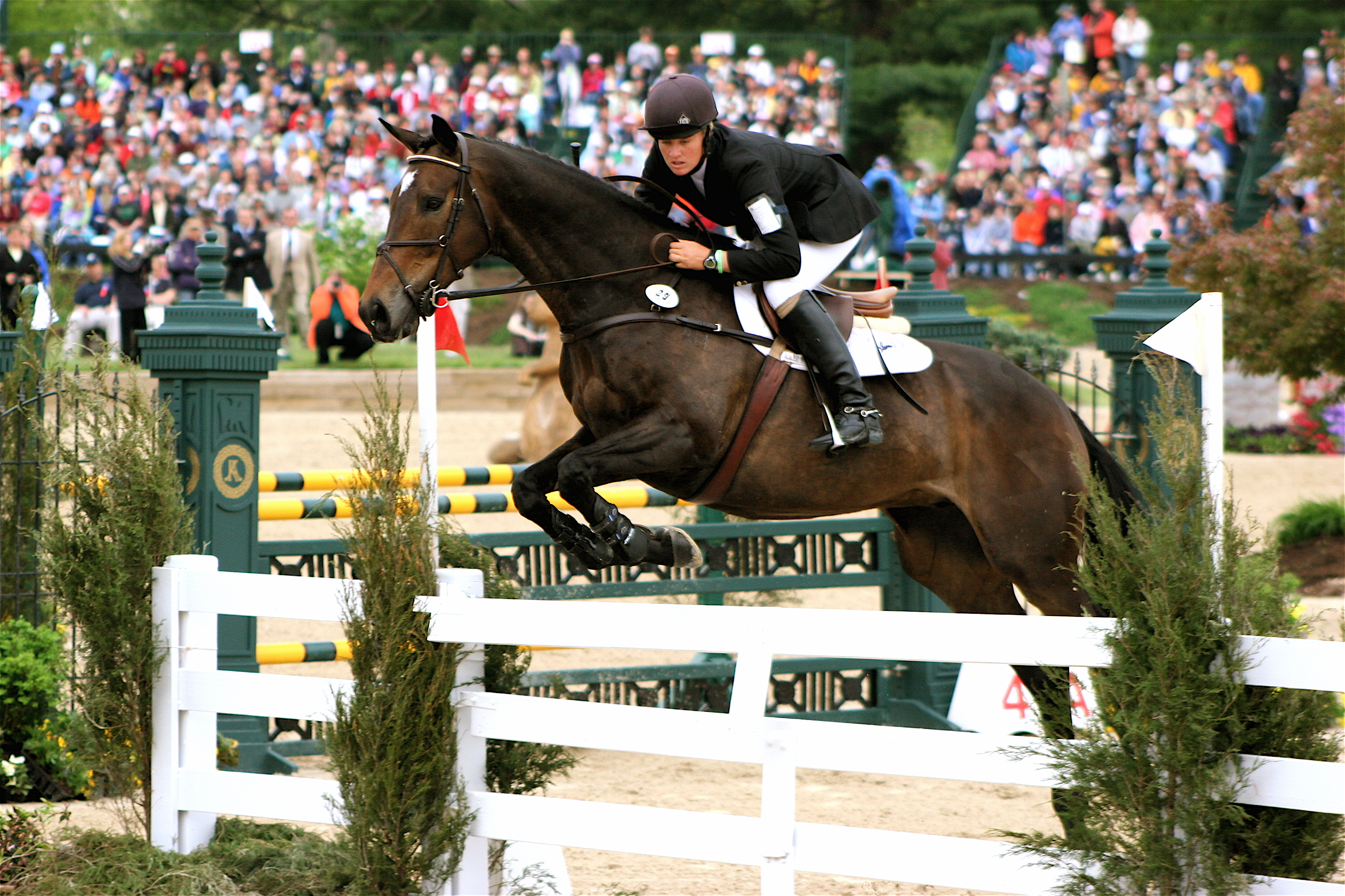
Show Jumping
Show jumping is a part of a group of English riding equestrianism, equestrian events that also includes dressage, eventing, Show hunter, hunters, and equitation. Jumping classes are commonly seen at horse shows throughout the world, including the Equestrian at the Summer Olympics, Olympics. Sometimes shows are limited exclusively to jumpers. Sometimes jumper classes are offered in conjunction with other English-style events. Sometimes, show jumping is but one division of a very large, all-breed competition that includes a very wide variety of disciplines. Jumping classes may be governed by various national horse show sanctioning organizations, such as the United States Equestrian Federation or the British Showjumping Association. International competitions are governed by the rules of the International Federation for Equestrian Sports. Hunters or jumpers Show jumping events have show hunter, hunter classes, jumper classes and hunt seat equitation classes. Hunters are judged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
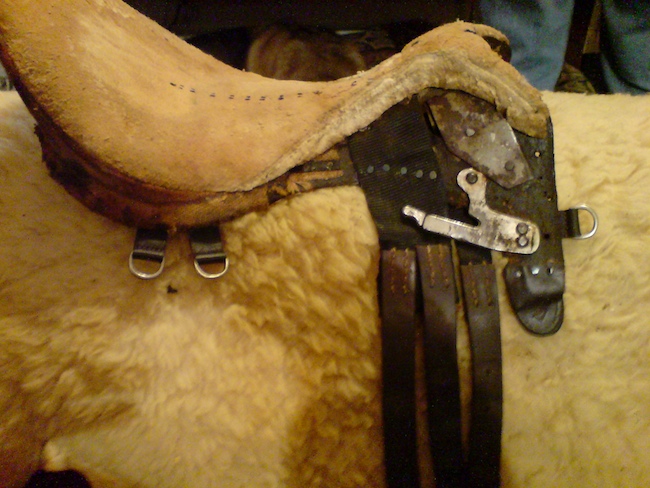
English Saddle
English saddles are used to ride horses in English riding disciplines throughout the world. The discipline is not limited to England, the United Kingdom in general or other English-speaking countries. This style of saddle is used in all of the Olympic and International Federation for Equestrian Sports (FEI) equestrian disciplines, except for the newly approved FEI events of equestrian vaulting and reining. Most designs were specifically developed to allow the horse freedom of movement, whether jumping, running, or moving quickly across rugged, broken country with fences. Unlike the western saddle or Australian Stock Saddle, there is no horn or other design elements that stick out above the main tree of the saddle. Construction The English saddle is based on a solid tree, over which webbing, leather and padding materials are added. Traditionally, the tree of an English saddle is built of laminated layers of high quality wood, reinforced with steel underneath the front arch, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Missouri
The University of Missouri (Mizzou, MU, or Missouri) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Columbia, Missouri. It is Missouri's largest university and the flagship of the four-campus University of Missouri System. MU was founded in 1839 and was the first public university west of the Mississippi River. It has been a member of the Association of American Universities since 1908 and is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". To date, the University of Missouri alumni, faculty, and staff include 18 Rhodes Scholars, 19 Truman Scholars, 141 Fulbright Scholars, 7 Governors of Missouri, and 6 members of the U.S. Congress. Enrolling 31,401 students in 2021, it offers more than 300 degree programs in thirteen major academic divisions. Its well-known Missouri School of Journalism was founded by Walter Williams (journalist), Walter Williams in 1908 as the world's first journalism school; It publishes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saddle
The saddle is a supportive structure for a rider of an animal, fastened to an animal's back by a girth. The most common type is equestrian. However, specialized saddles have been created for oxen, camels and other animals. It is not known precisely when riders first began to use some sort of padding or protection, but a blanket attached by some form of surcingle or girth was probably the first "saddle", followed later by more elaborate padded designs. The solid saddle tree was a later invention, and though early stirrup designs predated the invention of the solid tree, the paired stirrup, which attached to the tree, was the last element of the saddle to reach the basic form that is still used today. Today, modern saddles come in a wide variety of styles, each designed for a specific equestrianism discipline, and require careful fit to both the rider and the horse. Proper saddle care can extend the useful life of a saddle, often for decades. The saddle was a crucial step ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levade
The airs above the ground or school jumps are a series of higher-level, Haute ecole, classical dressage movements in which the horse leaves the ground. They include the capriole, the courbette, the mezair, the croupade and the levade. None are typically seen in modern competitive dressage. They are performed by horses of various riding academies such as the Spanish Riding School in Vienna and the Cadre Noir in Saumur, and may be seen in other dressage performances. The levade and courbette are a particular feature of the Doma Menorquina, the riding tradition of the island of Menorca. Horses such as the Andalusian, Lusitano, Lipizzan and Menorquín are the breeds most often trained to perform the airs today, in part due to their powerfully conformed hindquarters, which allow them the strength to perform these difficult movements. There were originally seven airs, many of which were used to build into the movements performed today. There is a popular conception that these mov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rein Back
The rein-back is a dressage term to indicate the two-beat movement in which a horse is asked to back up. The horse picks up and sets down its feet almost in diagonal pairs, and moves straight backwards with the line of his forelegs following those of his hind. The horse should remain on the aids during the rein-back. The rein-back should be practiced sparingly, as it can easily over-stress the horse's back and joints. This is especially true if the rider tries to force the horse into the movement. Asking for the Rein-Back To perform the rein-back, the rider applies both leg aids and a resisting hand. The leg asks the horse to move, but the hand prevents the horse from going forward, so it instead releases that energy in a step back. As soon as the horse begins to step back, the aids are released. The rein-back should be performed in a straight line, with the rider's legs used softly behind the girth to keep the hindquarters straight. The upper body of the rider stays upright, l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jumping (horse)
Jumping plays a major role in many equestrian sports, such as show jumping, fox hunting, steeplechasing, and eventing. The biomechanics of jumping, the influence of the rider, and the heritability of jumping prowess have all been the focus of research. Jumping process The airborne phase of the jumping process occurs between stance phases of the fore and hind limbs and is therefore biomechanically equivalent to a highly suspended or elevated canter stride. For this reason, horses typically approach obstacles at the canter. The jumping process can be broken down into five phases: Approach The "approach" is the final canter stride before the jump, during which the horse places all four legs for the optimal take-off. The horse reaches forward and down with his neck to lower the forehand and his center of mass. The forelegs are propped or strutted out in front of the body. This relatively sudden braking action allows momentum to carry the hindlegs further under the body of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canter
The canter and gallop are variations on the fastest gait that can be performed by a horse or other equine. The canter is a controlled three-beat gait, while the gallop is a faster, four-beat variation of the same gait. It is a natural gait possessed by all horses, faster than most horses' trot, or ambling gaits. The gallop is the fastest gait of the horse, averaging about . The speed of the canter varies between depending on the length of the horse's stride. A variation of the canter, seen in western riding, is called a lope, and is generally quite slow, no more than . Etymology Since the earliest dictionaries there has been a commonly agreed suggestion that the origin of the word "canter" comes from the English city of Canterbury, a place of pilgrimage in the Middle Ages, as referred to in ''The Canterbury Tales'', where the comfortable speed for a pilgrim travelling some distance on horseback was above that of a trot but below that of a gallop. However a lack of compelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |