|
Censoring (statistics)
In statistics, censoring is a condition in which the value of a measurement or observation is only partially known. For example, suppose a study is conducted to measure the impact of a drug on mortality rate. In such a study, it may be known that an individual's age at death is ''at least'' 75 years (but may be more). Such a situation could occur if the individual withdrew from the study at age 75, or if the individual is currently alive at the age of 75. Censoring also occurs when a value occurs outside the range of a measuring instrument. For example, a bathroom scale might only measure up to 140 kg. If a 160-kg individual is weighed using the scale, the observer would only know that the individual's weight is at least 140 kg. The problem of censored data, in which the observed value of some variable is partially known, is related to the problem of missing data, where the observed value of some variable is unknown. Censoring should not be confused with the related idea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German: '' Statistik'', "description of a state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments.Dodge, Y. (2006) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', Oxford University Press. When census data cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample to the population as a whole. An ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
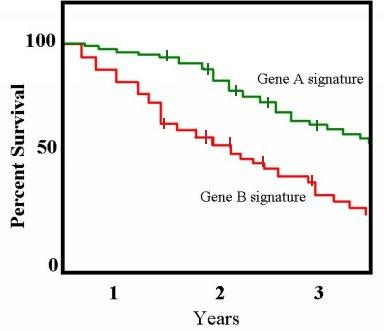
Kaplan–Meier Estimator
The Kaplan–Meier estimator, also known as the product limit estimator, is a non-parametric statistic used to estimate the survival function from lifetime data. In medical research, it is often used to measure the fraction of patients living for a certain amount of time after treatment. In other fields, Kaplan–Meier estimators may be used to measure the length of time people remain unemployed after a job loss, the time-to-failure of machine parts, or how long fleshy fruits remain on plants before they are removed by frugivores. The estimator is named after Edward L. Kaplan and Paul Meier, who each submitted similar manuscripts to the ''Journal of the American Statistical Association''. The journal editor, John Tukey, convinced them to combine their work into one paper, which has been cited almost 61,000 times since its publication in 1958. The estimator of the survival function S(t) (the probability that life is longer than t) is given by: : \widehat S(t) = \prod\limits_ \ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean Time To First Failure
Mean time (to) first failure (MTFF, sometimes MTTFF) is a concept in reliability engineering, which describes time to failure for non-repairable components like an integrated circuit soldered on a circuit board. For repairable components like a replaceable light bulb the concept of mean time between failures is used to describe the failure rate Failure rate is the frequency with which an engineered system or component fails, expressed in failures per unit of time. It is usually denoted by the Greek letter λ (lambda) and is often used in reliability engineering. The failure rate of a .... MTFF and MTTF (mean time to failure) have identical meanings. The key is that this is a non-repairable and non-recoverable failure. For example, the failure of a TV typically isn't measured by this criterion because the TV can be repaired. However, if this failure was due to a burned out integrated circuit that circuit itself can't be repaired and must be replaced. The failure of that circ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Likelihood Estimation
In statistics, maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) is a method of estimating the parameters of an assumed probability distribution, given some observed data. This is achieved by maximizing a likelihood function so that, under the assumed statistical model, the observed data is most probable. The point in the parameter space that maximizes the likelihood function is called the maximum likelihood estimate. The logic of maximum likelihood is both intuitive and flexible, and as such the method has become a dominant means of statistical inference. If the likelihood function is differentiable, the derivative test for finding maxima can be applied. In some cases, the first-order conditions of the likelihood function can be solved analytically; for instance, the ordinary least squares estimator for a linear regression model maximizes the likelihood when all observed outcomes are assumed to have Normal distributions with the same variance. From the perspective of Bayesian infere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exponential Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the exponential distribution is the probability distribution of the time between events in a Poisson point process, i.e., a process in which events occur continuously and independently at a constant average rate. It is a particular case of the gamma distribution. It is the continuous analogue of the geometric distribution, and it has the key property of being memoryless. In addition to being used for the analysis of Poisson point processes it is found in various other contexts. The exponential distribution is not the same as the class of exponential families of distributions. This is a large class of probability distributions that includes the exponential distribution as one of its members, but also includes many other distributions, like the normal, binomial, gamma, and Poisson distributions. Definitions Probability density function The probability density function (pdf) of an exponential distribution is : f(x;\lambda) = \begin \l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Failure Rate
Failure rate is the frequency with which an engineered system or component fails, expressed in failures per unit of time. It is usually denoted by the Greek letter λ (lambda) and is often used in reliability engineering. The failure rate of a system usually depends on time, with the rate varying over the life cycle of the system. For example, an automobile's failure rate in its fifth year of service may be many times greater than its failure rate during its first year of service. One does not expect to replace an exhaust pipe, overhaul the brakes, or have major transmission problems in a new vehicle. In practice, the mean time between failures (MTBF, 1/λ) is often reported instead of the failure rate. This is valid and useful if the failure rate may be assumed constant – often used for complex units / systems, electronics – and is a general agreement in some reliability standards (Military and Aerospace). It does in this case ''only'' relate to the flat region of the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Survival Function
The survival function is a function that gives the probability that a patient, device, or other object of interest will survive past a certain time. The survival function is also known as the survivor function or reliability function. The term ''reliability function'' is common in engineering while the term ''survival function'' is used in a broader range of applications, including human mortality. The survival function is the complementary cumulative distribution function of the lifetime. Sometimes complementary cumulative distribution functions are called survival functions in general. Definition Let the lifetime ''T'' be a continuous random variable with cumulative distribution function ''F''(''t'') on the interval [0,∞). Its ''survival function'' or ''reliability function'' is: :S(t) = P(\) = \int_t^ f(u)\,du = 1-F(t). Examples of survival functions The graphs below show examples of hypothetical survival functions. The x-axis is time. The y-axis is the proportion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Likelihood Function
The likelihood function (often simply called the likelihood) represents the probability of random variable realizations conditional on particular values of the statistical parameters. Thus, when evaluated on a given sample, the likelihood function indicates which parameter values are more ''likely'' than others, in the sense that they would have made the observed data more probable. Consequently, the likelihood is often written as \mathcal(\theta\mid X) instead of P(X \mid \theta), to emphasize that it is to be understood as a function of the parameters \theta instead of the random variable X. In maximum likelihood estimation, the arg max of the likelihood function serves as a point estimate for \theta, while local curvature (approximated by the likelihood's Hessian matrix) indicates the estimate's precision. Meanwhile in Bayesian statistics, parameter estimates are derived from the converse of the likelihood, the so-called posterior probability, which is calculated via Baye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Tobin
James Tobin (March 5, 1918 – March 11, 2002) was an American economist who served on the Council of Economic Advisers and consulted with the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, and taught at Harvard and Yale Universities. He developed the ideas of Keynesian economics, and advocated government intervention to stabilize output and avoid recessions. His academic work included pioneering contributions to the study of investment, monetary and fiscal policy and financial markets. He also proposed an econometric model for censored dependent variables, the well-known tobit model. Along with fellow neo-Keynesian economist James Meade in 1977, Tobin proposed nominal GDP targeting as a monetary policy rule in 1980. Tobin received the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1981 for "creative and extensive work on the analysis of financial markets and their relations to expenditure decisions, employment, production and prices." Outside academia, Tobin was w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tobit Model
In statistics, a tobit model is any of a class of regression models in which the observed range of the dependent variable is censored in some way. The term was coined by Arthur Goldberger in reference to James Tobin, who developed the model in 1958 to mitigate the problem of zero-inflated data for observations of household expenditure on durable goods. Because Tobin's method can be easily extended to handle truncated and other non-randomly selected samples, some authors adopt a broader definition of the tobit model that includes these cases. Tobin's idea was to modify the likelihood function so that it reflects the unequal sampling probability for each observation depending on whether the latent dependent variable fell above or below the determined threshold. For a sample that, as in Tobin's original case, was censored from below at zero, the sampling probability for each non-limit observation is simply the height of the appropriate density function. For any limit observa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Censored Regression Model
Censored regression models are a class of models in which the dependent variable is censored above or below a certain threshold. A commonly used likelihood-based model to accommodate to a censored sample is the Tobit model, but quantile and nonparametric estimators have also been developed. These and other censored regression models are often confused with truncated regression models. Truncated regression models are used for data where whole observations are missing so that the values for the dependent and the independent variables are unknown. Censored regression models are used for data where only the value for the dependent variable is unknown while the values of the independent variables are still available. Censored dependent variables frequently arise in econometrics. A common example is labor supply. Data are frequently available on the hours worked by employees, and a labor supply model estimates the relationship between hours worked and characteristics of employees su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Censored Data Example
Censorship is the suppression of speech, public communication, or other information. This may be done on the basis that such material is considered objectionable, harmful, sensitive, or "inconvenient". Censorship can be conducted by governments, private institutions and other controlling bodies. Governments and private organizations may engage in censorship. Other groups or institutions may propose and petition for censorship.https://www.aclu.org/other/what-censorship "What Is Censorship", ACLU When an individual such as an author or other creator engages in censorship of his or her own works or speech, it is referred to as ''self-censorship''. General censorship occurs in a variety of different media, including speech, books, music, films, and other arts, the press, radio, television, and the Internet for a variety of claimed reasons including national security, to control obscenity, pornography, and hate speech, to protect children or other vulnerable groups, to promote or r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |